This blog is intended for Oracle Service-oriented Architecture (Oracle SOA) users familiar with Oracle SOA Cloud Service, Oracle Suite on Marketplace, and Disaster Recovery. It applies to Oracle SOA Cloud Service (SOACS) and Oracle Managed File Transfer Cloud Service (MFTCS).
Oracle SOA Cloud Service and Managed File Transfer Cloud Service are deprecated and replaced with Oracle SOA Suite on Marketplace (SOAMP). Oracle intends to retire SOACS and MFTCS (refer to MOS note 3006904.1 for details) and a tool has been provided to migrate from SOACS to SOA Suite on Marketplace: the Oracle SOA Suite Migration Manager. Review the following documentation for more information about this tool: Migrate Oracle SOA Cloud Service Instances to Oracle SOA Suite on Marketplace Using the Migration Manager.
If you are using Disaster Recovery protection in SOACS, you may wonder: how do I migrate my disaster recovery environment from SOACS to SOAMP?
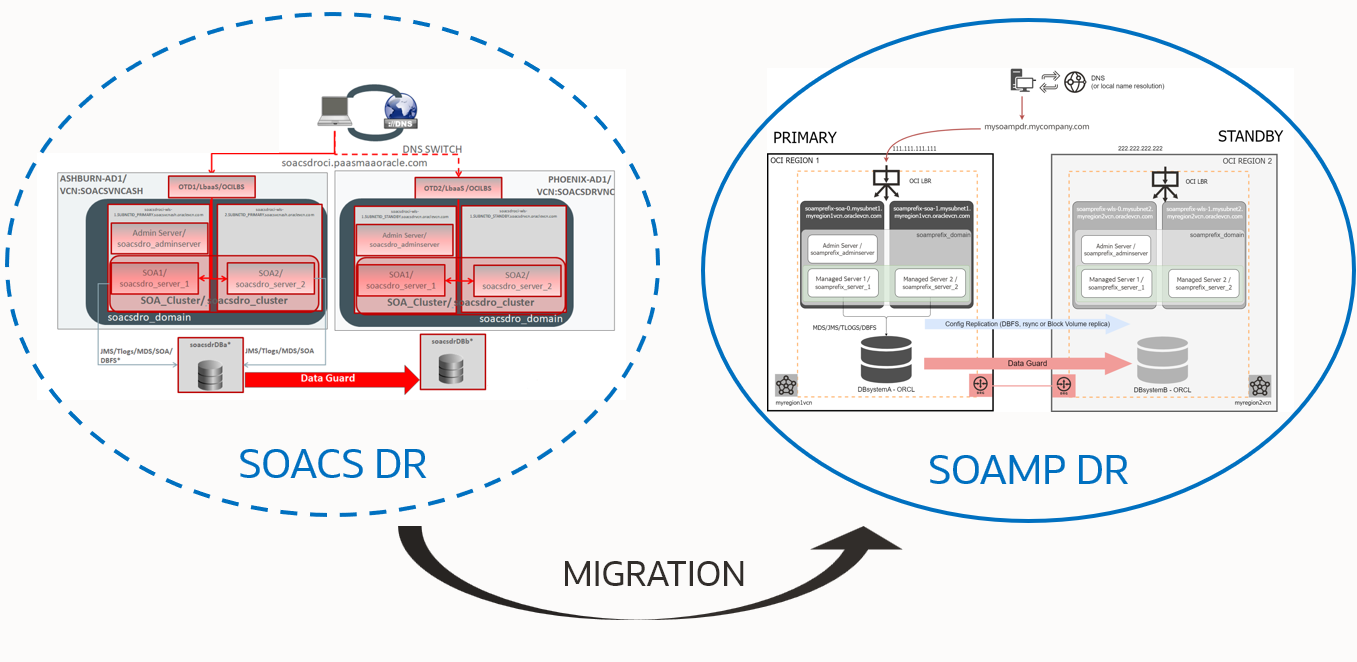
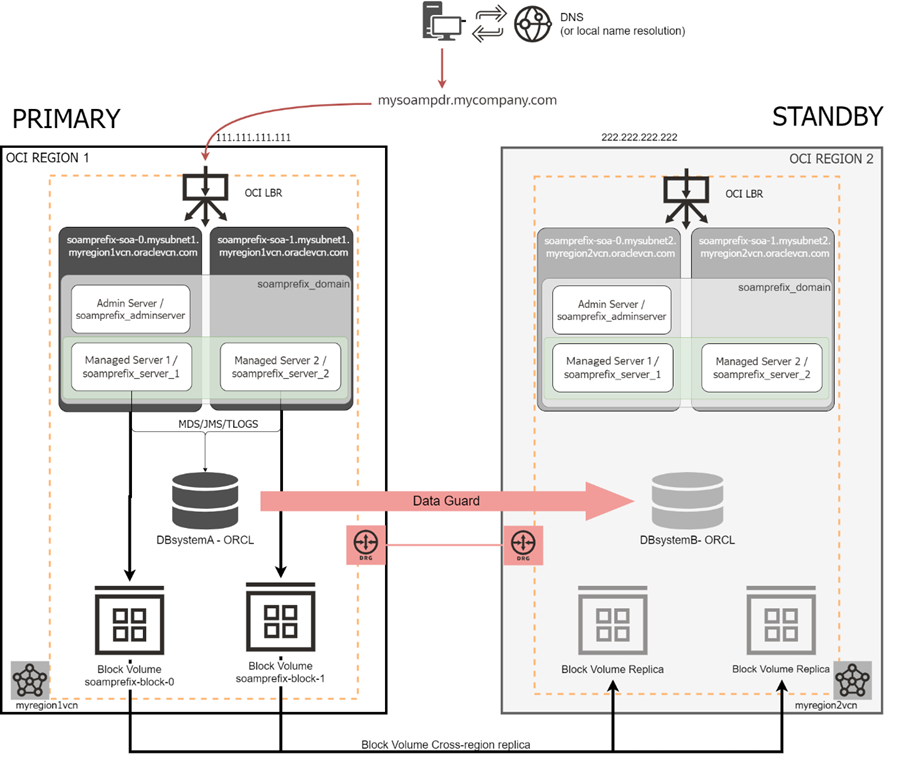
The Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA) team’s recommendation, in agreement with SOA product management, is to migrate only the primary SOACS environment using the Migration Manager. The secondary system, however, should be created like a new standby SOAMP instance from zero. The procedure described in the “SOA Marketplace Disaster Recovery” document (https://www.oracle.com/a/tech/docs/maa-soamp-dr.pdf) should be used to create this new standby. The Database system (configured with Oracle Data Guard) can be maintained as it was in SOACS.
Migrating to SOAMP DR allows you to take advantage of the new replication methods and features available only for SOAMP (all described in the SOAMP DR document). These new features include:
- Using the TNS alias in data sources simplifies the configuration of connect strings and switchover management.
- Using Block Volume cross-region replicas to automate configuration replication.
- Using Oracle Full Stack DR service to orchestrate switchover/failover.
- Using Private Views for hostname virtualization.
- … and automating multiple tasks in the lifecycle of a SOA Cloud DR system with new scripts provided by the MAA team.
In SOACS, the WebLogic domain configuration was replicated by copying the domain to a DBFS file system (aka “DBFS method”). In SOAMP, you can choose among three replication methods: 1) DBFS (same as in SOACS), 2) rsync with OCI FS storage as staging location, or 3) OCI native Block Volume Cross-region replication. In conjunction with Full Stack DR service, this last method is the recommended approach for optimum RTO and management simplicity.
Hence, the roadmap for migrating the SOACS DR to SOAMP DR should be the following:
- Migrate your primary SOACS to SOAMP with the Migration Manager tool.
- Reuse your existing Oracle Data Guard system; there is no need to recreate the standby database.
- Refer to the table in the “Replication Methods Comparison” section of the SOAMP DR document to decide which replica method best suits your business needs. Notice that the MAA recommendation is to use Block Volume cross-region replication with FSDR.
- Then, set the SOAMP secondary system by following the procedures (described in the same SOAMP DR document) for the precise replication method that you have selected :
- Both the replica based on “DBFS staging” and the replica based on “OCI FS filesystem staging” use Disaster Recovery Setup (DRS) utilities described in the document.
- To use the model based on Block Volume cross-region replica (preferred method), you just provision secondary and configure native Block Volume cross-region replica (also explained in the document). You don’t need to run the DRS tool for the setup.
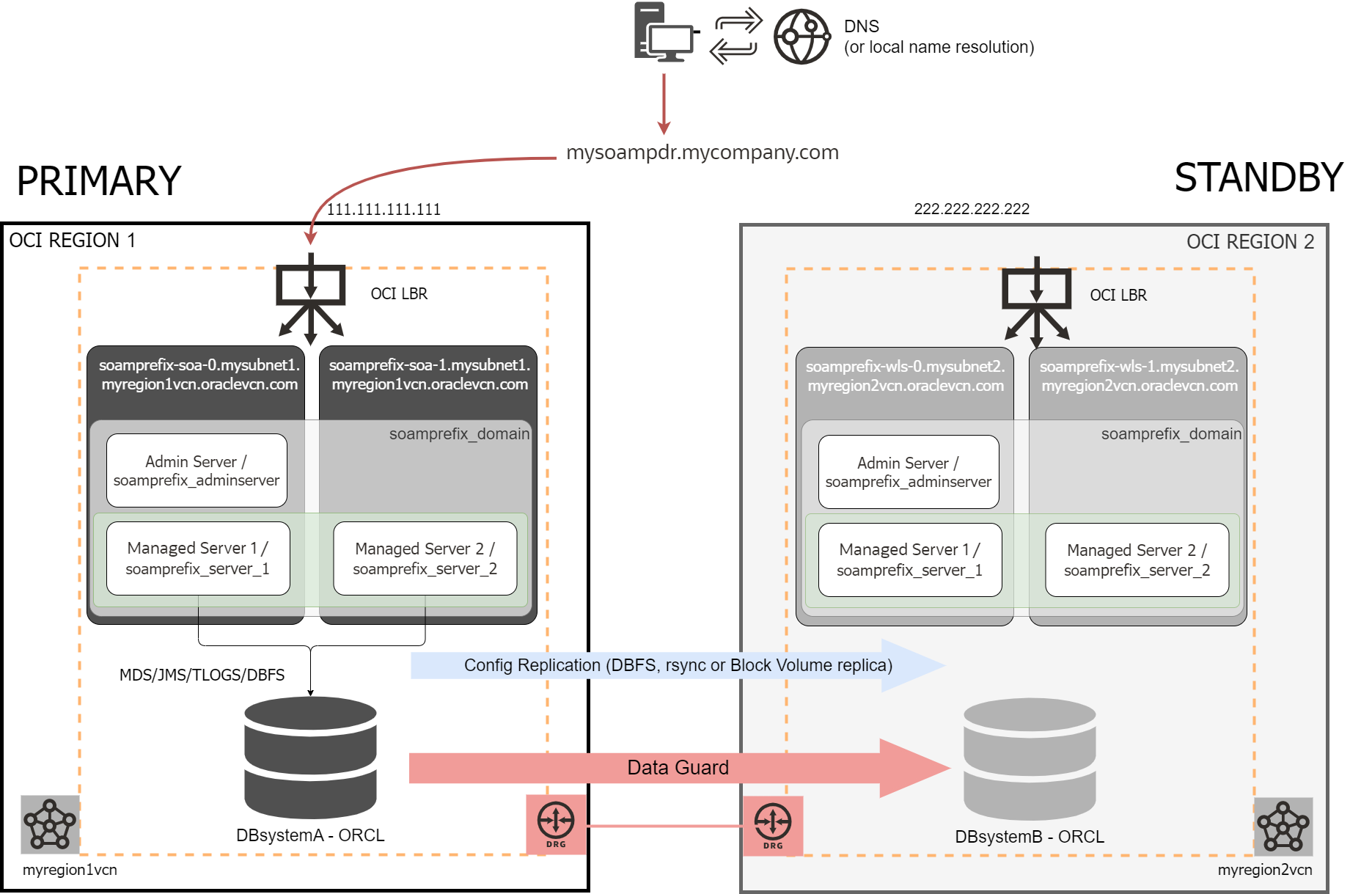
Considerations for the migration scenario
These are particular considerations when providing the secondary SOAMP instance when the primary was migrated from SOACS.
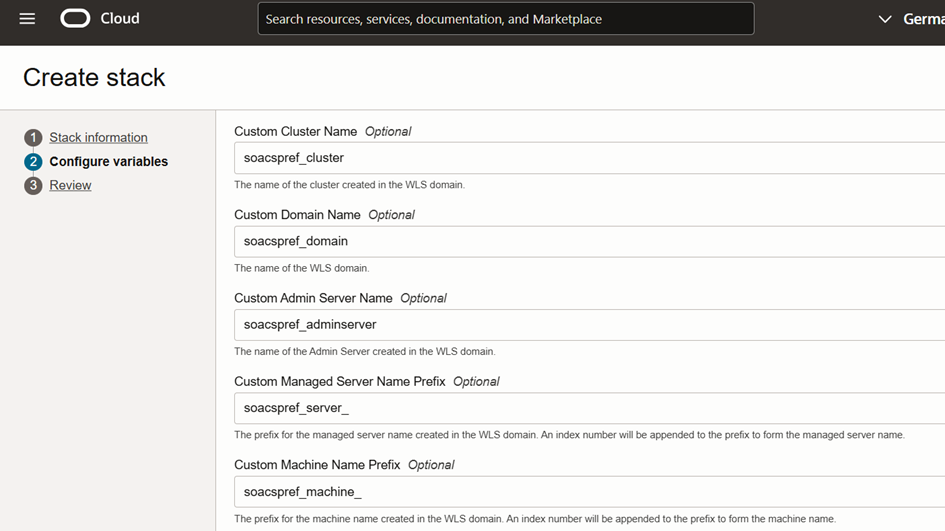
- When you provision the secondary SOAMP, use the same names as in the primary SOAMP for the domain, cluster, admin server, and servers. To customize these names, use the “Service Instance Advanced Configuration” option of the SOAMP provisioning wizard. If you don’t do this, the names are based on the secondary instance name prefix. Due to the differences between SOACS and SOAMP, naming conventions may not match the primary resource names, which can cause issues when configuring DR.

Figure 3. Check “Service Instance Advanced” when provisioning the secondary SOAMP instance.
So, for example, if the primary uses the prefix “soacspref_” in the names (soacspref_domain, soacspref_cluster, soacspref_adminserver, and soacspref_server_1, soacspref_server_2, etc.) then provide these values for the custom names when provisioning secondary SOAMP with the wizard:
Custom Cluster Name: soacspref_cluster
Custom Domain Name: soacspref_domain
Custom Admin Server Name: soacspref_adminserver
Custom Managed Server Name Prefix: soacspref_server_
Custom Machine Name Prefix: soacspref_machine_
- Similarly, to be consistent with the ports used by primary SOACS, use the option “Service Instance Advanced Configuration” when provisioning the secondary SOAMP:
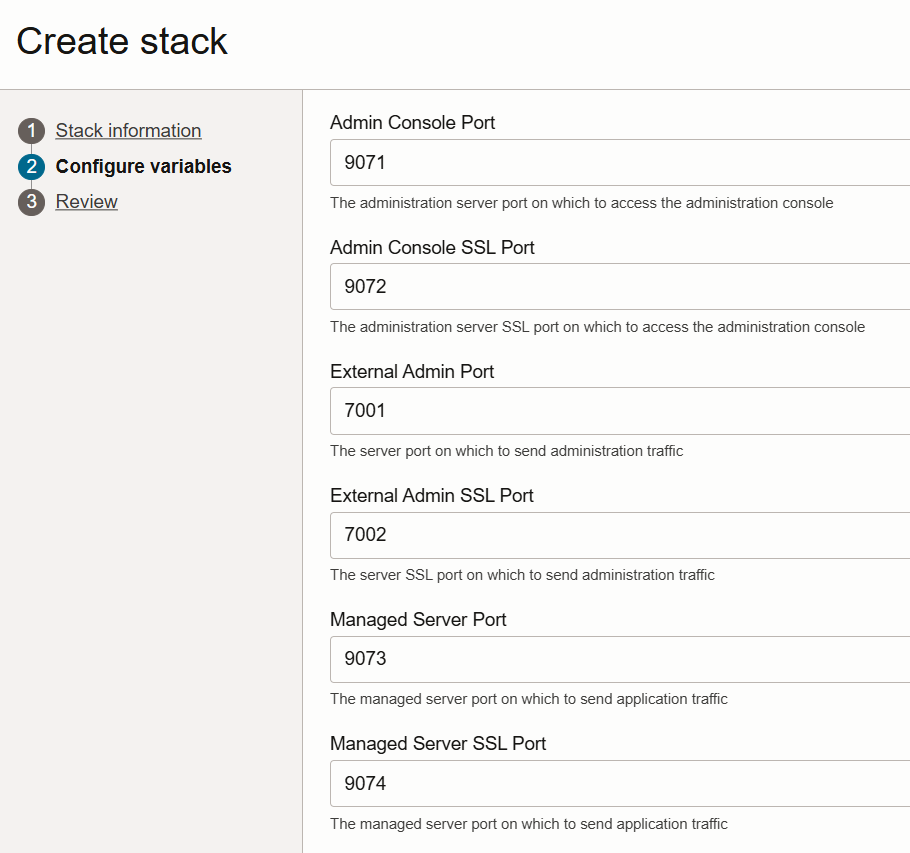
Post-migration steps
During the DR setup process for SOACS, the tnsnames.ora, the wallet file, and the dbfsMount.sh script in the $DOMAIN_HOME/dbfs folder are updated. These files are modified in the WebLogic Administration Server’s primary node and all the standby system nodes. The default alias used to mount the DBFS filesystem is modified from its default “ORCL” value to the “PDB_name” (this is done in all the artifacts required: tnsnames,ora, wallet, dbfsMount.sh script). Additionally, aliases pointing to the primary and standby CDB are added to the tnsnames.ora. The script that copies the configuration in SOACS (dbfscopy.sh) required these changes to work properly.
These changes are carried over when you migrate primary from SOACS to SOAMP. However, the DR setup in SOAMP doesn’t use these modifications. Hence, once you have configured DR in the new SOAMP environment, it is recommended that these files be cleaned up.
- If you continue using DBFS for replication in SOAMP, you can remove the TNS entries that point to the primary and standby CDBs from the $DOMAIN_HOME/dbfs/tnsnames.ora. You can leave just the entry that points to the PDB; only this one is needed to mount the DBFS filesystem. Perform this action in the primary administration node only. The rest of the nodes are expected to already have the entry for the PDB only.
Not doing this will not cause issues, but it is recommended to keep the file simple.
- If you switch to rsync with OCI FS in SOAMP, you can remove the TNS entries that point to the primary and standby CDBs from the $DOMAIN_HOME/dbfs/tnsnames.ora. You can leave just the entry that points to the PDB; only this one is needed to mount the DBFS filesystem. Perform this action in the primary administration node only. The rest of the nodes are expected to already have the entry for the PDB only.
In addition, in all the secondary nodes, ensure that the entry name in the $DOMAIN_HOME/dbfs/tnsnames.ora file that points to the PDB is consistent with the alias used by the dbfsMount.sh script and wallet. You will need to change it in the tnsnames.ora from the default entry alias “ORCL” to the PDB alias. If you don’t do this, the DBFS filesystem will not mount properly in the secondary nodes.
- If you use the Block Volume DR model in SOAMP (preferred method), you can remove the entries that point to the primary and standby CDBs from the $DOMAIN_HOME/dbfs/tnsnames.ora. You can leave just the entry that points to the PDB; only this one is needed to mount the DBFS filesystem. This action is only required in the primary admin node. The rest of the nodes are expected to already have the entry for the PDB only.
Not doing this will not cause issues in mounting the DBFS mounts. However, due to the string replacements required in this model in each switchover, the entries that point to the CDB will be broken. They are not used, so it is recommended that they be removed to keep it simple.
Finally, review the document. Use OCI Full Stack Disaster Recovery Service with Oracle WebLogic Server domains to use FSDR. It explains how to perform switchovers in just one click with FSDR service. We recommend this especially when using the Block Volume DR method because FSDR simplifies the steps of unmount, detach, attach and mount the replicated block volumes.

Conclusion
The Oracle SOA Suite Migration Manager can migrate your primary SOACS in a Disaster Recovery topology. Then, use the SOAMP Disaster Recovery document https://www.oracle.com/a/tech/docs/maa-soamp-dr.pdf to configure your DR system with all the considerations and recommendations in this blog. This offers multiple advantages and improvements in the target system while allowing you to maintain your SOA deployments, Metadata, Runtime data, and existing Data Guard configuration.