Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Resource Manager is an OCI service that allows you to automate the process of provisioning your OCI resources. Using Terraform, Resource Manager helps you install, configure, and manage resources through the infrastructure-as-code model. Recently, Resource Manager added Ansible to the Docker and Fn packages that are included in the Resource Manager Terraform host. Ansible is a great complement to Terraform to configuring OCI resources. The Resource Manager Terraform host, also referred as Terraform host, is the host where you run your Terraform stack to provision resources.
In this blog, I cover how you can deploy OCI resources using Terraform and use Ansible playbooks to install the httpd service on an OCI virtual machine (VM).
Use case
Using the add-on feature of the Resource Manager host, you can configure your cloud infrastructure. This blog covers the following use case around this Terraform stack:
-
Deploy a virtual cloud network (VCN), subnet, route tables, and a Compute VM.
-
Deploy OCI Bastion service and session.
-
Use a Bastion session as a proxy to allow access to the VM’s private IP address.
-
Use Ansible as part of Resource Manager host to install httpd application.
-
Optionally create a custom image of a running instance.
Prerequisites
-
An Oracle Cloud account. If you don’t have an account, you can sign up for an Oracle Cloud Free Tier account.
-
Download the Quick Start and follow the README instructions.
-
Correct permission and resources required to deploy terraform stack.
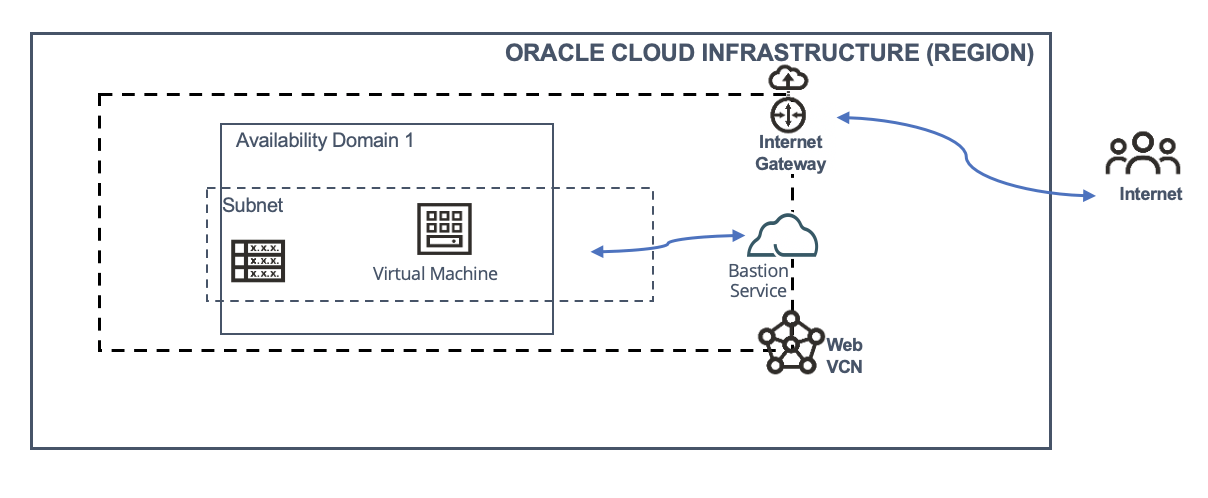
Topology
The following graphic shows this architecture:
Configuration
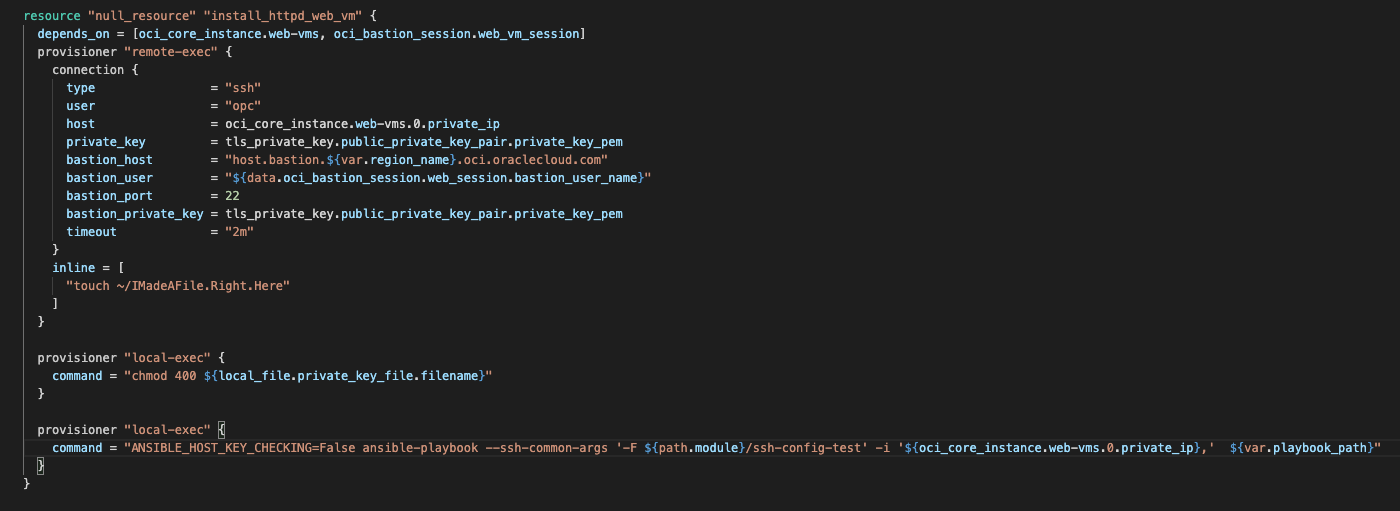
You can follow the instructions available in the Quick Start provided in the Prerequisites section to support this use case. As part of this Terraform stack, the following snippet tells you how we’re using OCI Bastion and a local-exec provisioner to support running the Ansible playbook.
Deploy the Terraform stack using Oracle Resource Manager
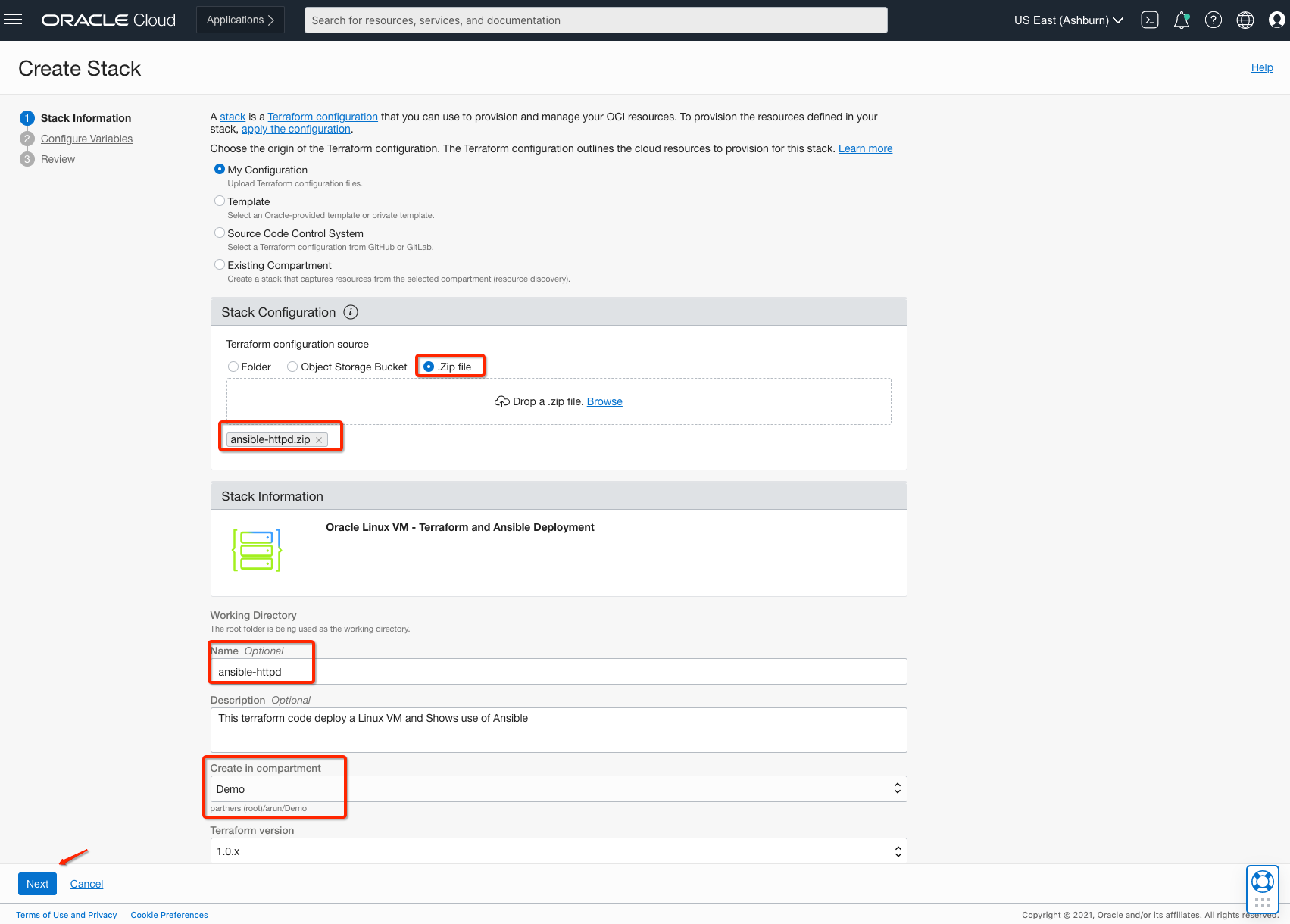
You can download the Terraform stack locally or click the Deploy button of this Quick Start.
Select the compartment where you want to deploy this stack.
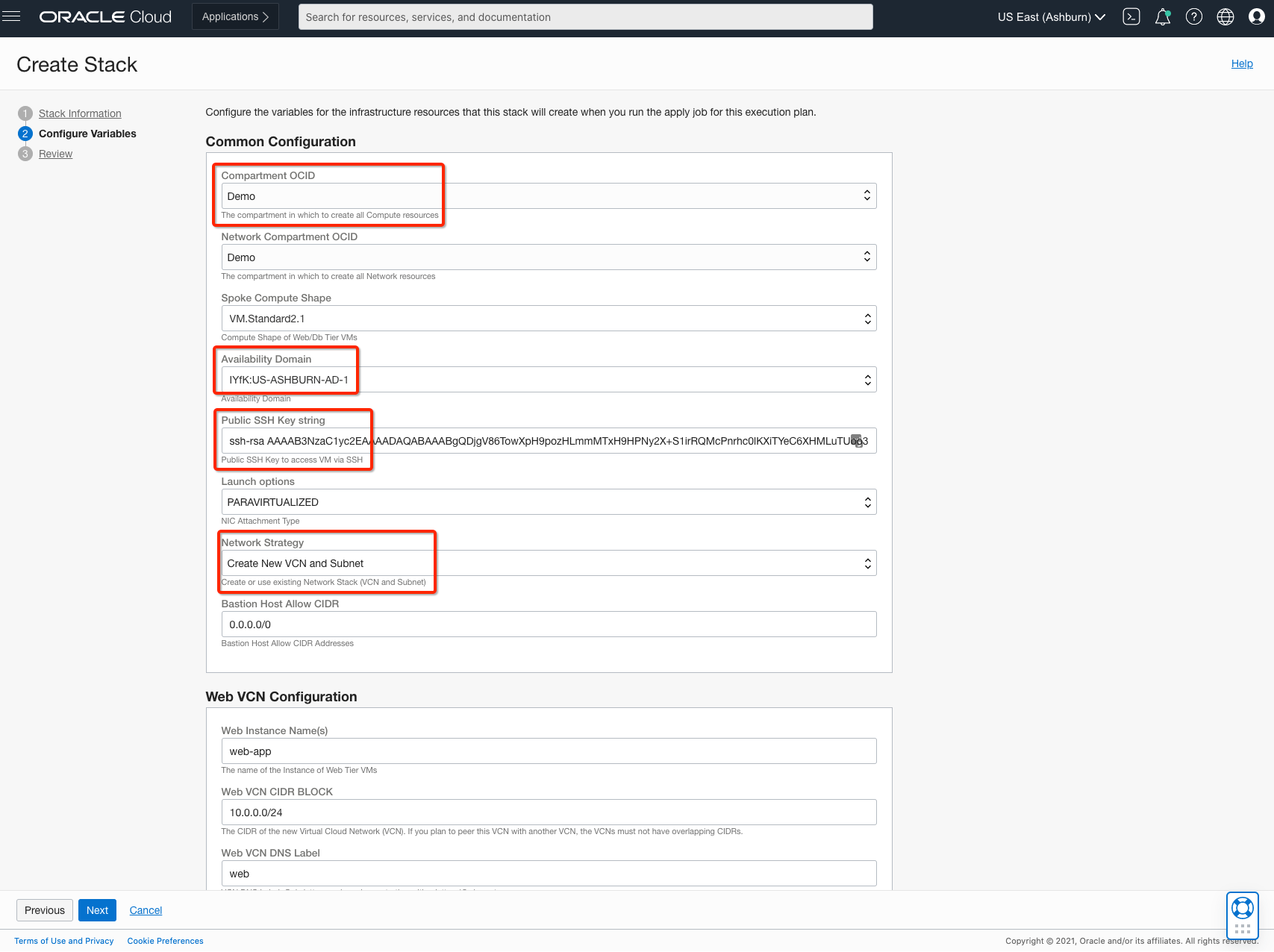
Update the following configuration variables to support the Terraform stack:
-
Select the compartment.
-
Select your availability domain.
-
Add an SSH public key.
-
Select the Create New VCN and Subnet network strategy.
-
Ensure that you have the correct region value, such as us-ashburn-1 for the Ashburn region, to support your Bastion connection.
-
Keep the other values as default.
You can also enable a variable to create a custom image for a running instance by clicking the check box. This image runs after a successful Ansible run.
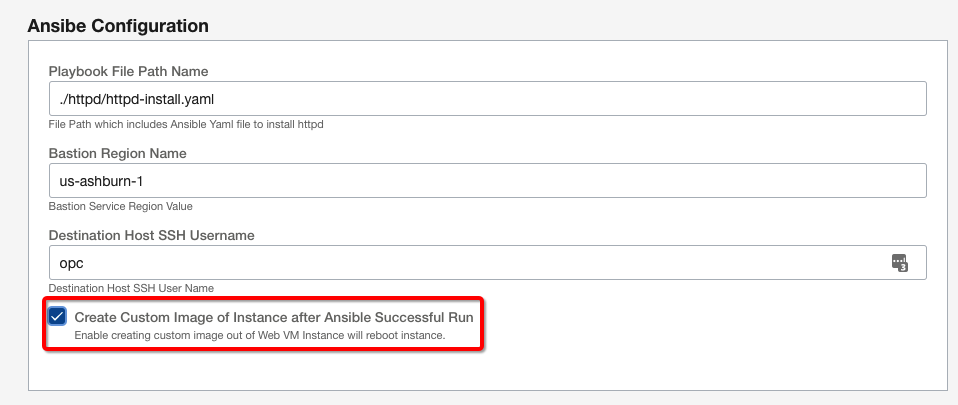
Click the Next button and complete the stack creation. Now you can proceed with Terraform plan and apply actions to ensure that stack gets deployed. Verify that the Terraform stack was applied successfully and the Ansible playbook is complete.
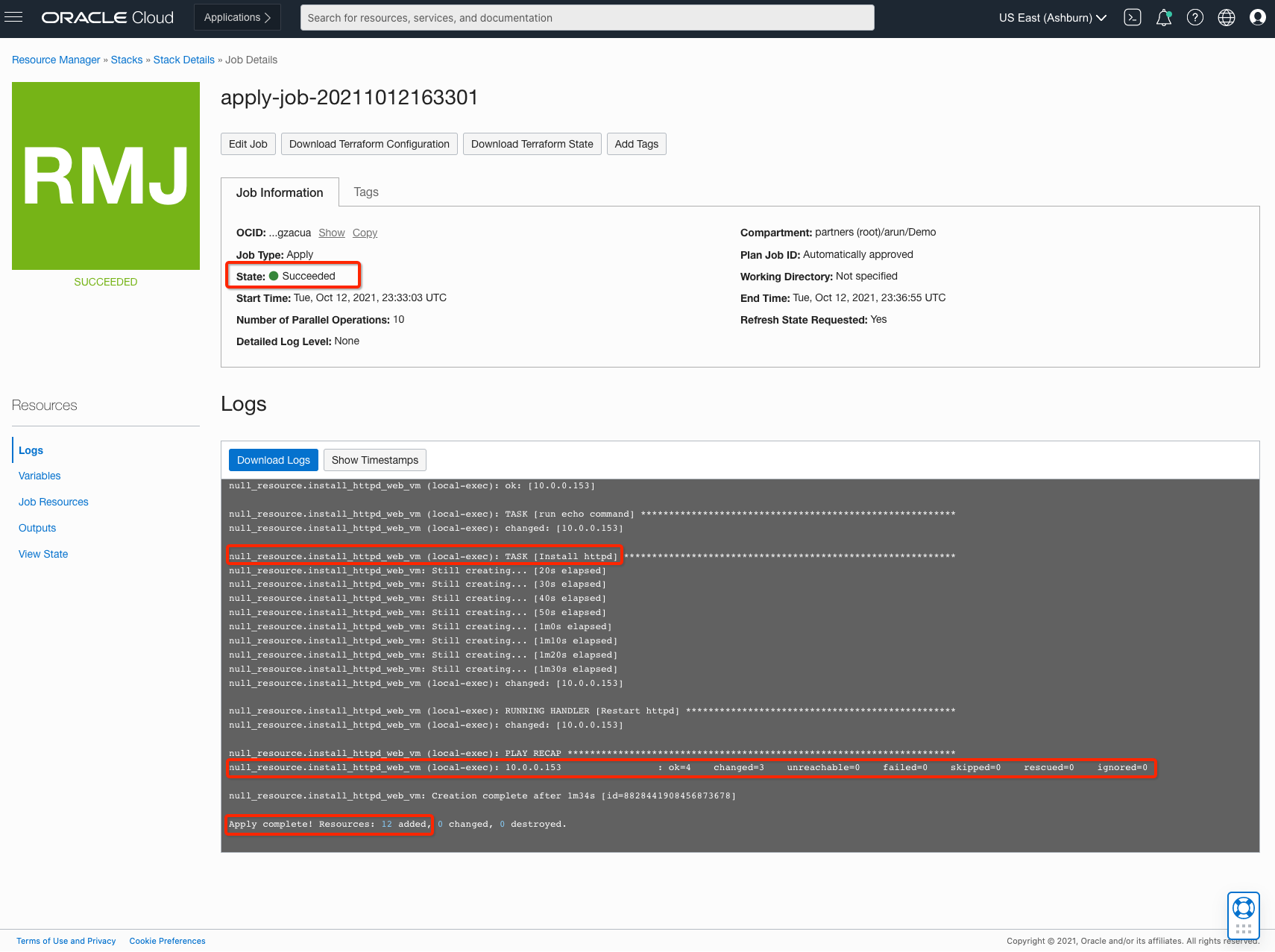
Validation
Now, you can connect to the Compute VM to ensure that the HTTPD service is installed and running successfully. Connect to the web VM and validate your service status using the command, systemctl status httpd. If the service is running, the output looks like the following screenshot:
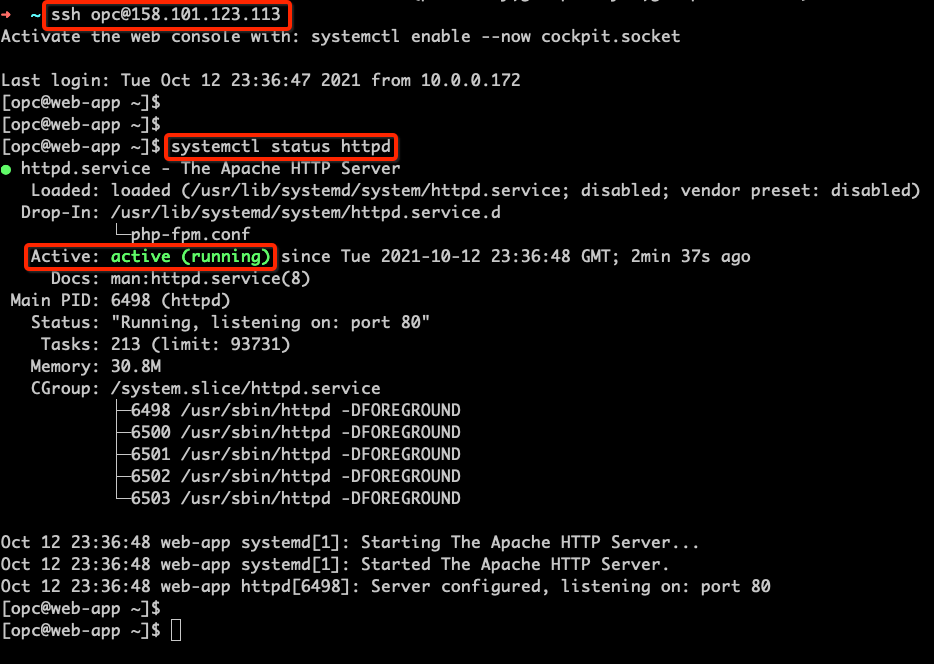
Conclusion
This post explained and showcased the Ansible tool uses within Oracle Resource Manager’s host to support the configuration of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. We covered a simple httpd service deployment, but you can enhance your use case as needed.
To learn more about Oracle Resource Manager, see the following resource:
