Acknowledgements: Michael Brey, Director of NoSQL Database Development, Oracle
An industry in flux
Financial services industries are at crossroads and are experiencing massive changes in response to shifting customer demands. With the increasing adoption of cloud technologies, digital-only enterprises are offering innovative solutions at the lowest cost.
Customer experience is a strategic imperative for most organizations today, but delivering an engaging experience across the growing number of digital customer touchpoints can be challenging, especially if they have an aging technology stack.
Additionally, organizations have to navigate these transformational changes while managing vast volumes of digital transactions, a variety of data, and velocity without straining their business systems, experiencing data loss, breaches, and/or downtime.
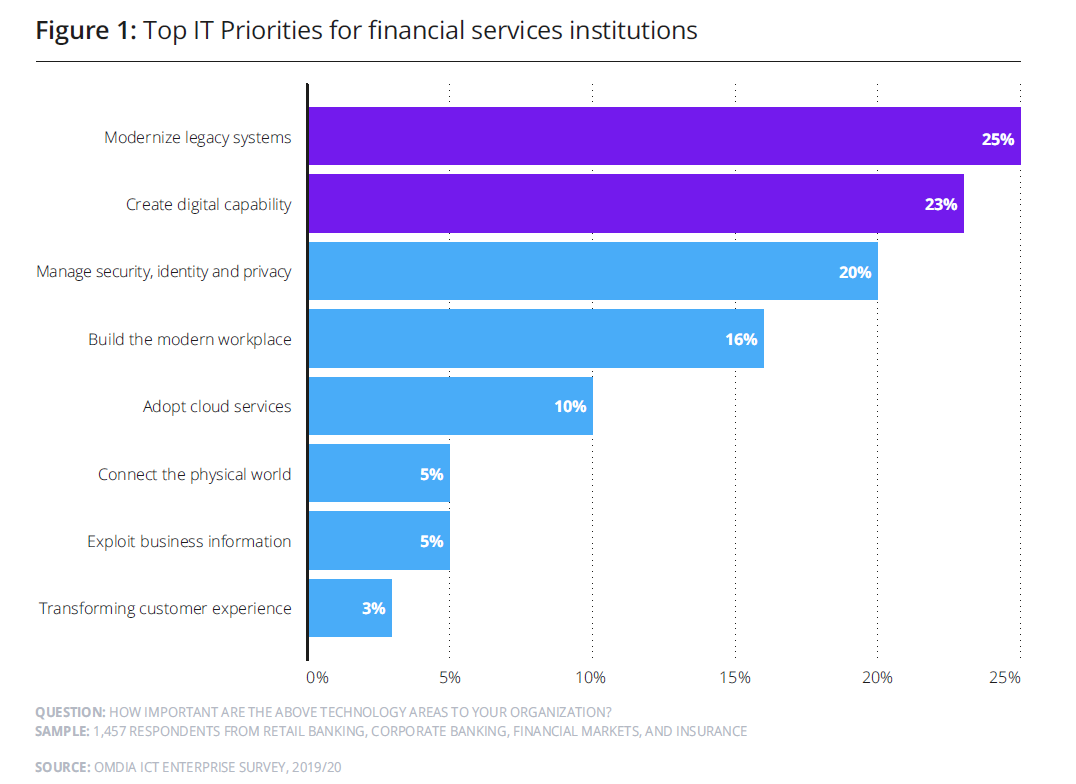
The below graphic shows the IT priorities of financial services institutions, and it is no surprise that 25% of them want to modernize their systems and equally the same % want to ramp up on their digital touchpoints.
This blog will examine how one of India’s leading private banks modernized and expedited its digital presence, providing an enhanced experience for their customers using Oracle NoSQL Database.
Some of the bank’s challenge:
- Exceeding customer expectations: India has more than 50% of its population below age 25 and more than 65% below age 35. Banks customers are increasingly comparing banking experiences to other areas of their digital lives. These digital natives aren’t looking to check their balances and deposit checks. They are looking for more meaningful online experiences, e.g., they are looking to start and finish applications to open an account without ever walking into a bank, and they want it to happen fast. The bank was looking at a system that can provide an engaging and personalized digital customer experience in real-time under strict SLA (e.g., process a loan under 10 sec).
- Ability to provide comprehensive services: Provide ‘Always-on’ digital services and delight customers by assisting them through chatbot interactions. Additionally, they want to experiment and deliver new services such as enhanced payment and block-chain technologies valued by their customers.
- Provide customer 360 experience: The bank offers various services, and their customers interact with those services in many different ways. However, customers want a consistent experience, regardless of the business division they are interacting with or the device they use in the process. Delivering an engaging and personalized customer experience with a single customer view and a unified view of all interactions encompassing each touchpoint with the bank is challenging.
- Managing change without disruption: The bank needed agility to launch new services and make their development staff more productive. They want to minimize outages with high availability built into the system.
Choosing the right data management strategy
A comprehensive data management strategy sets the stage for establishing a deeper understanding of customer experience. It can offer a single view by collecting all the customer’s structured and unstructured data from across the organization and other relevant external sources into one place. A NoSQL database is an ideal choice. It can store personal and demographic information and customer interactions with the company, including calls, chats, emails, texts, social media responses, product/service activity history, past and present purchases. McKinsey’s study suggests that data-driven companies tend to be 19X profitable when they use data as a differentiation, as they tend to acquire 23X more customers and retain 6X more customers.
Why Oracle NoSQL Database
Oracle NoSQL Database multi-data model makes it easy for developers to store and combine data of any structure within the database without giving up sophisticated validation rules to govern data quality.
- Support for flexible data model:
With the JSON document model, the schema can be dynamically modified without application or database downtime. Bank can localize all data for a given entity – such as a financial asset class or user class – into a single document, rather than spreading it across multiple relational tables. Customers can access entire documents in a single database operation, rather than joining separate tables spread across the database. As a result of this data localization, application performance is often much higher when using Oracle NoSQL Database, which can be the decisive factor in improving customer experience.
- Predictable scalability with always-on availability
As banking use cases evolve, data sources and attributes grow. Onboarding additional applications, various digital channels, and users’ demands, processing and storage capacity quickly grow.
Oracle NoSQL database supports scale-out architecture and sharding technology. With sharding, the data is distributed across multiple database instances spread across different machines, thus overcoming limitations of a single server and associated resources such as CPU, RAM, or I/O. An Oracle NoSQL cluster can be expanded horizontally online without incurring any application downtime and one hundred percent transparent to the application. Oracle NoSQL Database maintains multiple copies of data for high availability purposes.
- Scale-out architecture for business continuity
The bank needed the ability to deploy the system across multiple data centers for disaster recovery purposes and also for the ability to perform local writes to the data center. Oracle NoSQL Database supports active-active architecture with multi-region tables. A multi-region architecture is two or more independent, geographically distributed Oracle NoSQL Database clusters bridged by bi-directional replication, ensuring the customers always have fast access to services and the latest data.
- Simplify application development with rich query and APIs
Oracle NoSQL provides a rich query language and extensive secondary indexes giving users fast and flexible access to data with any query pattern. This can range from simple key-value lookups to complex search, traversals, and aggregations across rich data structures, including embedded sub-documents and arrays. It also supports several easy-to-use SDKs in various programming languages – in particular, the customer was looking at NodeJS drivers.
High-level architecture of the proposed solution
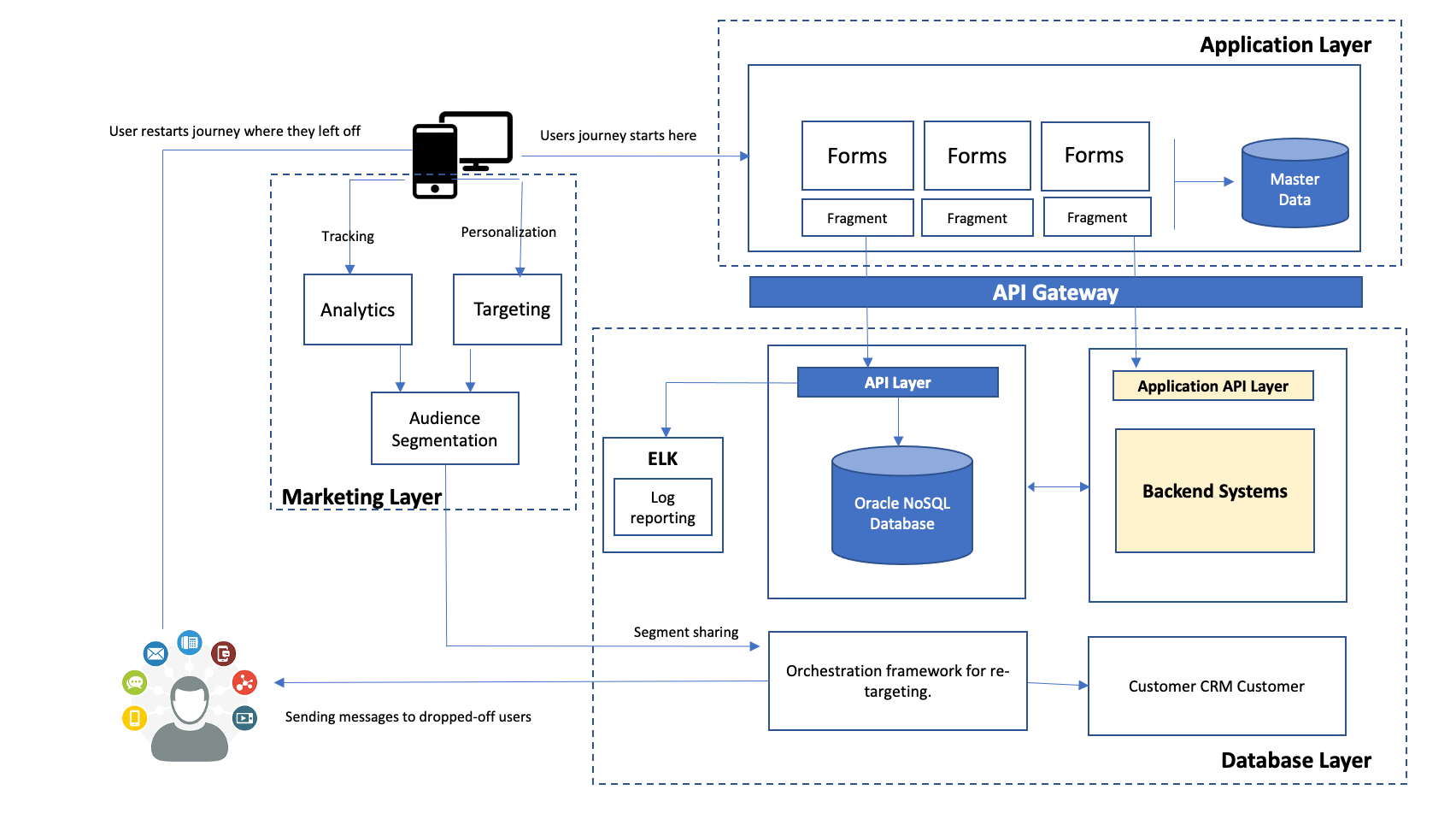
Critical components in the architecture include:
- Applications Layer: This layer manages all user input applications, e.g., loan or credit card applications. The applications are based on forms technology, allowing the developers to create adaptive and responsive documents to capture information. The forms have a notion of fragments that allows for pulling out standard segments such as personal details like name and address, family details, income details, etc. The application layer is responsible for doing all the “application plumbing”: interacting with the database, enforcing validation at event points, etc. It interacts with the bank’s backend system through the API gateway and doesn’t store any personal or sensitive information.
- Database Layer: A CRM system is used primarily for lead generation to target customers. Also available in this layer is the ELK stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), which is primarily used to audit the log data stored in the NoSQL Database. Oracle NoSQL Database has an out-of-box integration with Elasticsearch. Oracle NoSQL Database also feeds the user drop-off (incomplete form activity) data to the orchestration framework primarily used for retargeting the users.
- Marketing Layer: This layer hosts various servers that drive the business decision process. It comprises servers and tools used for customer segmentation (identify groups of individuals who are similar in attitudes, demographic profile, etc.) and customer journey analysis (a sum of all customer experiences with the bank). Additionally, it handles personalization (showing the product or service a customer would be interested in buying) and retargeting (persuading the potential customers to reconsider bank’s products and services after they left or got dropped off from their app) based on the drop-off campaign’s data that’s coming out the Oracle NoSQL Database.
Banking experience re-imagined
A typical user’s journey, e.g., loan processing, starts with a user interacting with banks loan processing applications via – the web, mobile device, email, or even branch. The application is served off the forms in the application layer. At this stage, the user fills in details and submits the scanned supporting documents. These scanned forms are classified, and information is extracted, and the data is sent to the NoSQL Database store. The data is sent to the processing system that triggers the underwriting process, beginning with the rule engine and credit scoring engine. Depending on the underwriting process results, an application will be approved, denied, or sent back to the user for additional information. If the application is approved, the loan amount is deposited into the user’s account. Suppose the user drops off at any point while filling the form. In that case, this drop-off information is stored in the NoSQL Database and feeds into the orchestration system to kick start the retargeting campaign that allows the bank to target the customer who got dropped off. The process is repeated with specific ads, emails, or WhatsApp messages retargeting the customers. In the event the customer returns, they can start the journey where they left off.
In conclusion, one of India’s leading private banks modernized and expedited its digital presence and provided an enhanced experience for its customers using Oracle NoSQL Database.
More information
Oracle NoSQL Database is a multi-model, multi-region database designed to provide a highly-available, scalable, flexible, high-performant, and reliable data management solution to meet today’s most demanding workloads. It is well-suited for high volume and velocity workloads, like the Internet of Things, customer 360, online contextual advertising, fraud detection, mobile application, user personalization, and online gaming. Developers can use a single application interface to build applications that run in on-premise and cloud environments quickly. Visit NoSQL Database Cloud Service page to learn more.