AAA framework (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) is a commonly used security framework for managing information security. It is the basic security framework to control access to data\resources, enforce proper policies, and monitor audit logs. In this article we will review various controls available in Oracle Cloud HCM to help you form your defense in-depth strategy. Goal is to introduce you to high level concepts in this blog and provide deep dive into specific topic using supplemental blogs.
*As I write this article- 23B is the current release of Cloud HCM so please watch for updates in the release notes, as we continue to add more features.

Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user. User will present the login credentials stating they are who they claim. Oracle Cloud will validate those credentials to grant (or deny) access to the system. The most basic form of authentication is via username & password, hence the buzzword ‘basic auth’ but we recommend you implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) using Oracle Cloud Identity Service or your existing SSO provider.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) involves using any two of the following factors:
- Something you know, like a password.
- Something you have, like a device or token.
- Something you are, like your fingerprint.
Under the authentication section we will review – User Categories, Sign-on Chooser Page, SSO, and API Authentication.
User Category:
As name suggests, it is simply a way to group a set of users such that the specified settings apply to everyone in that group. These settings include password controls and notification templates. Out of the box, every user is assigned to the DEFAULT user category but you can define your own user categories for pre-boarding, offboarding, etc. business processes. We also offer REST APIs and batch loaders to update the user category in bulk.
Chooser page
Chooser page will allow both the company SSO sign-in as well as local authentication using cloud HCM built-in IDP. Customers have the option to disable the chooser page, and this will force the authentication to happen via SSO.
Single Sign-on (SSO):
Cloud HCM supports SSO with any SAML2.0 compliant Identity Provider. It also supports more than one IDPs but remember, only one can be the default IDP and others must use IDP initiated SSO . Self service configuration is available using Security Console –> Single Sign-on.
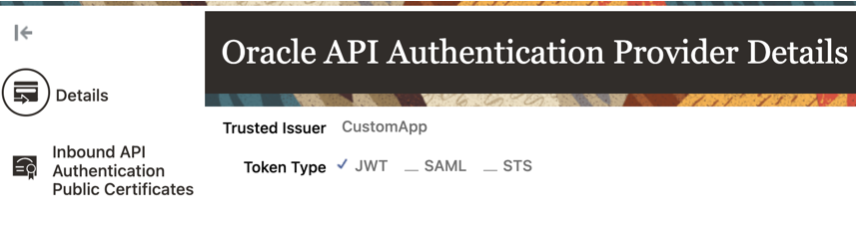
API Authentication:
You might be using real time updates via REST for inbound or outbound integrations. Often times the preference is to use ‘token based auth’ instead of using ‘basic auth’ (username\password). In simpler terms, one party generates the token & signs it using their private key. The other party will verify that token using the pre-shared public key and access to be granted if the token is validated successfully. Since this is system to system integration, we may have inbound or outbound API calls so let’s review this from the context of Cloud HCM.
| Inbound API Authentication |
Outbound API Authentication |
| 3rd party App invoking Cloud HCM API. 3rd party app to provide JWT token as per Cloud HCM requirements, generate the token and sign it using their private key. You need to upload the corresponding public cert via security console when you define the API Auth Provider. |
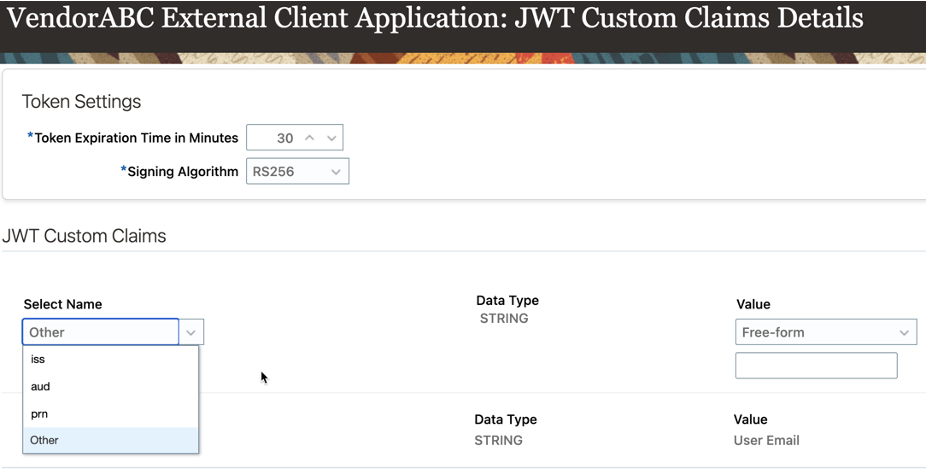
Oracle Cloud invoking 3rd party APIs. It means Oracle HCM should send the token to 3rd party app and they may require custom claims. So you need to define those claims via security console when you setup External Client Application. |
| Security Console: API Authentication: Oracle API Authentication Provider
|
Security Console: API Authentication: Create External Client Application
|
|
|
|
Oracle Cloud HCM supports the JSON Web Token (JWT), Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML), and Security Token Service (STS) tokens. We recommend that you use JWT for inbound API authentication.
Authorization
Once you are successfully authenticated, the next control is Authorization. Authorization controls what the user is allowed (or not allowed) to do, so in this phase the end-user is granted with set of roles\privileges to access various resources (User interface, data, apis, reports, etc). Next we will review the Role Based Access Controls (RBAC), Data Security, Location Based Access Controls and Automated Role Provisioning & Account Maintenance.
Role Based Access Controls (RBAC)
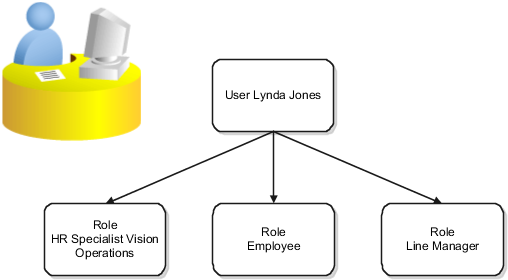
In Fusion, the functions and data that a user can access come from a combination of the roles assigned to the user. Users can have more than one role, and when they sign in to Fusion Applications, all of their roles are active concurrently. For e.g. User Lynda Jones has 3 roles assigned – Employee, Line manager and HR Specialist for Vision Operations.
Role Based Access Controls (RBAC) Data Access
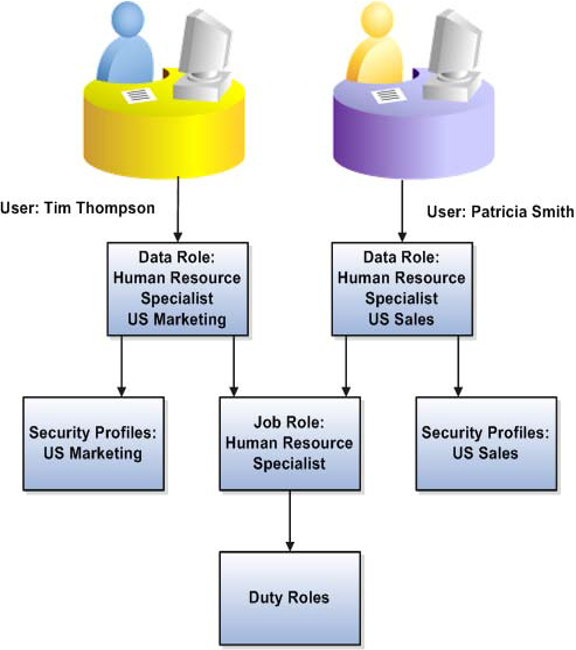
Just because you have access to the UI, does not mean you can view all the data rows for that objects. This is where data security comes into the play. WHO can do WHAT on WHICH set of data? For e.g. Line managers can only do performance documents for their reporting hierarchy or employees can only view their own payslip or HR Specialist can do employee transfers for specified AOR\LDG\Business Unit etc. In this diagram below, both Tim Thompson and Patricia Smith have access to same set of pages as they both have Human Resource Specialist Role but Tim can only see the data from US Marketing unit and Patricia from US Sales.
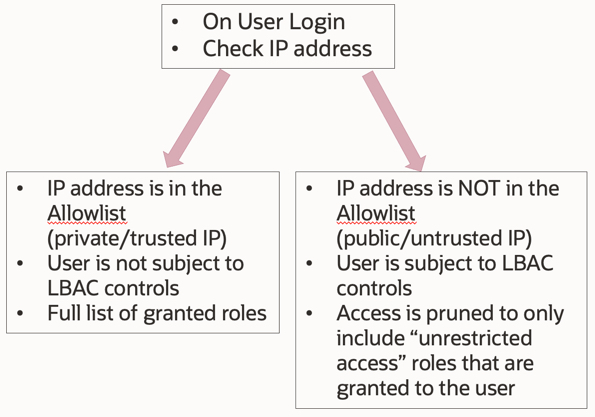
Location Based Access Controls (LBAC)
Oracle Cloud HCM offers Location Based Access Control to limit access to applications or functionality based on the IP address of the user. This is a very useful if you want to expose only a part of the application (e.g. Supplier Portal\Career Site\Named APIs) to the public internet. Please note LBAC is a post-authentication control (kicks-in only when user is authenticated) whereas WAF is a pre-authentication control. Here is the blog to understand how the LBAC is enabled via security console.
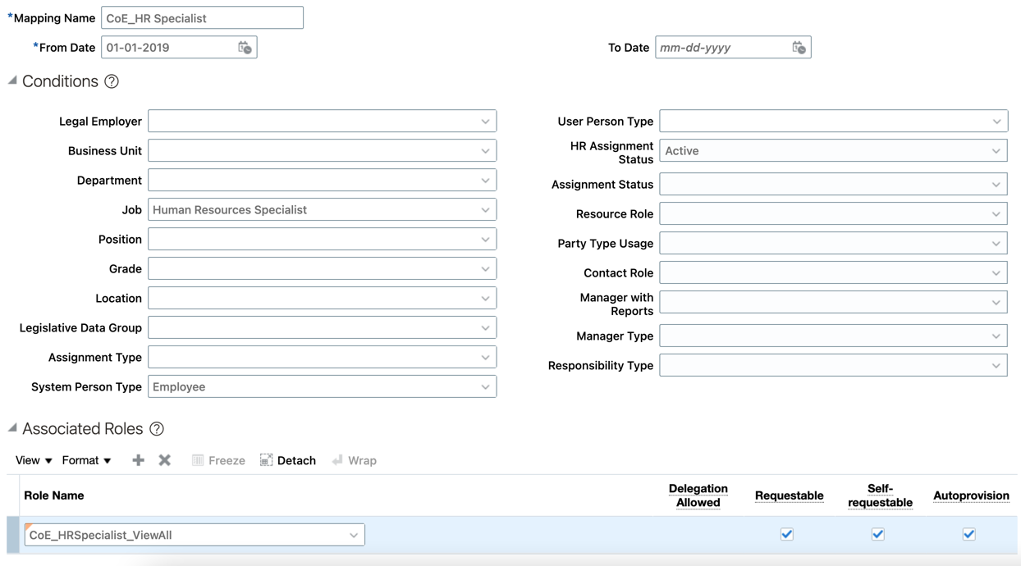
Automated Role Provisioning (and Deprovisioning)
Cloud HCM offers template based configuration to provision (or deprovision) roles based on rules you have configured. Users acquire a role automatically when at least one of their assignments satisfy the conditions in the relevant role mapping. Likewise, users lose automatically provisioned roles when they no longer satisfy the role-mapping conditions. All changes to assignments cause review and update of a worker’s automatically provisioned roles.
Navigator>Setup and Maintenance – On the All Tasks tab, search for task Name ‘Manage HCM Role Provisioning Rules’ (or ‘Manage Role Provisioning Rules’)
Automated User Maintenance
User life cycle management can be fully automated within Cloud HCM. Please pay attention to these options and do proper setup before rushing into data conversions.
Navigator>Setup and Maintenance – On the All Tasks tab, search for task Name ‘Manage Enterprise HCM Information’
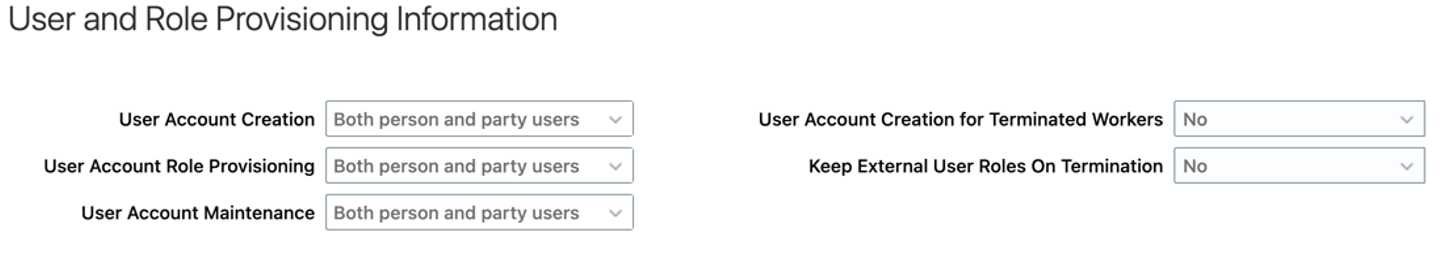
- User Account Creation: option controls whether user accounts are created automatically when you hire an employee or add pending worker, etc.
- User Account Role Provisioning: option controls whether users acquire\lose roles as specified by current role-provisioning rules
- User Account Maintenance: option controls whether user accounts are suspended and reactivated automatically (LOA\termination\rehires\etc life events)
- User Account Creation for Terminated Workers: useful option esp during cutover\go-live to save some time by not creating the user account for terminated employees (as opposed to having system create the user account and then suspend it based on assignment status)
- Keep External User Roles On Termination: useful option to remove externally assigned roles post termination. We recommend you set this to No (unless you allow access to the application post termination e.g. Pensioners)
Auditing
Auditing is the last component of the AAA framework. It keeps track of all the changes performed on the various objects & attributes. Oracle Cloud HCM Auditing framework provides the option to enable Auditing for specific business objects &attributes as well as configuration changes (meta data, platform security, sandbox), user access logs, and lot more. Here is the blog to get more information on enabling audits & audit reports.
Additional Controls
WAF4SaaS
The Web Application Firewall (WAF) for Fusion further strengthens layer-7 security and safeguards both public and private facing Fusion applications from incoming traffic, reducing the associated risks. WAF is completely transparent to customers, always-on (customers don’t need to request the enablement, etc..it is always-on!), and managed by Oracle 24/7. If you need additional information, then here is the blog from Oracle CISO of SaaS Security.
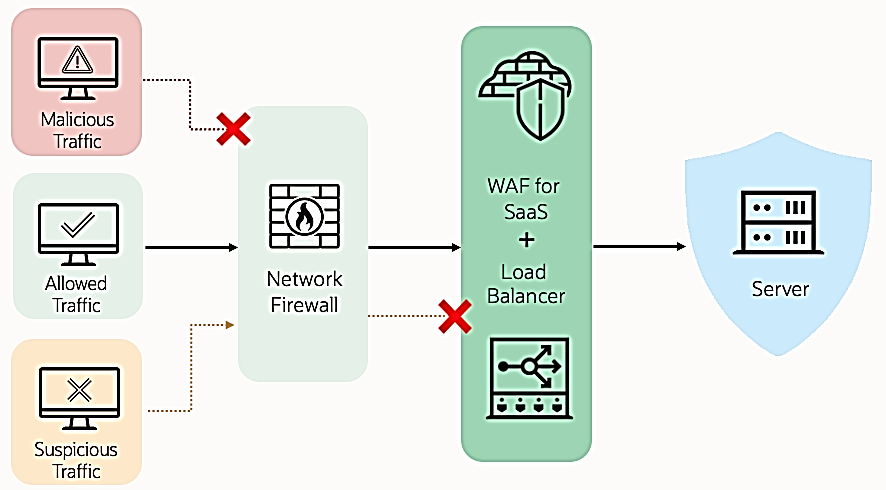
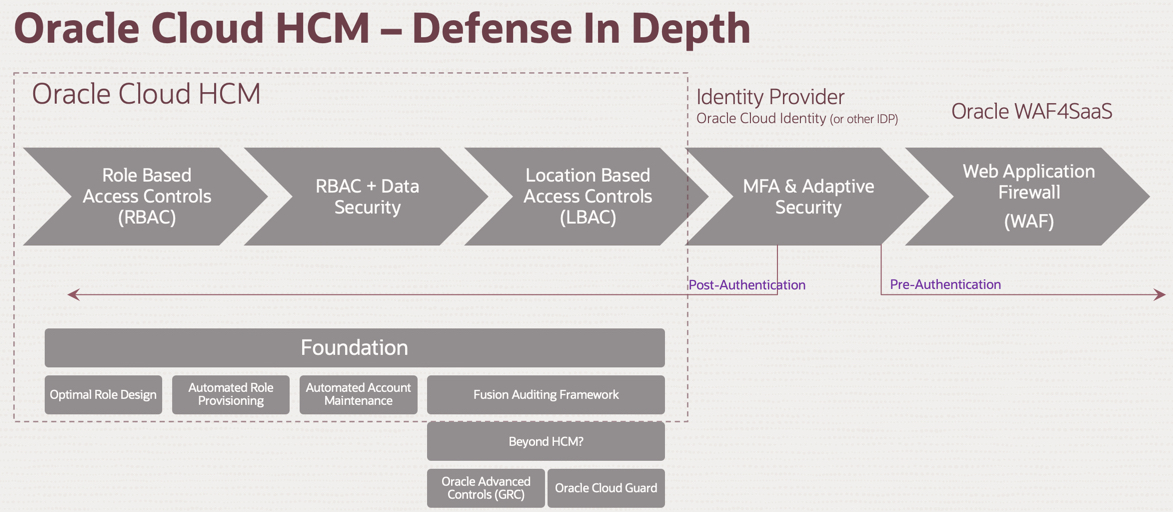
Putting it All Together
- Security is more than just assigning roles
- Authentication – consider adding in SSO, MFA to reduce complexity for users and enhance security
- Authorization – Start with RBAC+Data Security and then supplement with LBAC for better perimter security. LBAC can control the set of roles assigned based on IP address. Automate role provisioning & deprovisioning
- Auditing – There’s a rich set of auditing capabilities built-in… why wait? take the advantage
- Other offerings can augment what comes with HCM e.g. Advanced Controls, Cloud Guard
- WAF4SaaS – WAF is Always-On!
Good luck with your implementation.