Understanding prompt types, anatomy, and structure in Oracle AI Agent Studio for Fusion Applications — the foundation you need before writing your first agent prompt.
What Is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is the practice of designing and refining the instructions you give to a large language model (LLM) to produce accurate, relevant, and useful responses. In Oracle AI Agent Studio, prompts are the core mechanism through which you control how AI agents behave, reason, and interact with users and Fusion Application data.
A well-engineered prompt turns a general-purpose LLM into a focused, domain-specific agent capable of handling payroll inquiries, routing service requests, or analyzing supply chain data. A poorly written prompt leads to hallucinations, inconsistent responses, and frustrated users.
| KEY INSIGHT In AI Agent Studio, you’re not just writing prompts for a chatbot — you’re programming the behavior of an intelligent agent that can invoke tools, call APIs, and orchestrate multi-step workflows across Oracle Fusion Applications. |
Agent Patterns in AI Agent Studio
Before diving into prompts, it’s important to understand the three agent patterns available in AI Agent Studio. Each pattern requires a different prompting approach, and choosing the right pattern for your use case is the first decision you’ll make.
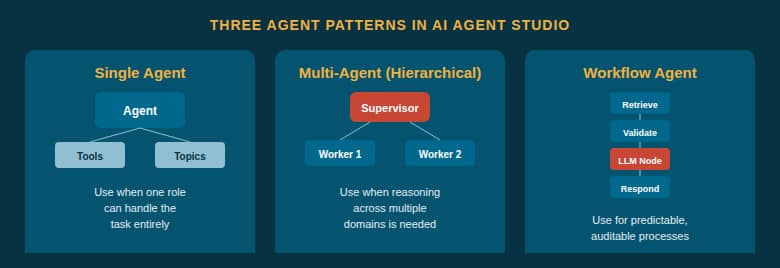
Fig 1 — The three agent patterns: Single Agent, Multi-Agent (Hierarchical), and Workflow Agent.
A single agent is ideal when one persona with a small set of tools (1–5) can handle the entire task. Multi-agent (hierarchical) teams use a supervisor agent to coordinate specialist workers — best for exploratory, analytical, or multi-domain tasks. Workflow agents follow deterministic, step-by-step execution using various node types — best for auditable, repeatable processes touching systems of record.
The Four Prompt Types in AI Agent Studio
AI Agent Studio uses four distinct prompt types, each serving a different purpose and executing at a different point in the agent lifecycle. Understanding when and how to use each one is essential to building effective agents.

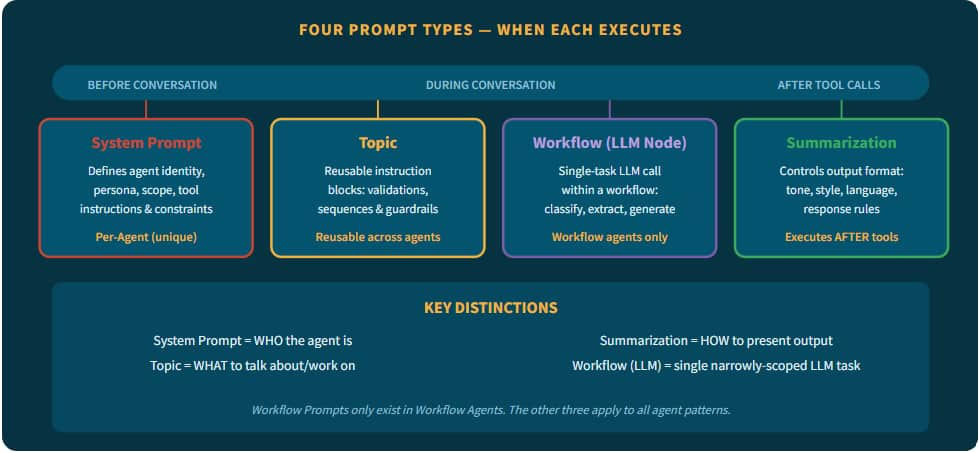
Fig 2 — The four prompt types execute at different points and serve distinct purposes.
System Prompt — The Agent’s Identity
The system prompt is the foundational instruction set for every agent. It defines the agent’s persona, capabilities, operational scope, and the tools it can access. Think of it as the agent’s job description — it establishes who the agent is and how it should think about achieving its goals. System prompts can include high-level orchestration logic, such as when to call certain tools and required sequencing.
System Prompt Example:
// Worker Agent: Personal & Employment Details
You are a helpful assistant that will answer questions about a worker’s personal and employment details.
Limit responses strictly to personal and employment details related topics, ensuring accurate and relevant information.
Never generate facts. All answers should rely on tool call response.
If the user asks questions that do not belong to the above topic:
– Politely decline to answer the question
– Emphasize to the user the scope of topics you are able to address
Topic — Reusable Instruction Blocks
A topic is a reusable instruction block that gets added to the system prompt. Topics encapsulate repeatable logic and rules — including validations, pre-checks, multi-step sequences that must execute in order, and guardrails that should apply across multiple agents. They are used to modularize and scale system-level logic.
Summarization Prompt — Output Format Control
The summarization prompt controls how retrieved and processed data is presented to the user. It enforces tone, formatting, language, and response rules. Critically, it executes after tools and logic have completed — meaning it shapes the final response the user sees.
| IMPORTANT In AI Agent Studio, output format is configured through the summarization prompt, not the system prompt. When you need to control how the agent formats its responses — whether as bullet points, tables, executive summaries, or conversational text — configure it in the summarization prompt. |
Workflow Prompt (LLM Node) — Single-Task LLM Calls
The Workflow Prompt is the fourth prompt type, and it exists only within Workflow Agents. It directly calls a language model to perform a specific, narrowly scoped task within a deterministic workflow. Unlike system prompts that define broad agent behavior, a workflow prompt executes a single task — such as intent extraction, classification, or structured output generation.
The LLM Node transforms unstructured input into structured output for downstream steps. It sits alongside other workflow nodes (data retrieval, code, branching) and is only invoked at points where AI reasoning is needed in an otherwise deterministic process.
Workflow Prompt (LLM Node) Example:
| WHEN TO USE WORKFLOW PROMPTS VS. SYSTEM PROMPTS System Prompts are for conversational agents that reason across multi-turn dialogues. Workflow Prompts (LLM Nodes) are for single-task reasoning steps within a deterministic pipeline — they execute once, produce structured output, and feed the next node. Use LLM Nodes mainly at decision points, not for deterministic actions that code nodes can handle. |
Anatomy of a System Prompt
A well-structured system prompt in AI Agent Studio contains several key elements that work together to fully define agent behavior.

Fig 3 — The five layers: Persona, Scope, Tools, Constraints, and Topic References.
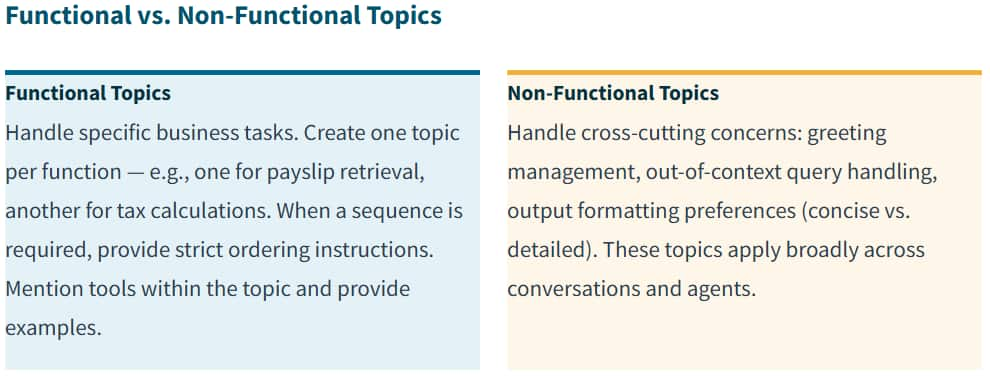
Topics: Reusable Instructions for Agents
Topics provide detailed instructions for handling specific conversation scenarios. They are one of the most powerful features in AI Agent Studio because they are reusable across agents and agent teams, enabling consistency and modularity.
Topic Expressions
Topic expressions let you reference any associated topic inside the system prompt using: $topic.<topic_code>
Writing Good Topics
| Principle | Good Example | Bad Example |
| Be specific | “Best practices for secure API integration” | “API integration” |
| Be concise | “Data retention policy for Europe” | “Storing data” |
| Neutral language | “Monthly customer support satisfaction statistics” | “Customer happiness” |
| Single subject | One topic per function | Multi-part compound topics |
| SEQUENCING TIP When a topic spans multiple steps, enforce strict ordering with validation gates: “Authenticate user. If step 1 fails, do not proceed to steps 2 or 3.” |
Supervisor vs. Worker Agent Prompts
In multi-agent teams, the supervisor and worker agents have fundamentally different prompting needs.
Supervisor Agent Prompts focus on decision-making, assignment distribution, monitoring, and quality control. Typical elements: assigning tasks to workers, aggregating or validating outputs, handling exceptions or escalations, providing feedback based on intermediate results.
Worker Agent Prompts focus on clear, actionable direction for a discrete task. Typical elements: focusing on a single well-defined assignment, reporting status or results back to the supervisor, following guidelines or templates for output.
Optimizing Prompts for Different LLMs
AI Agent Studio supports a wide range of LLMs including models GPT 5.1 mini, GPT 4.1 mini and GPT OSS. Different models react differently to instruction formats and languages. AI Agent Studio allows you to replace or customize system prompts and topics for specific models to get the best performance.
What’s Next?
Now that you understand the fundamentals — the agent patterns, four prompt types, prompt anatomy, and practical patterns — you’re ready to explore optimization. Check out our companion blog post, “Best Practices for Prompts in Hierarchical Agents”, for role definitions, responsibility boundaries, description writing, troubleshooting techniques, and a deployment checklist.
Oracle AI Agent Studio — Built in. Not Bolted on.
