The Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service was announced at Oracle CloudWorld in 2023. https://blogs.oracle.com/maa/post/introducing-recovery-service
Since then, a common customer question has emerged: What makes this service “autonomous”? To answer that, it’s useful to first review the typical work required to prepare, perform, and maintain Oracle Database backups. While specifics may vary, the key tasks generally fall into these categories:
- Allocating backup capacity
- Securing backups
- Configuring RMAN
- Scheduling RMAN jobs
It is important to remember that backups are not just a set-it-and-forget-it operation. In addition to initial setup, there are several ongoing operational tasks that should be performed regularly:
- Monitoring jobs
- Verifying backup integrity
- Rotating backup passwords
- Balancing the backup load
- Patching the backup infrastructure
- Managing backup capacity
Managing all these responsibilities can quickly become overwhelming. In reality, some vital steps such as password rotation and validation can be skipped simply because teams do not have enough time to address everything. This is precisely where the unique “autonomous” capabilities of Autonomous Recovery Service become invaluable.
Simple, Guided Setup
Autonomous Recovery Service makes setup easy by asking for a few straightforward inputs in the user interface.
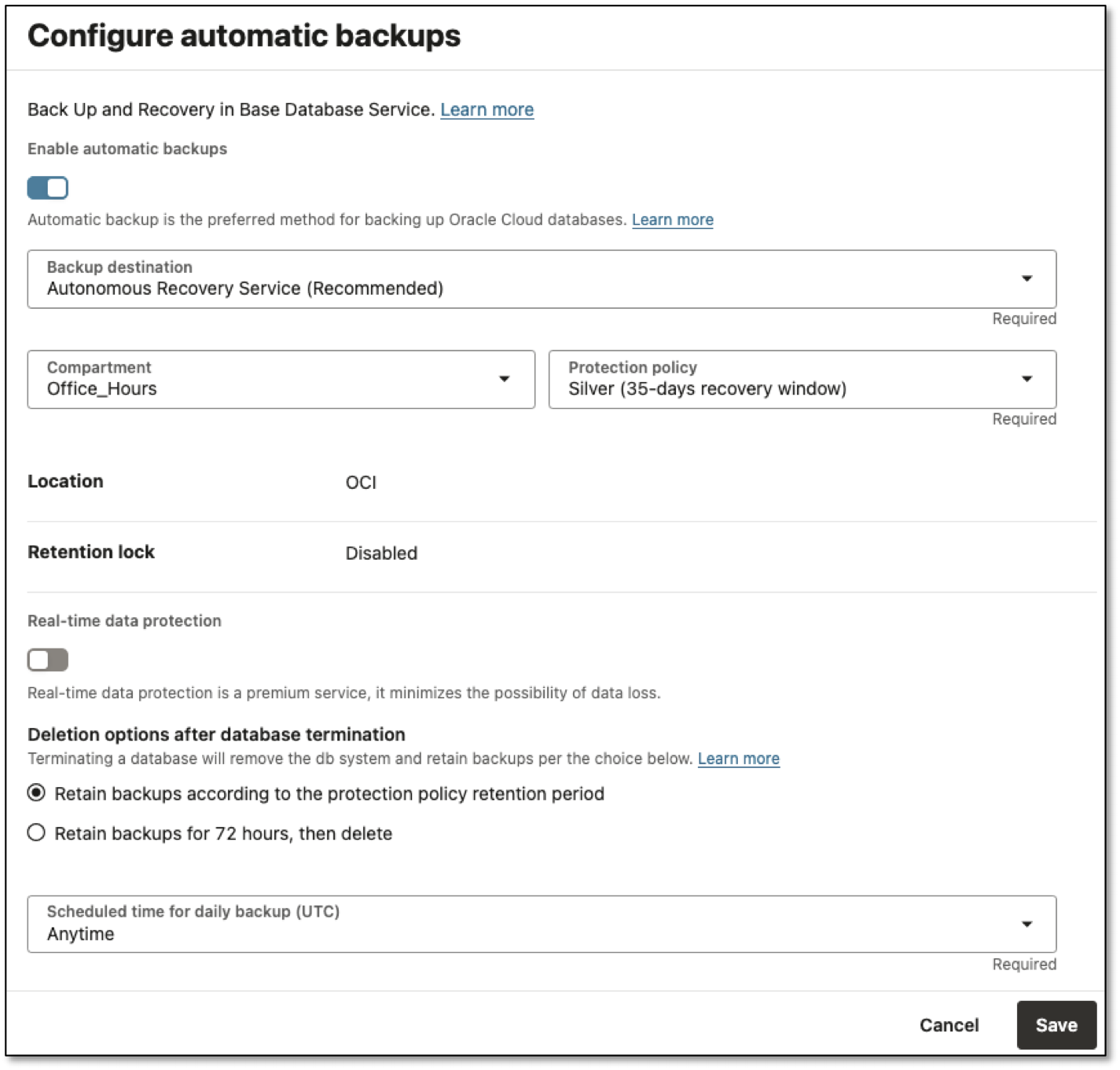
Once you set these parameters, the service takes care of the rest.
- Allocating Backup capacity: The service collects statistics from your databases to gauge backup sizes and automatically assigns storage within Oracle’s hardware fleet.
- Securing backups: Strict security is maintained by enforcing OCI Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies, providing backup immutability via a simple policy setting, and enabling private endpoints for secure database-to-backup communication.
- Configuring RMAN: The service configures and maintains the RMAN environment for you. It dynamically adjusts backup resources as your database scales, so performance keeps pace with your needs.
- Scheduling RMAN jobs: Everything is scheduled and executed automatically, minimizing manual intervention.
- Monitoring jobs: Monitoring is integrated into OCI, offering visibility at both the individual database console and a consolidated central dashboard.
- Verifying backup integrity: Data anomaly checks are offloaded to the service, ensuring validation runs with every backup and periodically on existing backups, all without impacting production workloads.
- Rotating backup passwords: Credentials are rotated automatically every few days, reducing risk from stale passwords.
- Balancing the backup load: Oracle’s infrastructure underpins the service, seamlessly load-balancing jobs across the fleet for consistent performance.
- Patching the backup infrastructure: The underlying hardware is highly available, allowing zero-downtime patching.
- Managing backup capacity: As storage requirements grow and change over time underlying storage transitions are fully automated, with no disruption to backup or restore processes.
By transferring routine tasks to automation, Autonomous Recovery Service delivers reliable database protection with less manual effort and reduced risk. This approach allows teams to focus on higher-value work while knowing that core backup and recovery processes are handled autonomously using Oracle best practices.
You can start using Autonomous Recovery Service today for Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure, Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure, and Base Database Service in OCI, Azure, Google and AWS.
