Manufacturers work under strict requirements and quality controls, often because of industry regulations and contract terms. These companies use both visual inspections and electronic means to monitor product quality. Visual inspection is one of the major quality inspection steps in the overall quality assurance of the manufacturing process. Visual inspection still relies on manual efforts to a large extent because of the challenging task of the logic of what constitutes a defect. Visual inspection is a highly manual process that can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
OCI Vision AI to rescue
With the advent of artificial intelligence technologies, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Vision for image recognition, you can now automate visual inspection by training the custom AI models with labelled high-definition images showing defective and nondefective samples. Automated model training enables businesses to recognize and manage the defect labels on the images that are captured from different cameras across lines and sites. You can then retrain the custom model with new defect categories in no time.
Using OCI Vision AI services gives you all these capabilities, which help in monitoring the product health at all stages of the manufacturing, covering the following stages:
- Inspection of raw materials as incoming or receiving inspection
- Inspection of work in process inventory in shop floor
- Final inspection or the outgoing inspection during shipping
Customers can use AI-powered visual inspection in the following example use cases:
- Automobile door paint finish, press shop inspection (scratch, dents, cracks, and staining)
- Defective or missing printed circuit board (PCB) and components (screws, springs, foam, connectors, and shields)
- Glass product inspection for automotive, consumer durables, and lab equipment
- Smartphone and smartwatch display units inspection
- Final packaging and label inspection for outbound shipping
The following figure shows the technical layout for a solution using OCI Vision.
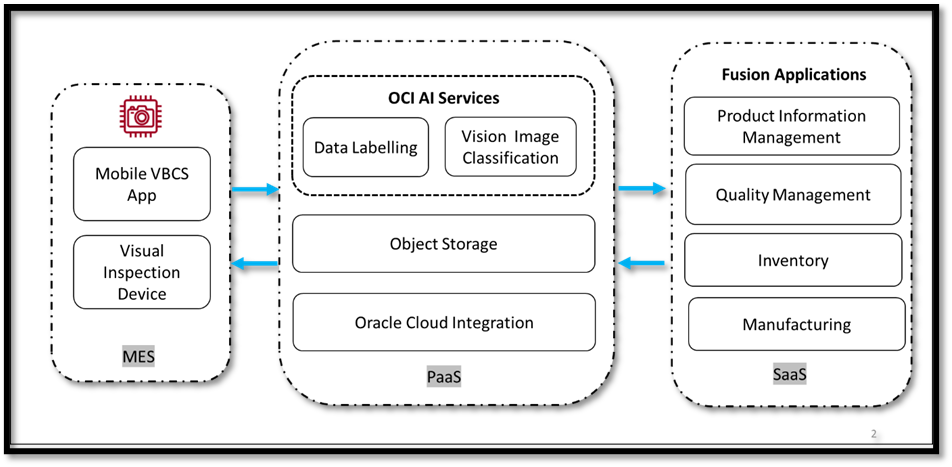
The technical architecture solution includes the following components:
- Visual Builder Cloud service (mobile application)
- Manufacturing execution system (MES): Visual inspection device and high-definition camera
- OCI AI services: Data Labelling and Vision
- Oracle Integration Cloud
- Fusion Quality Management
- Fusion Product Information Management
- Fusion Inventory
- Fusion Manufacturing
Image recognition with AI in manufacturing
As an example use case, we show how an AI-powered solution helps with visual inspection in the casting process. The manufacturing process of casting usually involves pouring liquefied metal into the cavity of a mold of the wanted shape.
Manual inspection is done to identify defects in casting like blow holes, pinholes, burr, shrinkage defects, mold material defects, and pouring metal defects. Because of human inaccuracy, this time-consuming process isn’t 100% accurate.
An AI-powered, automated solution for visual inspection can use OCI Vision AI services and Fusion Apps REST APIs to create the inspection results against a preconfigured inspection plan.
The AI-powered automated solution for visual inspection includes the following stages:
- Populate datasets and perform data labelling to train the custom AI model
- Define an inspection plan with a product characteristic target
- Develop an interface to capture the sample product image
- Classify the product image using the OCI Vision AI image classification service
- Interface for Fusion Quality Management to record inspection results
Let’s explore the details of each of these stages in the following sections.
Populate datasets and perform data labelling to train the custom AI model
The OCI Data Labeling service is an OCI-native service that allows customers to create and browse datasets, view data records, such as text and images, and apply labels for the purposes of building AI and machine learning (ML) models.
Populate the datasets with defective and nondefective images of the product. Use bulk data labelling service to label data as defective and nondefective. When records are labeled, you can export the dataset as line-delimited JSON for use in AI and ML model development.
The custom AI model is trained with the dataset, and results are validated for confidence figures.
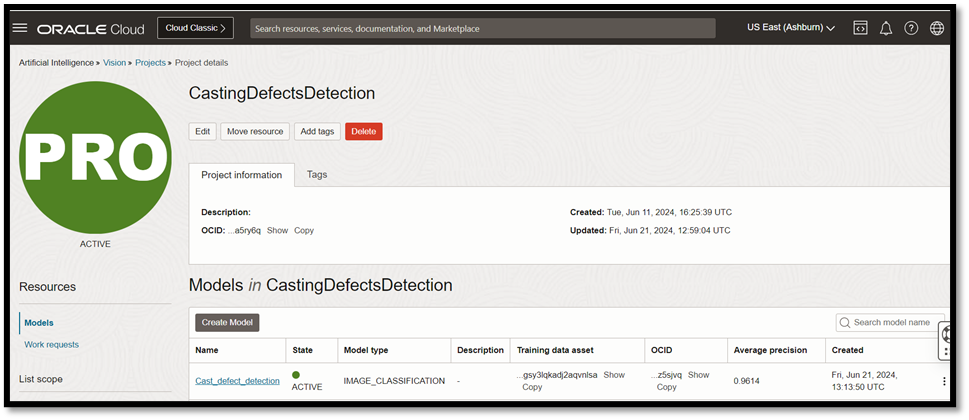
Use OCI Vision for image recognition tasks like classifying images, detecting objects, detecting faces, and extracting text. OCI Vision is a fully managed, multitenant, native cloud service that helps you with all your common computer vision tasks.
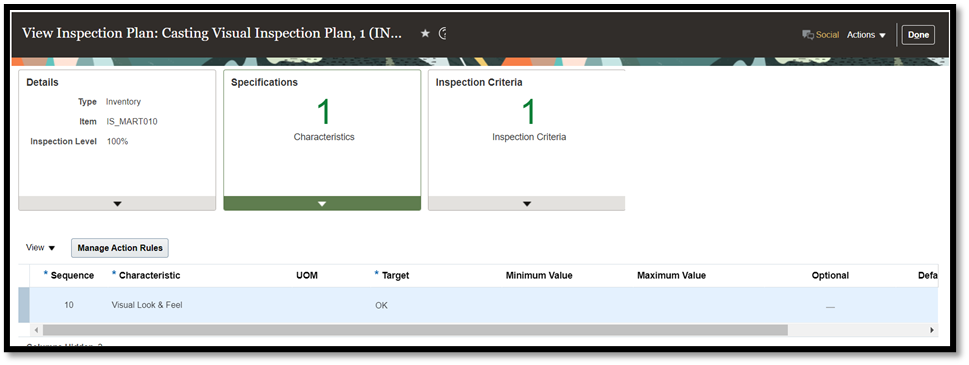
Define an inspection plan with a product characteristic target
Inspection plans are set up for item and organization combination with the following types:
- Receiving: For incoming material
- Work in process: For material in shop floor
- Inventory: For final inspection of the outgoing or shipping material
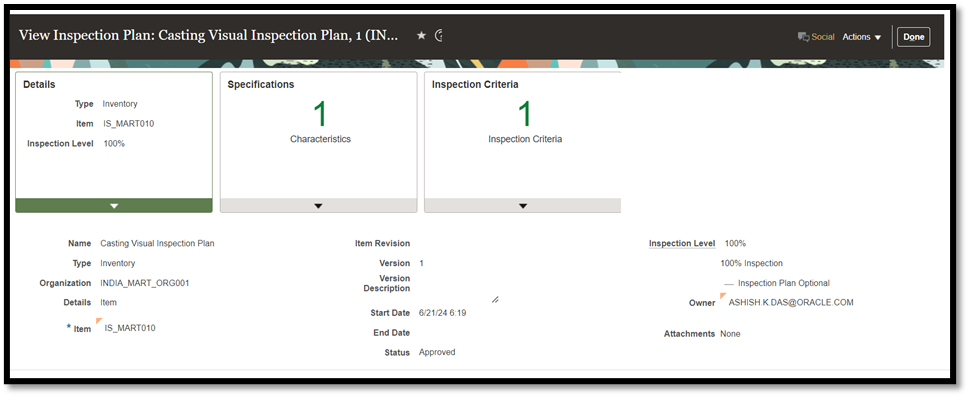
You can identify and include target characteristics, like visual specification for good or bad products, in the inspection plan.
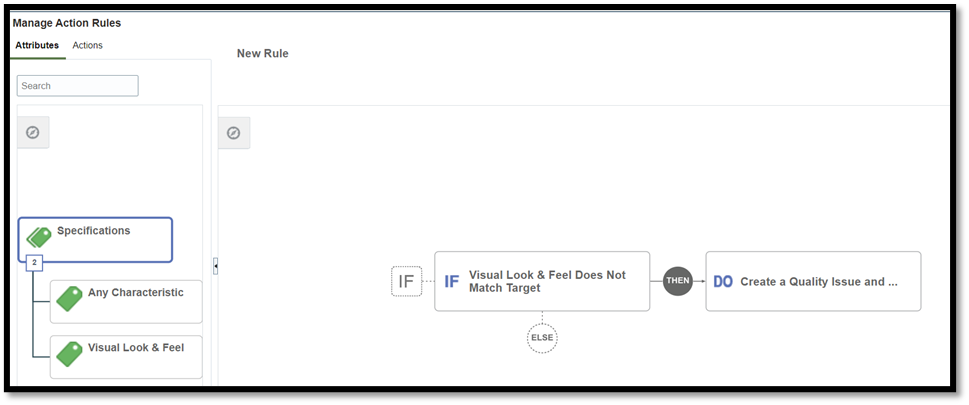
Configure action rules to raise quality issues if inspection results are observed to be different from the set target value.
Develop an interface to capture the sample product image
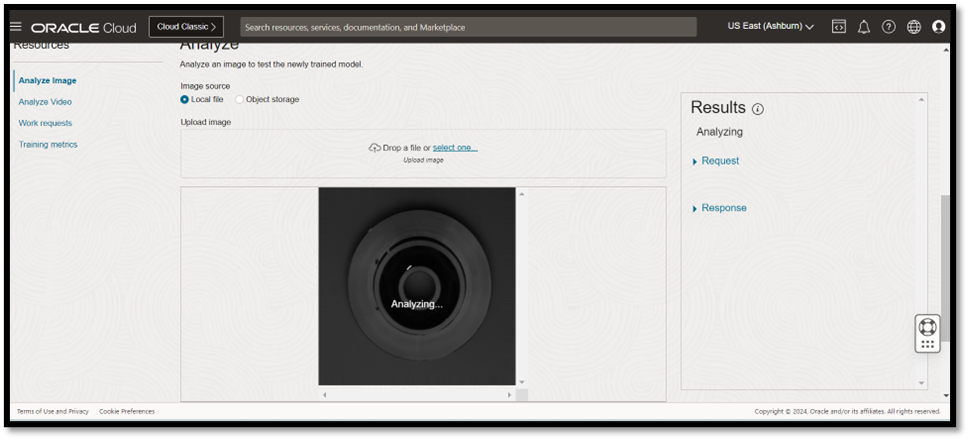
You can develop a mobile app to capture instant product images using cameras, with images uploaded to OCI Object Storage for further processing. The alternate option is to integrate directly with a visual inspection device feed or get the feed from your MES application.
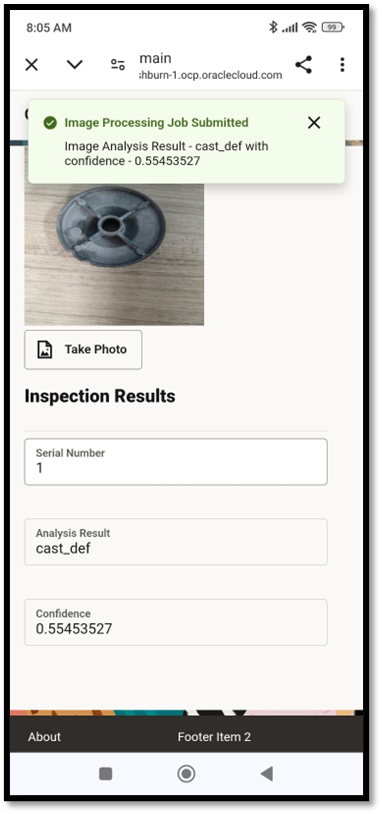
Classify the product image using OCI Vision AI image classification
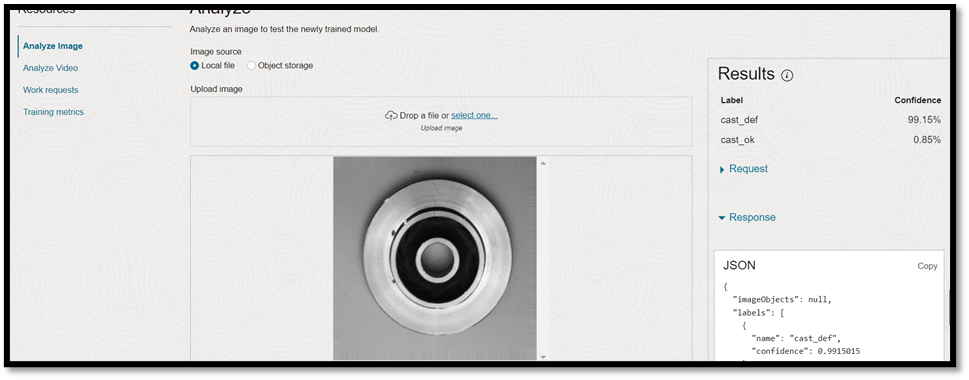
When you invoke the image classification service, OCI Vision, it analyzes the image using the custom-trained model to classify it as defective or nondefective. For this classification, the service uses the OCI Vision REST API.
The following block shows the request payload:
{
“image”: {
“source”: “OBJECT_STORAGE”,
“namespaceName”: {namespaceName},
“bucketName”:{bucketName},
“objectName”:{imageName}
},
“features”: [
{
“modelId”: {modelId},
“featureType”: “IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION”,
“maxResults”: 5
}
],
“outputLocation”: {
“bucketName”: {bucketName},
“namespaceName”: {namespaceName},
“prefix”: “result”
},
“compartmentId”: {compartmentId}
}
The following block shows the response payload:
{
“imageObjects”: null,
“labels”: [
{
“name”: “cast_ok”,
“confidence”: 0.8611984
},
{
“name”: “cast_def”,
“confidence”: 0.13880153
}
],
“ontologyClasses”: [
{
“name”: “cast_ok”,
“parentNames”: [],
“synonymNames”: []
},
{
“name”: “cast_def”,
“parentNames”: [],
“synonymNames”: []
}
],
“imageText”: null,
“objectProposals”: null,
“detectedFaces”: null,
“imageClassificationModelVersion”: “version”,
“objectDetectionModelVersion”: null,
“textDetectionModelVersion”: null,
“objectProposalModelVersion”: null,
“faceDetectionModelVersion”: null,
“errors”: []
}
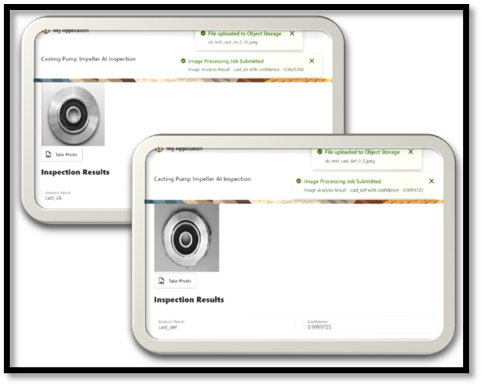
After getting the image analysis result, OCI Integration is invoked to create inspection results with the following payload.
{
“items”: [{
“ItemNumber”: {ItemNumber},
“SerialNumber”: {SerialNumber},
“InspectedBy”: {InspectedBy},
“InspectionDate”: {InspectionDate},
“EventType”: {EventType},
“PlanName”: {PlanName},
“SubinventoryCode”: {SubinventoryCode},
“Result”: {AnalysisResult}
}]
}
Interface for Fusion Quality Management to record inspection results
Oracle Integration Cloud services uses with REST APIs to create the inspection result in Fusion applications.
The following chart shows the Fusion REST resource URIs used to create inspection event and result:
| Sr.No |
Step |
Method |
REST Resource URI |
| 1 |
Get InspectionPlanId for specific item number, status and effective end date |
GET |
/fscmRestApi/resources/11.13.18.05/inspectionPlans?q=ItemNumber={ItemNumber};Status=APPROVED;EffectiveEndDate is Null |
| 2 |
Create Inspection Event |
POST |
/fscmRestApi/resources/11.13.18.05/inspectionEvents |
| 3 |
Get the SampleId based on the Inspection Event Id received from the above REST Response |
GET |
/fscmRestApi/resources/11.13.18.05/inspectionEvents/{IpEventId}/child/Sample |
| 4 |
Get the SampleEventDispositionId based on the IpEventId and SampleID |
GET |
/fscmRestApi/resources/11.13.18.05/inspectionEvents/{IpEventId}/child/Sample/{SampleId}/child/SampleDisposition |
| 5 |
Get the SampleResultId based on the IpEventId and SampleID and SampleEventDispositionId |
GET |
/fscmRestApi/resources/11.13.18.05/inspectionEvents/{IpEventId}/child/Sample/{SampleId}/child/SampleDisposition/{SampleEventDispositionId}/child/SampleResult |
| 6 |
Update the Sample Results based on IpeventId-SampleId-SampleEventDispositionId-SampleResultId |
PATCH |
/fscmRestApi/resources/11.13.18.05/inspectionEvents/{IpEventId}/child/Sample/{SampleId}/child/SampleDisposition/{SampleEventDispositionId}/child/SampleResult/{SampleResultId} |
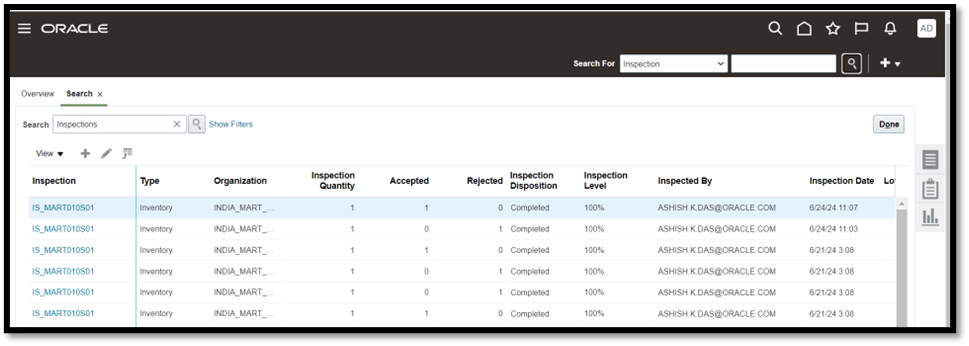
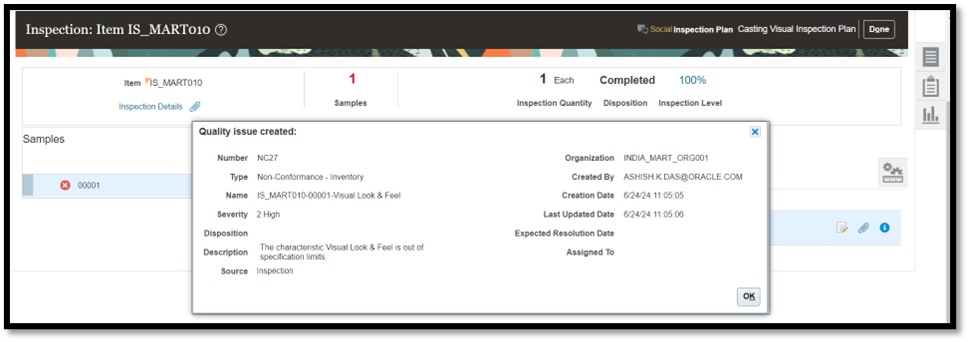
The following example shows an inspection event created in Fusion Quality Inspection:
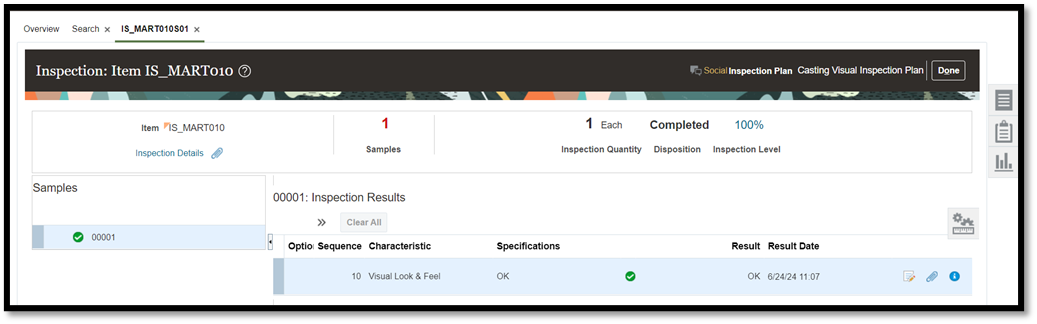
The inspection result is updated against the event.
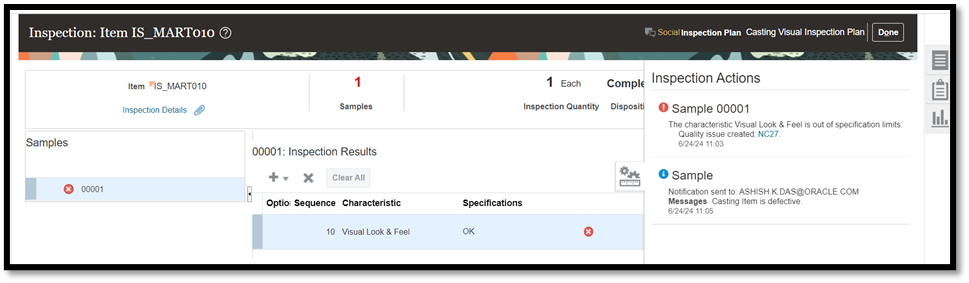
Quality issues are raised for cases where observed results are different from a set target.
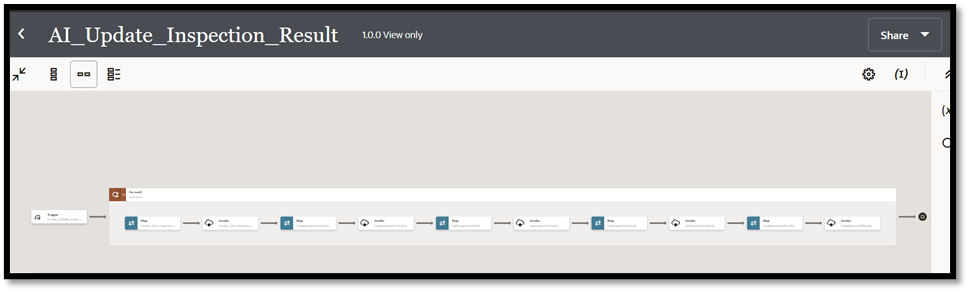
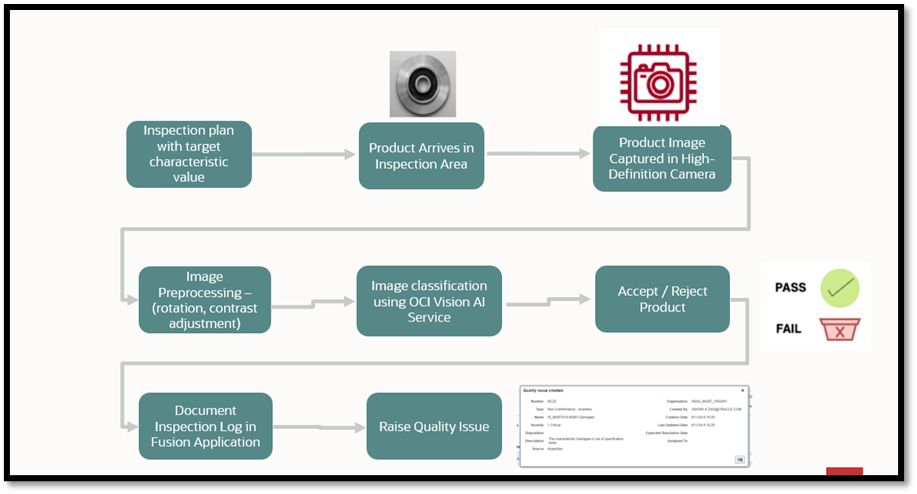
This process enables a hassle-free inspection process on the shop floor. The entire process flow for the AI-powered visual inspection is summarized and depicted in the following figure:
Benefits of AI-powered visual inspection solution
A visual inspection solution with OCI Vision offers the following beneftis:
- Improved efficiency and higher accuracy
- Learn intelligently and over time detect varying complexities of defects
- Free up human resources for other value-added tasks instead of involving them in routine manual inspection work
- Improve the accuracy of defect detection and prediction with constant updates to the AI model with latest training data with new defect categories
- Reduced Cost: Significant reduction in product warranty, rework, and repair cost and costly product recalls
- Improved workplace health and safety: Reduces human intervention, improving human health and safety, especially in hazardous working environments.
Conclusion
The use of artificial intelligence, particularly through Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Vision AI Services, represents a transformative step forward for manufacturers reliant on visual inspection processes.
By leveraging AI-powered image recognition, manufacturers can automate and enhance the accuracy of quality inspections throughout their production lines. This advancement not only improves efficiency and accuracy but also reduces costs associated with defects and recalls.
Furthermore, by minimizing human intervention in hazardous environments, AI-powered inspections contribute to enhanced workplace safety. As manufacturers continue to adopt and refine these technologies, they are poised to realize significant operational efficiencies and quality improvements across all stages of production, reinforcing the critical role of AI in modern manufacturing practices.
For more information, see the following resources:


