JDK 25 is Now Available!
Oracle is proud to announce the general availability of JDK 25 for developers, enterprises, and end-users.
New in this release
JDK 25 delivers sixteen enhancements that are significant enough to warrant their own JDK Enhancement Proposal (JEP), including four preview features, one experimental feature, and one incubator feature. These features cover innovations to the Java language to the libraries (with two improvements specifically to security libraries), performance and runtime, and monitoring improvements.
Language Innovation
Primitive Types in Patterns, instanceof, and switch 3rd Preview [JEP 507]
Enhances pattern matching by allowing primitive types in all pattern contexts and extends instanceof and switch to work with all primitive types. This is a preview language feature.
Module Import Declarations [JEP 511]
Enhances the Java programming language with the ability to succinctly import all of the packages exported by a module. This simplifies the reuse of modular libraries but does not require the importing code to be in a module itself.
Compact Source Files and Instance Main Methods [JEP 512]
Evolves the Java programming language so that beginners can write their first programs without needing to understand language features designed for large programs. Rather than using a separate dialect of the language, beginners can write streamlined declarations for single-class programs and later seamlessly expand those programs to use more advanced features as their skills grow. Experienced developers will likewise enjoy writing small programs succinctly, without the need for constructs intended for programming in the large.
Flexible Constructor Bodies [JEP 513]
In constructors in the Java programming language, allow statements to appear before an explicit constructor invocation, i.e., super(..) or this(..). The statements cannot reference the instance under construction, but they can initialize its fields. Initializing fields before invoking another constructor makes a class more reliable when methods are overridden.
Library Improvements
Structured Concurrency 5th Preview [JEP 505]
Structured concurrency treats groups of related tasks running in different threads as a single unit of work, thereby streamlining error handling and cancellation, improving reliability, and enhancing observability. This is a preview API.
Enable a method to share immutable data both with its callees within a thread, and with child threads. Scoped values are easier to reason about than thread-local variables. They also have lower space and time costs, especially when used together with virtual threads (JEP 444) and structured concurrency (JEP 505).
Stable Values Preview [JEP 502]
Introduces an API for stable values, which are objects that hold immutable data. Stable values are treated as constants by the JVM, enabling the same performance optimizations that are enabled by declaring a field final. Compared to final fields, however, stable values offer greater flexibility as to the timing of their initialization. This is a preview feature.
Vector API 10th Incubator [JEP 508]
Introduces an API to express vector computations that reliably compile at runtime to optimal vector instructions on supported CPU architectures, thus achieving performance superior to equivalent scalar computations.
Security Libraries Enhancements
PEM Encodings of Cryptographic Objects Preview [JEP 470]
Introduces an API for encoding objects that represent cryptographic keys, certificates, and certificate revocation lists into the popular Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) transport format, and for decoding from that format back into objects. This is a preview API.
Key Derivation Function API [JEP 510]
Introduces an API for Key Derivation Functions (KDFs), which are cryptographic algorithms for deriving additional keys from a secret key and other data.
Performance and Runtime Advancements
Compact Object Headers [JEP 519]
Reduces the size of object headers in the HotSpot JVM from between 96 and 128 bits down to 64 bits on 64-bit architectures. This will reduce heap size, improve deployment density, and increase data locality. This JEP does not make compact object headers the default object-header layout; users who want to benefit from this feature must opt in using command line options.
Ahead-of-Time Command-Line Ergonomics [JEP 514]
Makes it easier to create ahead-of-time caches, which accelerates the startup of Java applications, by simplifying the commands required for common use cases.
Ahead-of-Time Method Profiling [JEP 515]
Improves warmup time by making method-execution profiles from a previous run of an application instantly available, when the HotSpot Java Virtual Machine starts. This will enable the JIT compiler to generate native code immediately upon application startup, rather than having to wait for profiles to be collected.
Monitoring
JFR CPU-Time Profiling Experimental [JEP 509]
Allows JDK Flight Recorder (JFR) to capture more accurate CPU-time profiling information on Linux. This is an experimental feature.
JFR Cooperative Sampling [JEP 518]
Improves the stability of JDK Flight Recorder (JFR) when it asynchronously samples Java thread stacks. Achieves this by walking call stacks only at safepoints, while minimizing safepoint bias.
Method Timing & Tracing [JEP 520]
Extendss JDK Flight Recorder (JFR) with facilities for method timing and tracing via bytecode instrumentation.
A Reminder on Preview, Experimental, and Incubator Features
Preview features are fully specified and fully implemented Language or VM Features of the Java SE Platform; and yet impermanent. They are made available in JDK Feature Releases to allow for developer feedback based on real-world uses, before becoming permanent in a future release. This also affords tool vendors the opportunity to work towards supporting features before they are finalized into the Java SE Standard. Experimental features deliver early-stages of future functionality, primarily at the Virtual Machine (VM) level, that are still undergoing development and testing and are used to gather early feedback on potentially impactful enhancements to the HotSpot VM. APIs in Incubator modules put non-final APIs and non-final tools in the hands of developers and users so that we can gather feedback that will ultimately improve the quality of the Java platform.
Other Changes
Besides the changes described in the JEPs, there are many smaller changes listed in the release notes, which will be of interest to many application developers and system administrators. These include deprecation of obsolete APIs and removal of previously deprecated ones.
Some of the key updates from the Java 25 release notes:
Mechanism to Disable Signature Schemes Based on Their TLS Scope (JDK-8349583)
security-libs/javax.net.ssl
TLS protocol specific usage constraints are now supported by the jdk.tls.disabledAlgorithms property in the java.security configuration file, as follows:
UsageConstraint:
usage UsageType { UsageType }
UsageType:
HandshakeSignature | CertificateSignature
HandshakeSignature restricts the use of the algorithm in TLS handshake signatures. CertificateSignature restricts the use of the algorithm in certificate signatures. An algorithm with this constraint cannot include other usage types defined in the jdk.certpath.disabledAlgorithms property. The usage type follows the keyword and more than one usage type can be specified with a whitespace delimiter.
Turn on Timestamp and Thread Details by Default for java.security.debug (JDK-8350689)
security-libs/java.security
The debug output from the java.security.debug system property now includes thread id, caller information, and timestamp information.
Each debug output statement generated with the java.security.debug option is now formatted as:
componentValue[threadId|threadName|sourceCodeLocation|timestamp]: <debug statement>
where
componentValueis the security component value being logged.threadIdis the hexadecimal value of the thread ID.threadNameis the name of the thread executing the log statement.sourceCodeLocationis the source file and line number making this log call, in the format “filename:lineNumber”.timestampis the date and time in the format “yyyy-MM-dd kk:mm:ss.SSS”.- <debug statement> corresponds to the debug output from the security component.
The +thread and +timestamp options introduced in JDK 23 will no longer have an impact and are ignored.
More information on those legacy options is available in the JDK 23 release notes.
Add Support for TLS Keying Material Exporters to JSSE and SunJSSE Provider (JDK-8341346)
security-libs/javax.net.ssl
This enhancement adds support for TLS (Transport Layer Security) Keying Material Exporters, which allow applications to generate additional application-level keying material from a connection’s negotiated TLS keys.
This change enables support for several additional protocols, including those labels registered in the IANA TLS Parameters-Exporter Label document.
This functionality is described in RFC 5705 for TLSv1-TLSv1.2, and RFC 8446 for TLSv1.3. The feature can be accessed via two new APIs in the javax.net.ssl.ExtendedSSLSession class:
public SecretKey exportKeyingMaterialKey(String keyAlg,
String label, byte[] context, int length) throws SSLKeyException
public byte[] exportKeyingMaterialData(
String label, byte[] context, int length) throws SSLKeyException
Add Standard System Property stdin.encoding (JDK-8350703)
core-libs/java.lang
A new system property, stdin.encoding, has been added. This property contains the name of the recommended Charset for reading character data from System.in, for example, when using InputStreamReader or Scanner. By default, the property is set in a system-specific fashion based on querying the OS and user environment. Note that its value may differ from the value of the file.encoding property, the default Charset, and the value of the native.encoding property. The value of stdin.encoding may be overridden to be UTF-8 by providing the argument -Dstdin.encoding=UTF-8 on the command line.
New getChars(int, int, char[], int) Method in CharSequence and CharBuffer (JDK-8343110)
core-libs/java.lang
A new method, getChars(int, int, char[], int), has been added to java.lang.CharSequence and java.nio.CharBuffer to bulk-read characters from a region of a CharSequence into a region of a char[]. String, StringBuilder, and CharBuffer implements CharSequence. Code that operates on a CharSequence should no longer need to special-case and cast to String when needing to bulk-read from a sequence. The new method may be more efficient than a loop over characters of the sequence.
New connectionLabel Method in java.net.http.HttpResponse to Identify Connections (JDK-8350279)
core-libs/java.net
A new connectionLabel method has been added to java.net.http.HttpResponse. This new method returns an opaque connection label that callers can leverage to associate a response with the connection it is carried on. This is useful to determine whether two requests were carried on the same connection or on different connections.
New Methods on BodyHandlers and BodySubscribers to Limit the Number of Response Body Bytes Accepted by the HttpClient (JDK-8328919)
core-libs/java.net
Two new methods, java.net.http.HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.limiting(BodyHandler downstreamHandler, long capacity) and java.net.http.HttpResponse.BodySubsribers.limiting(BodySubscriber downstreamSubscriber, long capacity), have been added to the HttpClient API. These methods extend an existing BodyHandler or BodySubscriber with the ability to limit the number of response body bytes that the application is willing to accept in response to an HTTP request. Upon reaching the limit when reading the response body, an IOException will be raised and reported to the downstream subscriber. The subscription will be cancelled. Any further response body bytes will be discarded. This makes it possible for the application to control the maximum amount of bytes that it wants to accept from the server.
New Property to Construct ZIP FileSystem as Read-only (JDK-8350880)
core-libs/java.nio
The ZIP file system provider is updated to allow a ZIP file system to be created as a read-only or read-write file system. When creating a ZIP file system, the property name “accessMode” can be used with a value of “readOnly” or ” readWrite” to specify the desired mode. If the property is not provided then the file system is created as a read-write file system if possible.
The following example creates a read-only file system:
FileSystem zipfs = FileSystems.newFileSystem(pathToZipFile, Map.of("accessMode","readOnly"));
See the jdk.zipfs module description for more information on this and other properties supported by the ZIP file system provider.
Updates to ForkJoinPool and CompletableFuture (JDK-8319447)
core-libs/java.util.concurrent
java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool is updated in this release to implement ScheduledExecutorService. This API update can help the performance of delayed task handling in network and other applications where delayed tasks are used for timeout handling, and where most timeouts are cancelled.
In addition to the schedule methods defined by ScheduledExecutorService, ForkJoinPool now defines a new method submitWithTimeout to submit a task that is cancelled (or some other action executed) if the timeout expires before the task completes.
As part of the update, CompletableFuture and SubmissionPublisher are changed so that all async methods without an explicit Executor are performed using the ForkJoinPool common pool. This differs from previous releases where a new thread was created for each async task when the ForkJoinPool common pool was configured with parallelism less than 2.
java.util.zip.Inflater and java.util.zip.Deflater Enhanced To Implement AutoCloseable (JDK-8225763)
core-libs/java.util.jar
java.util.zip.Inflater and java.util.zip.Deflater now implement AutoCloseable and can be used with the try-with-resources statement. Applications could previously invoke the end() method to release the resources held by the Inflater/Deflater instance. Now, either the end() or the close() method can be invoked to do the same.
Thread Dumps Generated by HotSpotDiagnosticMXBean.dumpThreads and jcmd Thread.dump_to_file Updated to Include Lock Information (JDK-8356870)
core-svc
The thread dump generated by the com.sun.management.HotSpotDiagnosticMXBean.dumpThreads API, and the diagnostic command jcmd <pid> Thread.dump_to_file, now includes lock information.
The HotSpotDiagnosticMXBean.dumpThreads API is also updated to link to a JSON schema that describes the JSON format thread dump. The JSON format thread dump is intended to be read and processed by diagnostic tools.
Unlike the traditional thread dump generated by jstack and jcmd <pid> Thread.print, the thread dump generated by the HotSpotDiagnosticMXBean.dumpThreads and jcmd <pid> Thread.dump_to_file does not print information about deadlocks in this release.
G1 Reduces Remembered Set Overhead by Grouping Regions into Shared Card Sets (JDK-8343782)
hotspot/gc
The G1 garbage collector further reduces remembered set memory overhead and pause-time by allowing multiple regions to share a single internal structure (G1CardSet) when they are likely to be collected together during a Mixed GC.
Previously, each region maintained its own G1CardSet, resulting in high memory overhead and redundant tracking of references between regions that would eventually be collected as a group. In the new design, regions expected to be evacuated together are grouped after the Remark phase and assigned a shared G1CardSet, eliminating the need to track references between them individually.
This improves memory efficiency and reduces merge time during collection pauses.
New JFR Annotation for Contextual Information (JDK-8356698)
hotspot/jfr
A new annotation, jdk.jfr.Contextual, has been introduced to mark fields in custom JFR events that contain contextual information relevant to other events occurring in the same thread. For example, fields in a user-defined HTTP request event can be annotated with @Contextual to associate its URL and trace ID with events that occur during its execution, such as a jdk.JavaMonitorEnter event due to a contended logger.
Tools can now pair higher-level information, such as span and trace IDs, with lower-level events. The print command of the jfr tool, included in the JDK, displays this contextual information alongside JVM and JDK events, for example, in events for lock contention, I/O, or exceptions that occur during a trace span or an HTTP request event.
UseCompactObjectHeaders Is a Product Option (JDK-8350457)
hotspot/runtime
The flag -XX:+/-UseCompactObjectHeaders is now a product option. This allows users to enable compact object headers without the use of the -XX:+UnlockExperimentalVMOptions flag. Compact object headers are a feature introduced in JDK 24 under JEP 450. Enabling this feature reduces the Java heap footprint of applications and potentially provides performance benefits. The feature remains disabled by default in this release but may become the default in a future release.
To support use of compact object headers, two additional CDS archives for the JDK image called classes_coh.jsa and classes_nocoops_coh.jsa are provided to allow equivalent startup performance when UseCompactObjectHeaders is turned on.
SHAKE128-256 and SHAKE256-512 as MessageDigest Algorithms (JDK-8354305)
security-libs/java.security
Two new MessageDigest algorithms, SHAKE128-256 and SHAKE256-512, have been added to the SUN provider. These are fixed-length versions of the SHAKE128 and SHAKE256 Extendable-Output Functions (XOFs) defined in NIST FIPS 202.
Support for HKDF in SunPKCS11 (JDK-8328119)
security-libs/javax.crypto:pkcs11
The SunPKCS11 security provider now supports the following algorithms for the new Key Derivation Function API: HKDF-SHA256, HKDF-SHA384, and HKDF-SHA512. Please refer to JDK-8344464 for further details.
Update XML Security for Java to 3.0.5 (JDK-8344137)
security-libs/javax.xml.crypto
The XML Signature implementation has been updated to Santuario 3.0.5. Support for four new SHA-3 based ECDSA SignatureMethod algorithms has been added: SignatureMethod.ECDSA_SHA3_224, SignatureMethod.ECDSA_SHA3_256, SignatureMethod.ECDSA_SHA3_384, and SignatureMethod.ECDSA_SHA3_512.
Enhanced jar File Validation (JDK-8345431)
tools/jar
The jar --validate command has been enhanced to identify and generate a warning message for:
- Duplicate entry names
- Entry names which:
- contain a drive or device letter
- contain a leading slash
- contain backward slashes “\”
- the entry name or any path element is “.” or “..”
- Inconsistencies in the ordering of entries between the LOC and CEN headers
Finally, like all feature releases, JDK 25 includes hundreds of performance, stability, and security updates including adapting to underlying OS and firmware updates and standards. Users and application developers usually benefit from these changes without noticing them, but information on each of them can be found in the OpenJDK issue tracker.
And the constant feature, included in all JDK releases: Predictability
JDK 25 is the 16th Feature Release delivered on time through the six-month release cadence. This level of predictability allows developers to easily manage their adoption of innovation thanks to a steady stream of improvements.
Java’s ability to boost performance, stability, and security continues to make it the world’s most popular programming language.
Oracle will offer long-term support for JDK 25 at least until Sep of 2033.
Java 25, Together
As with previous releases, Java 25 is the result of the contributions of many individuals and organizations in the OpenJDK Community — we all build Java, together!
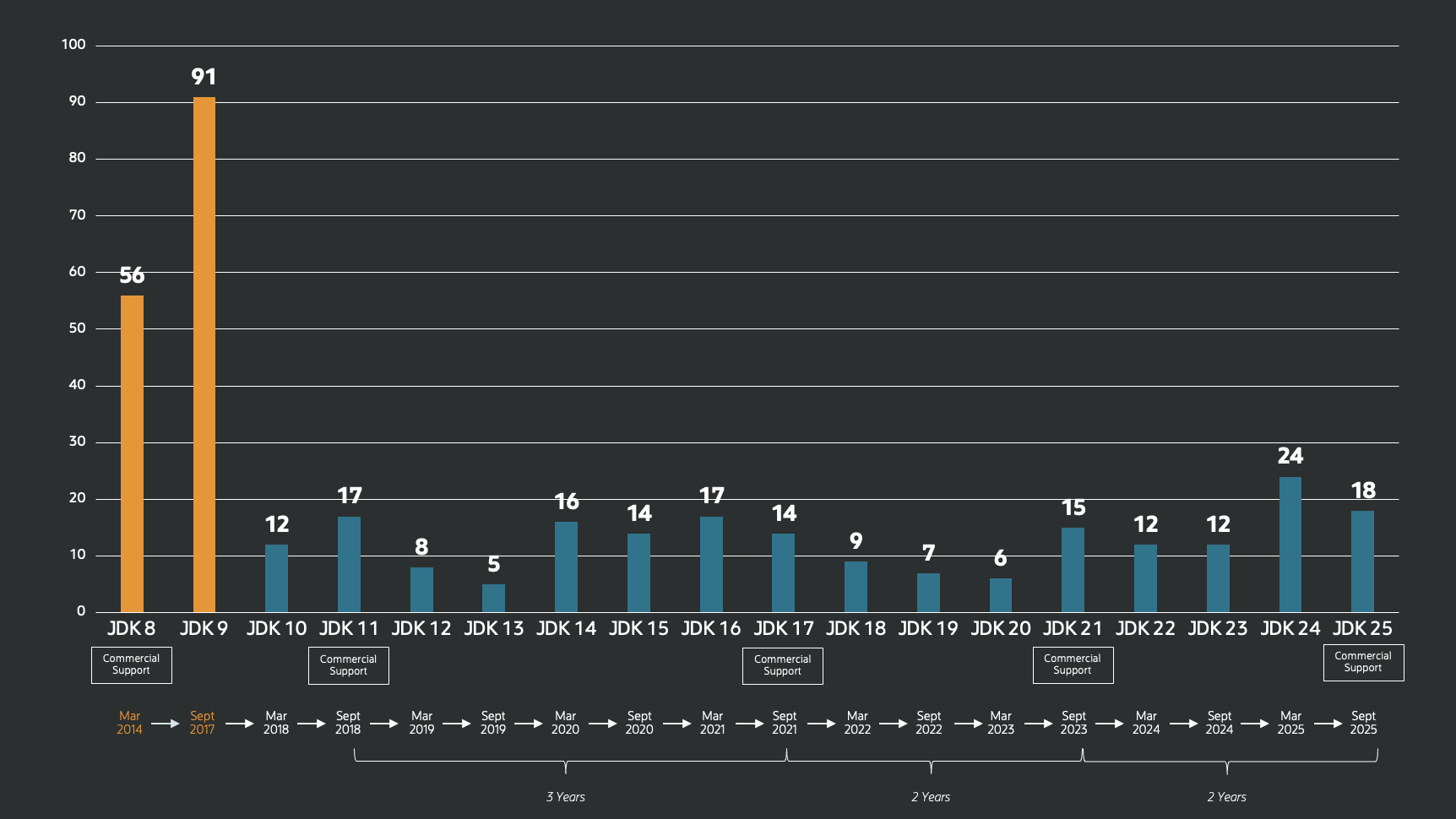
JDK 25 Fix Ratio
The rate of change over time in the JDK releases has remained largely constant for years, but under the six-month cadence the pace at which production-ready features and improvements are delivered has sharply increased.
The changes in JDK 25 range from significant new features to small enhancements to routine maintenance, bug fixes, and documentation improvements. Each change is represented in a single commit for a single issue in the JDK Bug System.
Of the 33,793 JIRA issues marked as fixed in Java 11 through Java 25 at the time of their GA, 23,762 were completed by Oracle employees while 10,031 were contributed by individual developers and developers working for other organizations. Going through the issues and collating the organization data from assignees results in the following chart of organizations sponsoring the development of contributions in Java:

In Java 25, of the 2,606 JIRA issues marked as fixed, 1,655 were completed by Oracle, while 951 were contributed by other members of the Java community.
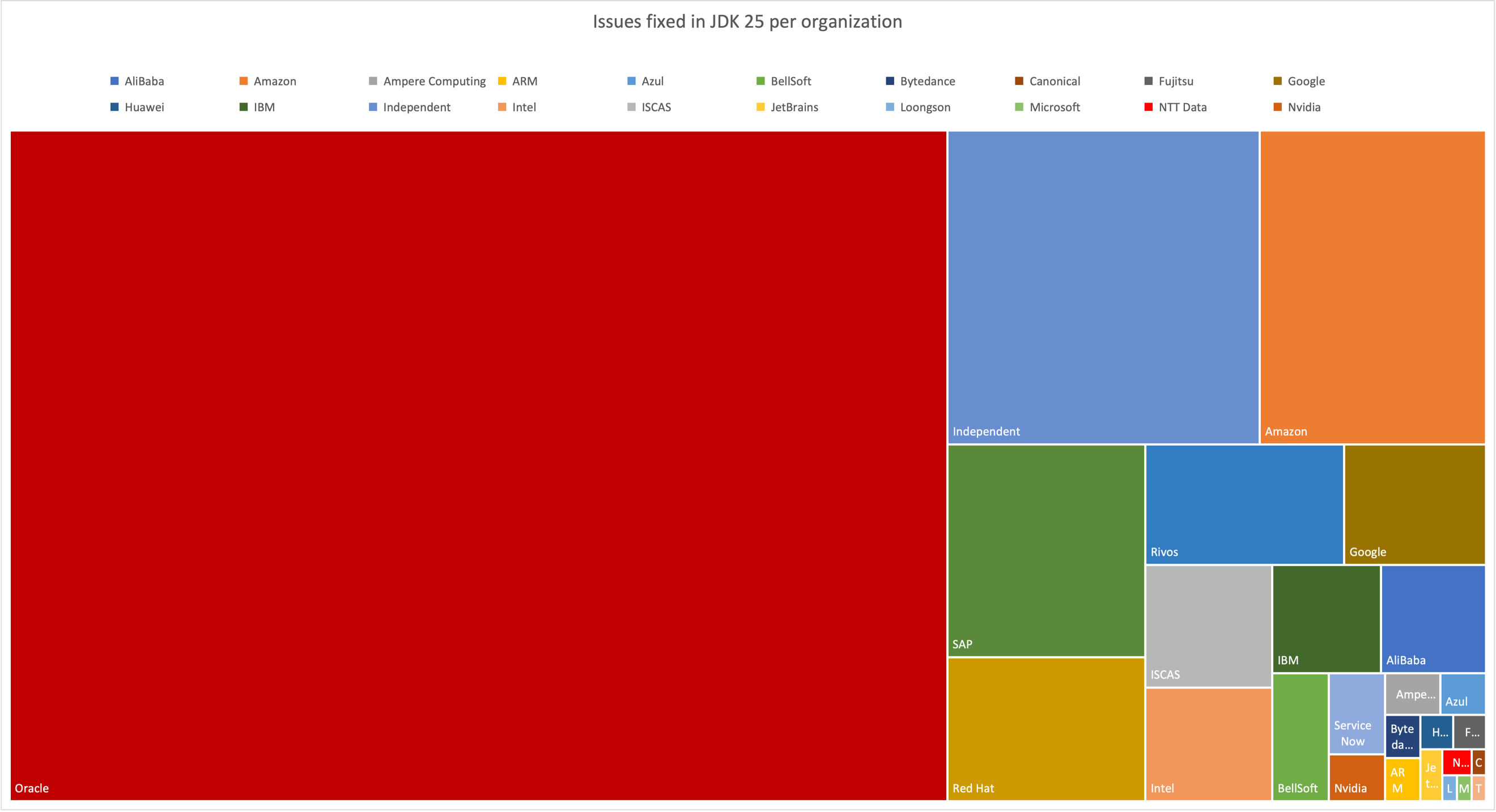
Oracle would like to thank the developers working for organizations including Alibaba, Amazon, Google, IBM, Intel, ISCAS, Red Hat, Rivos, SAP, and ServiceNow for their notable contributions. We are also thankful to see contributions from smaller organizations such as Bellsoft, as well as independent developers who collectively contributed 9% of the fixes in Java 25.
Additionally, we would like to thank the following individuals who provided invaluable feedback on build quality, logged good quality bugs, or offered frequent updates:
- Marc Hoffmann (JaCoCo)
- Uwe Schindler (Apache Lucene)
Further, through the OpenJDK Quality Outreach program we would like to thank the following FOSS projects and individuals who provided excellent feedback on testing early access builds of JDK 25 to help improve the quality of the release:
- Apache Ant (Jaikiran Pai)
- Apache Derby (Rick Hillegas)
Resources
Java continues to be the #1 programming language in overall enterprise organizational use. As the on-time delivery of improvements with Java 25 demonstrates, through unwavering thoughtful planning and ecosystem involvement, the Java programming language and platform are well-positioned for modern development and growth in the cloud.
Keep up with news and updates by:
- visiting Dev.java (Oracle’s dedicated portal to advance your Java knowledge and community participation).
- visiting Inside.java (an aggregation of news and views by the Java team at Oracle).
- listening to the Inside.java podcast (a technical audio show for Java developers brought to you directly from Oracle’s Java team).
- listening to the Duke’s Corner Podcast (a community-focused audio show that features the personal stories, experiences and expertise of Java ecosystem luminaries).
- watching Inside.java Newscasts (a video show summarizing many innovations in the Java programming language and platform).
- subscribing to Java on YouTube (the official Java channel on YouTube offering short and long-form videos to advance your Java expertise).
- watching JEP Café (Oracle’s technical exploration into popular JDK Enhancement Proposals).
- joining the OpenJDK mailing lists (transparently learn about the progress of your favorite OpenJDK projects).
- following Java on X (receive social updates on Java covering technical and community areas).
- subscribing to the Inside Java Newsletter (a monthly publication summarizing many of the key Java technology and community updates from Oracle).
- following the official Java LinkedIn group (receive both technical and community updates from Oracle’s Java DevRel team).
