Introduction
In this blog, we cover the basics of projects, workspaces, and environments and provide guidance on how to use them. Before using VB Studio, it’s helpful familiarize yourself with these key concepts, components, and terms.
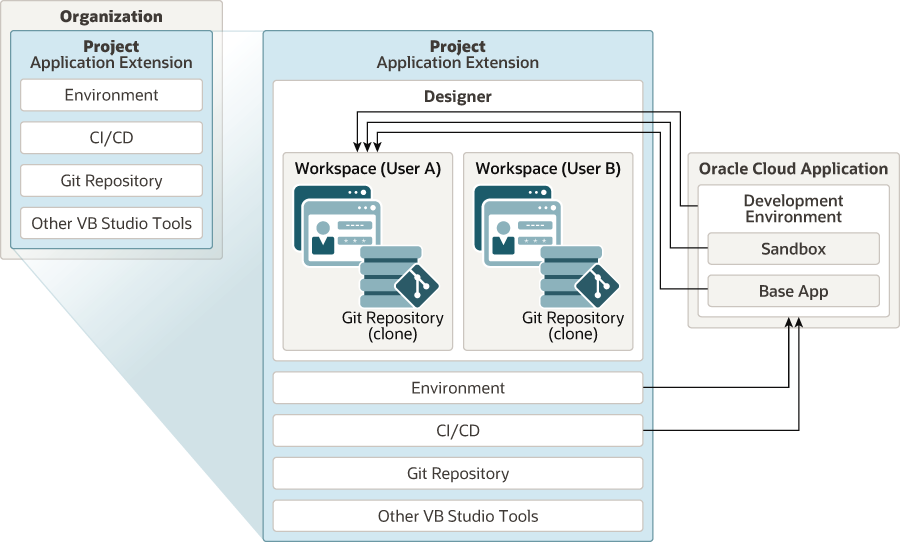
An Organization is the top-most entity in VB Studio’s project structure. It is a master container that manages all resources, projects, and development artifacts within a given project.
A Project gathers all the resources you need to develop an application extension. E.g., a Git repository for storing your source code, a pipeline to provide continuous integration and delivery, an issue tracking system, team wikis, and more.
A Workspace is where most of your work occurs. They are unique to a user and environment. When making personalizations, you enter the designer which is the UI where changes are made. Workspaces link all the different components together, coordinated through the designer. When a workspace is first created, a cached version of the Git repository is created and stored with the workspace. This is known as the local repository. The main repository, which is the official storage for changes associated with the project, is known as the remote repository. Any personalizations or changes made are stored in this local Git repository and ultimately get synced back to the project or remote repository.
Projects
A project is an overall container that manages all the work for personalizing a SaaS application. It contains several different items, including workspaces, source code repositories (Git) deployment and packaging pipelines, references to environments, etc. Your user must be granted permission to be part of a project. A Project is created automatically when you first navigate to Visual Builder Studio from Fusion (using “Edit Page in Visual Builder Studio”). Initially, a project will have an empty extension without changes to the delivered code. Use the default VB Studio Project for all personalizations. There is no need for a developer to create more projects or workspaces.
Using a single project for all Oracle Cloud Application personalization is recommended, even for multi-pillar customers. The system automatically creates separate repositories for each product family (HCM, SCM, etc.).
For further details, refer to the Extension Best Practices.
Setting up Environments
VB Studio Instance is pre-configured on all of your non-production pods, and that’s where you will do all of your development and unit testing.
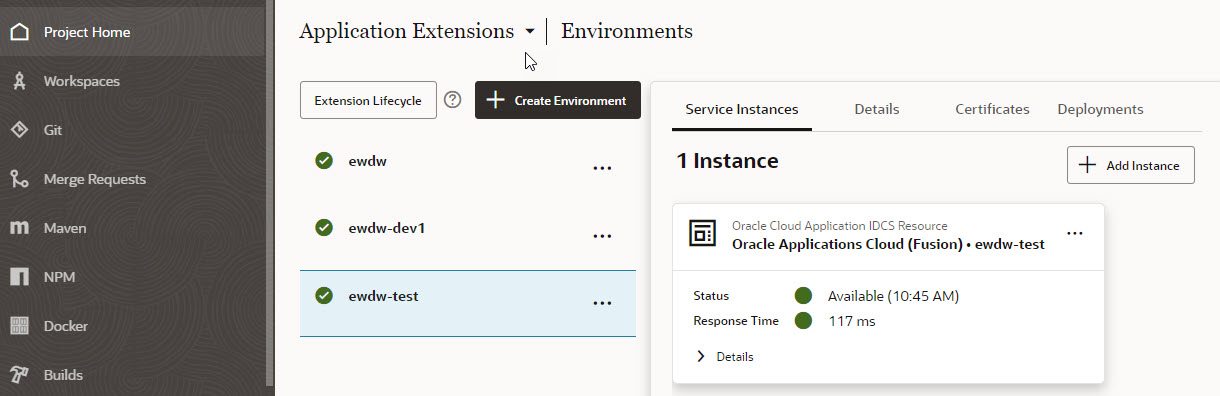
Configure additional environments for the project where you want to migrate the extensions for UAT or Production deployment. For further information on setting up Environments, please refer to this article- Define your Environments.
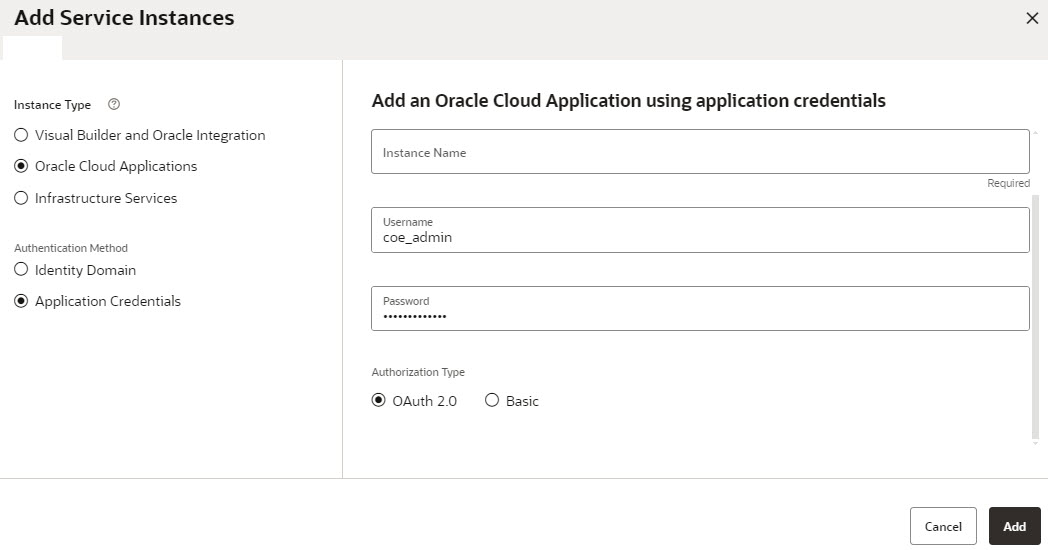
If the newly added instance stays in the Unknown status for some time, it typically indicates that the provisioning may have failed. In such a case, click Actions > Remove to remove the Oracle Cloud Applications instance from the environment, and then add it again
Good luck with your implementation!

