If you’re trying to scale cloud adoption without losing control, the new and improved OCI Service Catalog gives you a clean way to standardize what gets deployed —and how, —while letting teams move fast. It’s a governance and self-service layer for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure that turns approved blueprints into click-to-deploy experiences.
What is OCI Service Catalog?
OCI Service Catalog is a central library of curated, pre-approved solutions your organization can deploy for use in their tenancy and underlying compartments. Each solution can be an OCI Marketplace application, or a private application [private applications can be based on a Terraform (Resource Manager) stack]. Administrators define the inputs, constraints, and tagging standards up front; end users simply choose the pre-approved applications, configure allowed parameters, and launch. Approved or restricted sets of applications can reduce risks of misuse or overspending by end users, giving administrators peace of mind. End users can quickly deploy only approved applications that follow constraints set by the organization. Using a curated Service Catalog will help ensure better governance and self-service within your OCI tenancy. Now let’s look at what is new in the Marketplace Service Catalog.
What’s New?
- Enhanced Administrative Features:
- Streamlined catalog creation and management
- Inclusion of all Marketplace listings and private applications
- Enforced catalog access in console or via OCI CLI / API access
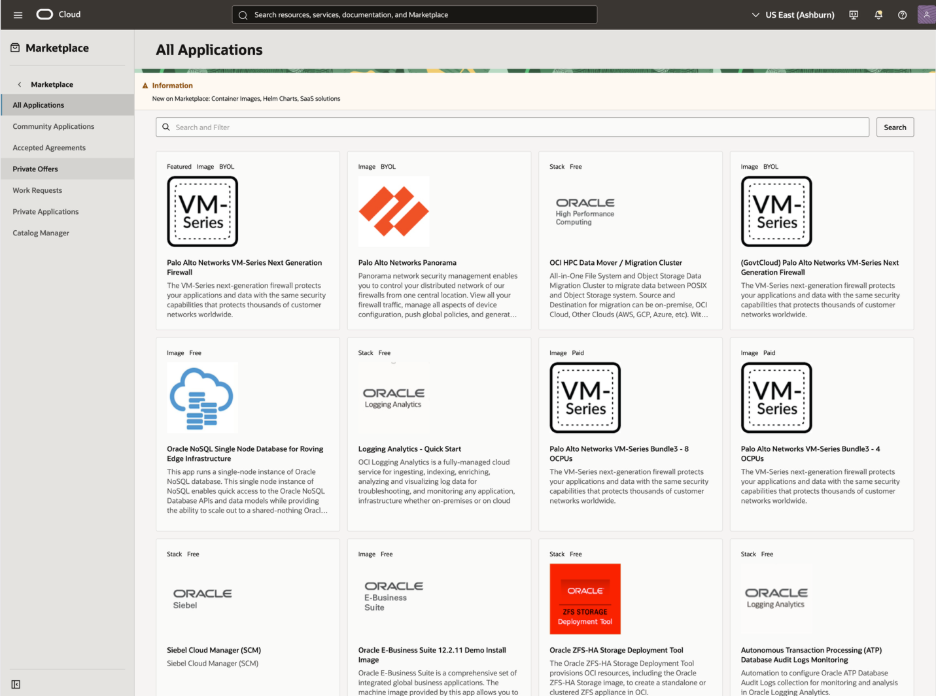
Figure 1.Default Marketplace Catalog
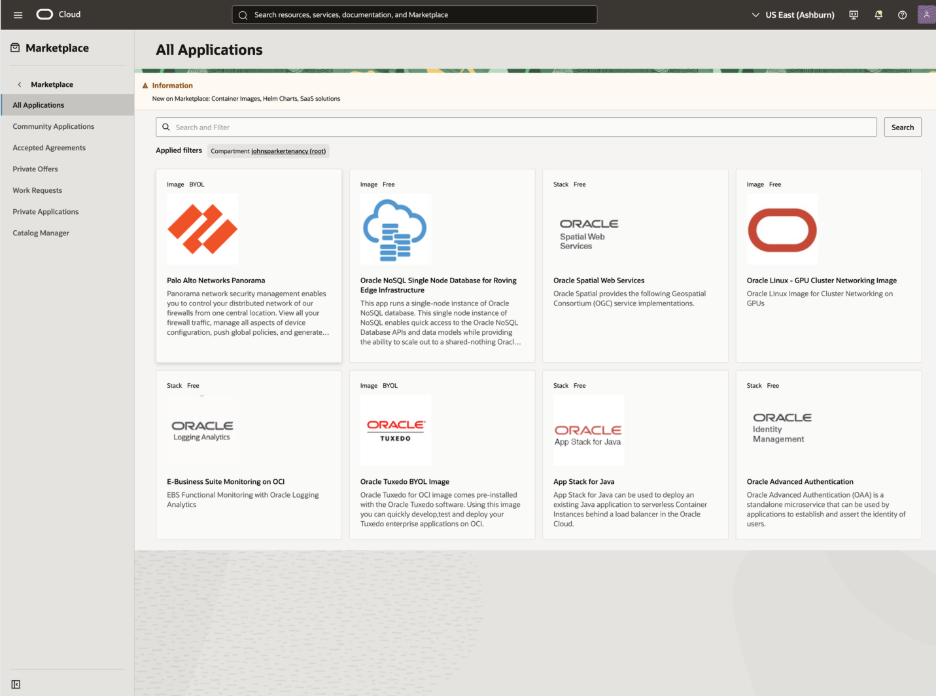
Figure 2. New Service Catalog
- Multiple Catalog Support:
- Create multiple catalogs to suit different needs (note: only one catalog per compartment can be active at a time)
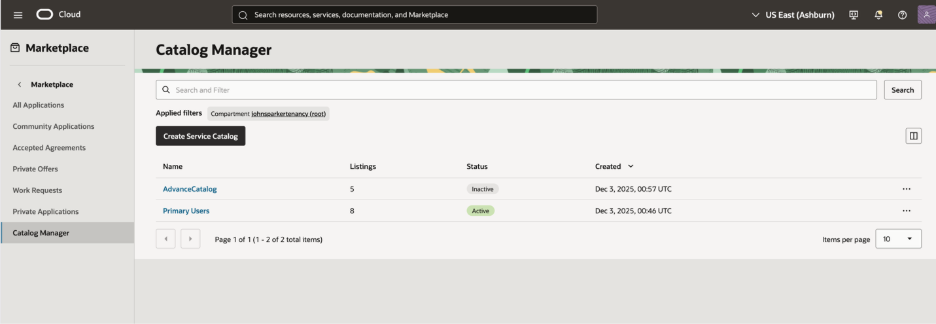
Figure 3. Multiple Catalog View
- Compartment-Level Control:
- Create separate catalogs for specific compartments
- Maintain active catalogs in different compartments for fine-grained governance
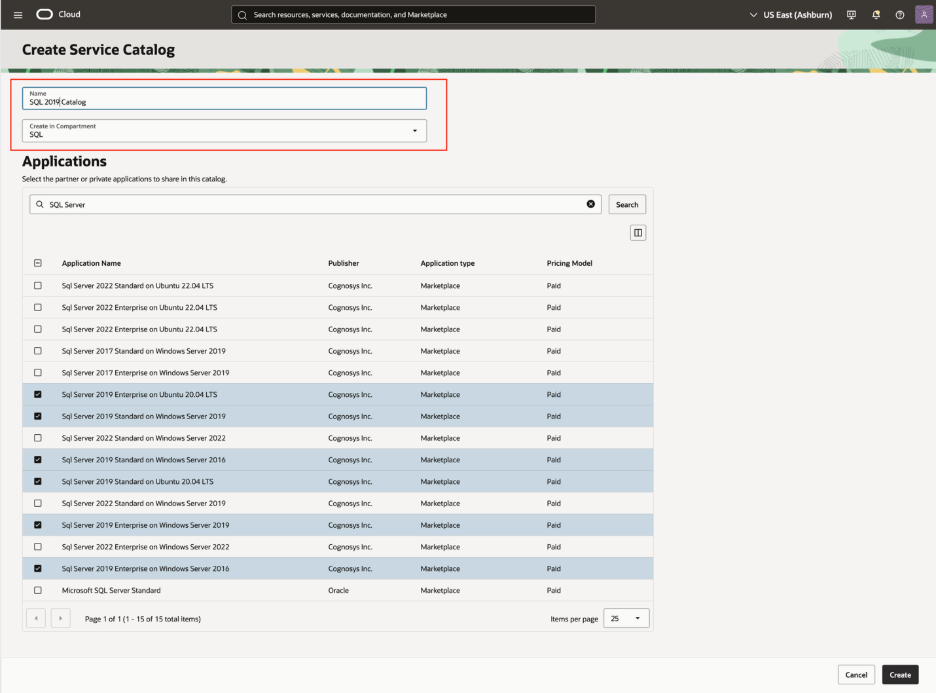
Figure 4. Compartment Level Catalog
Why it matters
- Speed with safety: Empower developers to self-serve deployments without granting broad permissions.
- Consistency at scale: Enforce standards for networking, security, images, and tagging across teams.
- Cost and compliance controls: Lock versions, restrict regions/compartments, and apply required tags for chargeback and audits.
- Reduced cognitive load: Hide complexity behind friendly forms; no deep Terraform expertise required for users.
Getting started in five steps (Managing Service Catalogs)
- Create a catalog in the target compartment. Note you will need to have at least one catalog active to opt into the service catalog mode. You can have multiple catalogs active in a tenancy but only one active per compartment.
- Add OCI Marketplace listings and private applications:
- Add applications that were created from Resource Manager: Point to a Terraform stack source (Object Storage, code repo).
- From the OCI Marketplace: Copy approved listings into your catalog.
- Define parameters and policies: Set defaults, constrain inputs, lock versions, and add required tags.
- Share and permission: Share the catalog with specific compartments and set IAM policies for viewing and deploying.
- Launch and operate: Users browse the catalog, deploy to their compartments, and manage lifecycle through Resource Manager.
IAM at a glance
- Viewers need permission to read the catalog and private applications.
- Launchers need permission to use the catalog and to run Resource Manager jobs in their target compartments.
- Admins manage who can curate catalogs versus who can consume them, aligning access with team boundaries.
Operational tips and best practices
- Start with the essentials: Ship a small set of high value blueprints (network baseline, OKE, database) before expanding.
- Parameter discipline: Expose only what users truly need to change; lock everything else to enforce standards.
- Tagging for accountability: Apply required tags (department, environment, cost center) to every deployment.
- Version with intent: Treat catalog entries like software; test and promote versions and retire outdated ones.
- Compartment strategy: Share catalogs narrowly to reduce blast radius and keep deployments aligned with ownership.
- Observe and iterate: Use audit logs and Resource Manager history to refine templates and guardrails over time.
What users experience
For consumers, OCI Service Catalog looks like a curated storefront. They search for a solution, provide a few allowed inputs, and launch. Under the hood, Resource Manager handles plan/apply, drift detection, and lifecycle operations. The result is faster, safer provisioning that matches your enterprise standards without frequent admin intervention.
Bottom line
OCI Service Catalog bridges the gap between central governance and developer autonomy. By turning approved Terraform and Marketplace solutions into easy, selfservice deployments—complete with constraints, tagging, and scoped access—you can scale your cloud footprint confidently and consistently. If you’d like help mapping this to your tenancy and compartments, share a bit about your layout and target use cases, and I can suggest concrete IAM policies and a starter catalog.
Additional Resources: Service Catalog documentation.
