Oracle NoSQL Database Migrator
We are very excited to announce Oracle NoSQL Database Migrator’s release to help move your workload to Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service (NDCS).
Before we dig into how to use the Migrator, let’s look at some situations that require you to migrate NoSQL tables from or to an Oracle NoSQL Database.
Deploying your app in multi-cloud topology
You have decided to run your workload across multiple cloud vendors. You have started your application development using Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service, and now you wish to run a portion of your workload on another cloud vendor. Using the Migrator, you can easily copy your Oracle NoSQL Database tables to an instance of Oracle NoSQL Database running on another cloud platform.
Migrate from On-premises to Cloud Service
NoSQL developers may need to move their application data from on-premise to the cloud and vice-versa, either for development or testing purposes. This migration can happen using the Migrator. An extension of this use case would be to use Cloudsim for automated unit testing purposes. Instead of incurring costs to test code changes directly against the cloud service, developers use Cloudsim, a free simulator, to unit test their code. Cloudsim is a single process test environment that is ideal for running automated nightly unit tests without incurring any extra cost. In this scenario, it is common to have a pre-production environment which contains a subset of the data in the production environment. The Migrator can be used to transfer this subset of production directly to Cloudsim for use in automated nightly unit testing.
Moving off of MongoDB
You have decided to move off of MongoDB and over to Oracle NoSQL Database. To assist with this migration, you can use the Migrator to copy MongoDB-formatted JSON input file into your Oracle NoSQL Database on-premise or the cloud service.
You can refer to our documentation to learn more about the demonstration of some of the above use-cases.
Oracle NoSQL Database Migrator
The NoSQL Database Migrator acts as a connector or pipe between the data source (the export entity) and the sink (the import entity.) In essence, this utility exports data from the selected source and imports that data into the sink. This tool is table-oriented; that is, you can move the data only at the table level. A single migration task operates on a single table and supports the following options:
- JSON file to Oracle NoSQL Database on-premise and vice versa
- JSON file to Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service and vice versa
- Oracle NoSQL Database on-premise to Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service and vice versa
- MongoDB Extended JSON (V1 and V2) format file to an Oracle NoSQL Database table
- MongoDB Extended JSON (V1 and V2) format file to an Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service table
- One Oracle NoSQL Database on-premise to another
- One Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service to another
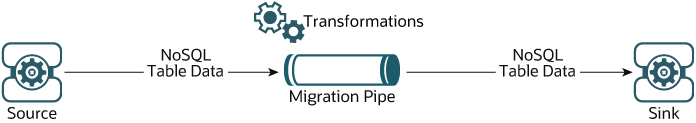
Figure 1. Migration Overview
You can transform the data by specifying one or more rules to modify the migration pipe’s data. Some examples of permitted transformations are:
-
- Drop or ignore one or more fields in a JSON document or column values from the source before writing to the sink
- Rename one or more top-level JSON fields before writing to the sink
- Aggregate multiple JSON fields from the source into a single field in the sink. As part of this transformation, you can also identify the JSON fields that you want to exclude in the aggregation.
If you take the following document from the source:
{
“_id”:1,
“name”:”jack”,
“addressinfo”: {
“street”: “network driver 35”,
“city: “burlington”
}
}
You may want to rename the field “_id” to “id” and the field “addressinfo” to “address.” Using the “renameFields” transformation configuration attribute, you can accomplish the rename with the following:
“renameFields” : {
“_id” : “id”,
“addressinfo” : “address”
}
There’s also a notion of a configuration JSON file where you define all the parameters required for the migration activity. Refer to the doc to understand the configuration file in more detail.
Using Oracle NoSQL Database Migrator
Running the Migrator is as easy as 1-2-3 – download it, identify your source/ sink and run it. We have two ways to run it, either from the dialog-driven approach or from an input file, a configuration file. For first time users, we recommend using the dialog-driven approach since it will guide you by creating a configuration file that you can use in future scripted or automated runs of the Migrator.
- Download the NoSQL Database Migrator Utility
The Oracle NoSQL Database Migrator utility is available for download from the Oracle NoSQL Downloads page. Once you download and unzip it on your machine, you can access the runMigrator command from the command line interface.
- Identify the Source and Sink
Before using the Migrator, you must identify the data source and sink. For instance, if you want to migrate a NoSQL table from Oracle NoSQL Database on-premise to a JSON formatted file, your source will be Oracle NoSQL Database, and sink will be a JSON file. Refer to the Supported Sources and Sinks.
- Run the Migrator
Finally, run the Migrator using runMigrator that is available when you extract NoSQL Database Migrator files. The utility requires you to install Java 8 or higher version. You can execute runMigrator in two ways:
- By using the runMigrator command, as shown below:
[~]$ ./runMigrator configuration file is not provided. Do you want to generate configuration (y/n) [n]: y
This will trigger the dialog-driven approach, which provides you with a series of options to create the configuration JSON file used to proceed with the migration activity. You can use this configuration for future migrations.
- By explicitly supplying a JSON configuration file:
That’s it. That is how easy it is to migrate the data to NoSQL Database Cloud Service.
Oracle NoSQL Database is a multi-model, multi-region database designed to provide a highly-available, scalable, flexible, high-performant, and reliable data management solution to meet today’s most demanding workloads. It is well-suited for high volume and velocity workloads, like the Internet of Things, customer 360, online contextual advertising, fraud detection, mobile application, user personalization, and online gaming. Developers can use a single application interface to build applications that run in on-premise and cloud environments quickly.
Visit our cloud page to learn more.