In this article we will discuss various key types supported by Oracle HCM Data loader a.k.a. HDL. Whether you are planning to implement coexistence with ongoing data sync, one time conversion or ongoing integrations you must select the right key type to identify records uniquely. If you select a wrong key type then it may result in huge amount of rework down the line. So please pay special attention to various key types and see what makes most sense in your situation, I do recommend using the system keys where possible.
Supported Key Types:
HCM Data Loader (HDL) supports 4 different types of keys as listed below (in the order of key resolution sequence)
- GUID – Oracle Fusion Global Unique ID
- Oracle Fusion Surrogate ID
- Source Keys
- User Keys
These key types are explained below:
| Oracle Fusion GUID
|
Oracle Fusion Surrogate ID
|
| Source Keys
|
User Keys
|
| Key Type |
Create |
Update |
Held on Object |
Type |
Generated Automatically |
| GUID |
No |
Yes |
No |
Hexadecimal |
Yes |
| Surrogate ID |
No |
Yes (see note #1) |
Yes |
Numeric |
Yes |
| Source Key |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Alphanumeric |
Conditionally (see note #2) |
| User Key |
Yes |
Yes (see note #3) |
Yes |
Alphanumeric |
No |
Notes:-
1. You can use surrogate IDs when updating objects, but the IDs may not be readily available to Oracle HCM Cloud users.
2. Default source keys are generated only if you don’t supply a source key when creating an object.
3. You can’t use user keys alone when updating some objects because their values are subject to change.
4. Keys that aren’t held on the object exist in the Integration Key Map table.
Integration Key Map table
Keys that aren’t held on the object are stored in the HDL integration key map table – HRC_INTEGRATION_KEY_MAP. You should be able to use BIP to fire up a SQL statement and view the contents of this table. e.g.
select OBJECT_NAME, SOURCE_SYSTEM_ID, SOURCE_SYSTEM_OWNER, SURROGATE_ID, RAWTOHEX(GUID) guid from fusion.HRC_INTEGRATION_KEY_MAP WHERE SOURCE_SYSTEM_OWNER =’STUDENT1‘
| Business Object |
Fusion GUID |
Source Key |
Surrage ID |
User Key |
| Location |
25DD4078E961A23BE053A697480AFB92 |
STUDENT1_LOC1 |
300000001572671 |
(Set code and Location Code) COMMON, HQ1 |
- Fusion GUID: System generated GUID
- Source Key: Source System Owner is the reference to source application like PS or EBS, Source System Key is the actual key\id provided in the Location.dat file.
- Surrogate ID: System generated. In this case it is the primary key from locations record. e.g. select * from PER_LOCATION_DETAILS_F_VL where location_code = ‘STUDENT1 Location1‘ (Result Location ID = 300000001572671)
- User Key:- Best way to get this info is the Business Object Documentation from MOS or other option is UI as shown below. Online page should highlight user keys with *
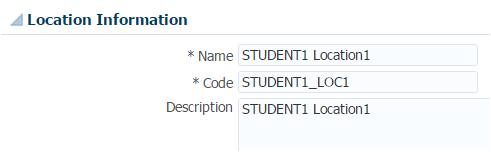
Supplying Keys in a HDL File
CREATE:
One can supply system keys or user keys (or both) while creating new objects. You can’t supply surrogate id or GUID because those fields are auto generated if the data load is successful.
Creating an Object Using Source Keys:
METADATA|Job|JobCode|EffectiveStartDate|EffectiveEndDate|Name|SetCode|SourceSystemOwner|SourceSystemId
MERGE|Job|SE|2010/01/01|4712/12/31|Software Engineer|COMMON|EBS-UK|12349
Creating an Object Using a User Key:
METADATA|Job|JobCode|EffectiveStartDate|EffectiveEndDate|Name|SetCode
MERGE|Job|SE|2010/01/01|4712/12/31|Software Engineer|COMMON
Update:
One can supply any of the 4 key types while doing updates.
Updating an Object Using Source Keys:
METADATA|Job|EffectiveStartDate|EffectiveEndDate|Name|SourceSystemOwner|SourceSystemId
MERGE|Job|2010/01/01|4712/12/31|Software Engineer – Java|EBS-UK|12349
Updating an Object Using a User Key:
METADATA|Job|JobCode|EffectiveStartDate|EffectiveEndDate|Name|SetCode
MERGE|Job|SE|2010/01/01|4712/12/31|Software Engineer – Java|COMMON
Updating an Object Using the Fusion GUID:
METADATA|Job|GUID|EffectiveStartDate|EffectiveEndDate|Name
MERGE|Job|2342UJHFI2323|2010/01/01|4712/12/31|Software Engineer – Java
Updating an Object Using the Fusion Surrogate ID:
METADATA|Job|JobId|EffectiveStartDate|EffectiveEndDate|Name
MERGE|Job|13413|2010/01/01|4712/12/31|Software Engineer – Java
Specifying Foreign Keys
Using the Fusion Surrogate ID as a Foreign Key:
METADATA|Assignment|JobId|EffectiveStartDate|EffectiveEndDate|AssignmentNumber|SourceSystemId|SourceSystemOwner
MERGE|Assignment|13413|2010/01/01|4712/12/31|5232|EBS-UK|234234
Using the User Key as a Foreign Key:
METADATA|Assignment|JobCode|SetCode|EffectiveStartDate|EffectiveEndDate|AssignmentNumber|SourceSystemId|SourceSystemOwner
MERGE|Assignment|SE|COMMON|2010/01/01|4712/12/31|5232|EBS-UK|234234
Using the Fusion GUID as a Foreign Key: Supply the value using hint ()
METADATA|Assignment|JobId(GUID)|EffectiveStartDate|EffectiveEndDate|AssignmentNumber|SourceSystemId|SourceSystemOwner
MERGE|Assignment|2342UJHFI2323|2010/01/01|4712/12/31|5232|EBS-UK|234234
Using the Source Key as a Foreign Key: Supply the value using hint ()
METADATA|Assignment|JobId(SourceSystemId)|EffectiveStartDate|EffectiveEndDate|AssignmentNumber|SourceSystemId|SourceSystemOwner
MERGE|Assignment|13143|2010/01/01|4712/12/31|5232|EBS-UK|234234
System Integration Considerations:
- What not to do?
- Include effective date or hire date as part of the unique key\source key
- Include first name or last name as part of unique key\source key for person name
- Bottom line: Please do not design keys which can be easily changed in the source application.
