Blog post updated on October 27, 2023
This blog post explains how you can accelerate your revenue process with Oracle Cloud Applications integration and automation.
The accounting standards ASC 606 and IFRS 15, effective since 2018, introduce a radical revenue reform worldwide.
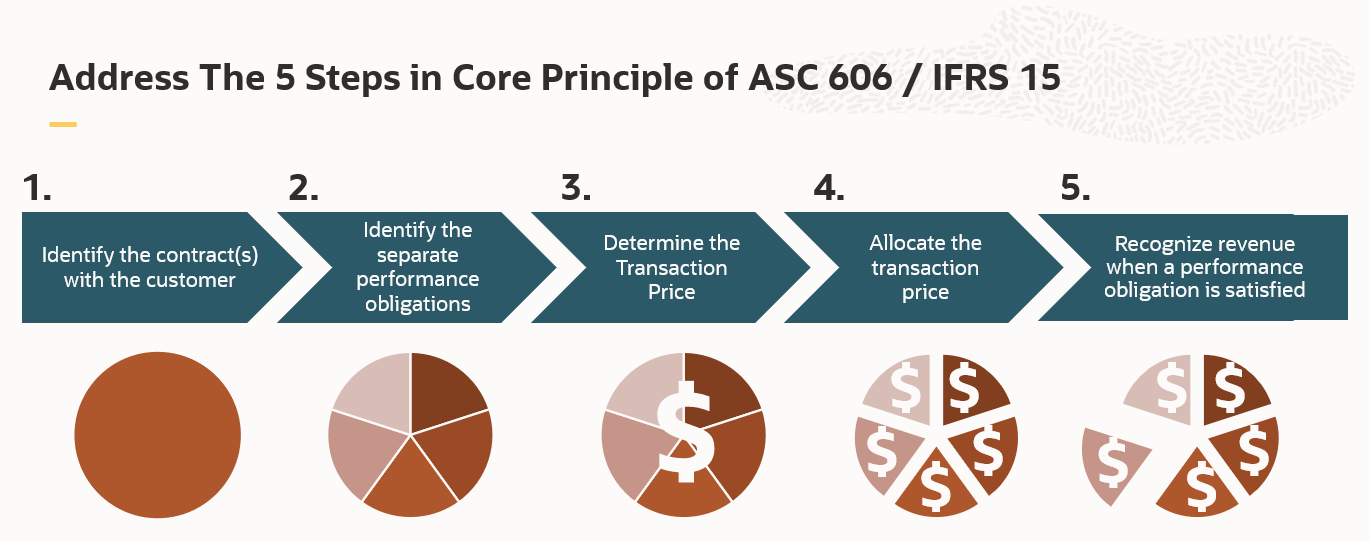
A five-step model summarizes the above accounting standards for recognizing revenue:
- Identify the contract(s) with the customer
- Identify the separate performance obligations
- Determine transaction price
- Allocate transaction price
- Recognize revenue when (or as) a performance obligation is satisfied
Revenue Management automatically executes the 5 steps based on user configurable rules and setup options. Sales cycle systems integrate with Revenue Management. You can use its capabilities to record your revenue in accordance with your enterprise policies.
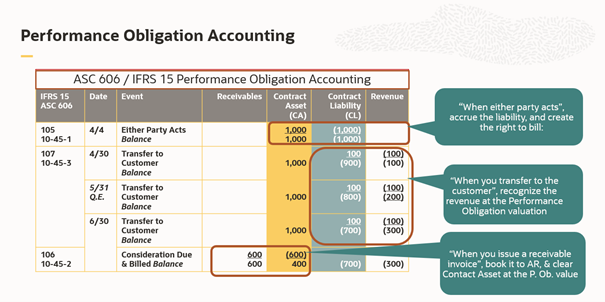
The accounting standards change the timing of accounting events and require extensive judgement of estimates.
This means that your enterprise reviews and values a sales deal with a customer at inception. When either party to your sales contract has performed, you record the performance obligation valuation amount. You then account for the accrued contract liability and right-to-bill contract asset. Your contract liability balance reduces as performance obligations are satisfied and revenue recognized. Your contract asset balance reduces, and accounts receivable balance increases, when sales invoices are processed.
Figure 2 illustrates an example of such accounting events.
Your enterprise may sell products, subscriptions, professional services, accessories, etc. to a customer. You can use Oracle Fusion Cloud CX, SCM, and ERP applications to record sales of goods, subscriptions, services, and charges. Benefit from the shared master data (customers, items, chart of accounts, etc.) and straight-through-processing with Oracle Cloud Applications native integration.
Quote to Cash Integration Overview
Figure 3 illustrates the Oracle Cloud Applications Quote to Cash native integration flow.
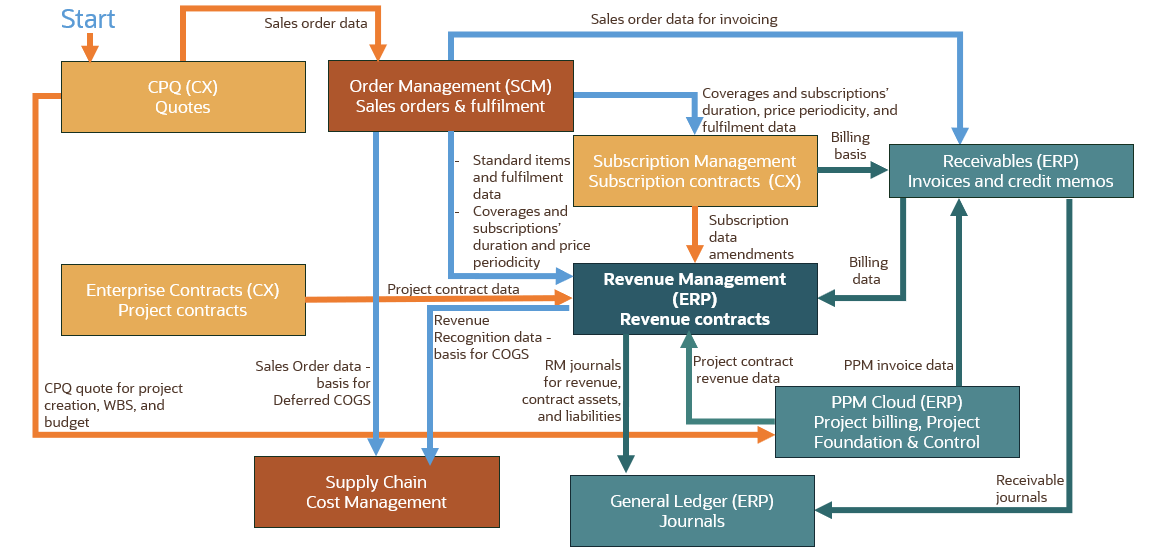
You start with the Oracle Configure, Price, and Quote (CPQ) capabilities. Follow the guided configuration process to create the quotes. Once your external customer approves the quotation it is seamlessly integrated to other Oracle Cloud Applications.
You can integrate quotes from CPQ to automatically create:
- sales orders in Oracle Order Management
- project, work breakdown structures and budgets in Oracle Project Management
You schedule integration to Revenue Management from the following products:
- Order Management (OM): integrate completed sales orders
- Project Management (PM): integrate project contract revenue data for enterprise and project contracts, and project billing.
- Subscription Management (OSS): integrate one time and recurring charges data
Revenue Management automatically creates revenue contracts and performance obligations based on configurable rules.
When you successfully ship, fulfil, or transfer an order line to the customer, Order Management relays the fulfillment data. The data relayed to Revenue Management includes Order Management attributes such as the fulfilled quantity and date.
With Oracle Cloud Financials 23B the integration between Order Management, Subscription Management, Receivables and Revenue Management was enhanced.
Sales Order data from Order Management is sent to Revenue Management upon submission of a sales order. For subscriptions and other services, when you enable integration between Order Management and Subscription Management, Order Management also sends the service duration and price periodicity information to Revenue Management. Revenue Management recognizes revenue in accordance with the satisfaction plan based on the integrated service duration and price periodicity.
Once a standard item is fulfilled, Order Management sends the fulfillment information to Revenue Management where revenue is recognized to the extent of fulfillment.
Once a service or subscription item is fulfilled, Order Management passes the information to Subscription Management where the service and subscription items are managed.
Once Subscription Management receives the service and subscription information from Order Management, Subscription Management processes the information and creates a subscription in Subscription Management. This subscription information is sent to Revenue Management as a revision line, regardless of whether there are any revisions to the line sent earlier by Order Management. If none of the revenue impacting attributes are revised in Subscription Management, then Revenue Management doesn’t perform any reallocation
When you process amendments, renewals, and terminations in Subscription Management, the data is integrated to Revenue Management.
When you generate revenue in Project Billing, the data is integrated to RM as satisfaction events.
When you amend project contracts in Enterprise Contracts to revise revenue-impacting attributes, the data is integrated to RM with the new contract version number.
Those updates trigger events for Revenue Management to recognize or revise revenue.
You schedule OM, OSS, and PM subledgers to integrate data with Oracle Receivables (AR) for invoicing. AR then integrates billing data to Revenue Management.
Revenue Management receives the above sales cycle source system data and for each performance obligation it processes:
- The initial performance event, when either party acts, with performance obligation valuation amounts for contract liability and contract asset.
- Revenue recognition at a point in time or over time based on satisfaction events or satisfaction plans. When revenue is recognized, it draws down the contract liability balance.
- Billing data, which draws down the contract asset balance.
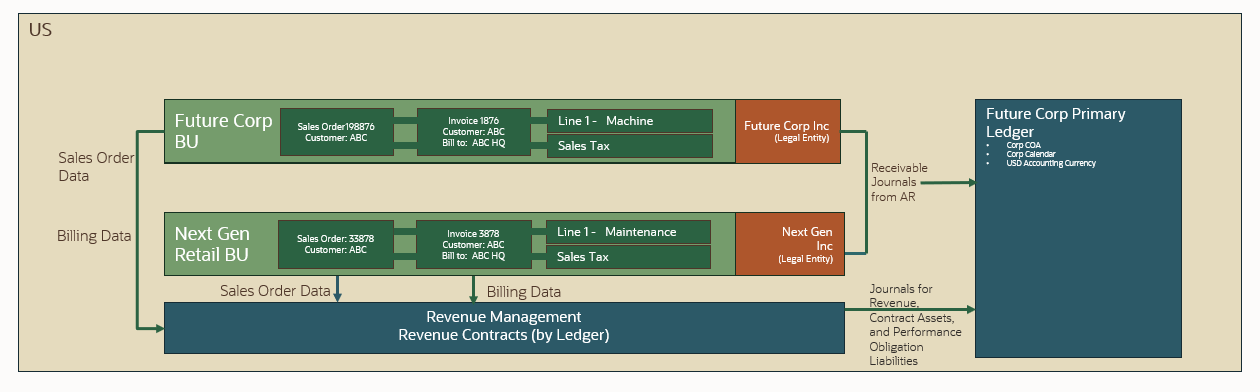
Figure 4 shows an example of data integration between Order Management, Revenue Management, Receivables, and General Ledger (GL).
Sales order and invoice data for multiple legal entities and business units within a single ledger integrates to Revenue Management. Revenue Management creates one or more revenue contracts with one or more performance obligations.
Receivables tracks the receivables control accounting entries. Revenue Management records contract assets, contract liabilities and revenue accounting entries.
You schedule subledger Accounting to generate the subledger journal accounting entries. It also summarizes the journals for these subledgers and posts them to the ledger in GL.
Industry Use Case Examples
Revenue contracts vary by industry with different performance obligations, as illustrated in figure 5 below.

Example on How to Model a Sales Deal at Inception with Expected Outcome
To delve a bit deeper let’s focus on a manufacturing use case.
Let’s say your manufacturing enterprise concludes a sales deal for machines and maintenance services.
Your enterprise gave large discounts to win the sales deal.
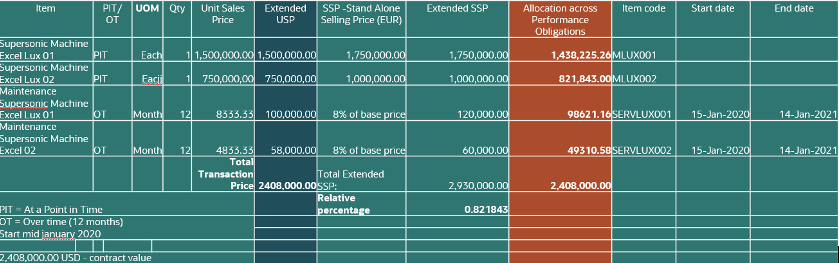
Figure 6 Example of Manufacturing Use Case Modelling with Expected Outcome
You model the expected outcome for the sales deal at inception in a spreadsheet.
Identify your distinct performance obligations, which are distinct machines and two maintenance services. You sum up the selling price of these to identify the total transaction price for the contract.
Identify standalone selling prices (SSPs) for each of the four performance obligations and sum these up for the contract.
You calculate the relative percentage of the total transaction price to the total for the SSPs in the contract. Apply the allocation percentage across the performance obligations. The outcome of the calculation is the valuation amount for each performance obligation. Each amount, in Figure 6 Allocation across Performance Obligations column, is used for subsequent revenue recognition.
You use the modeling above to help identify source systems and attributes needed for your configurable rules and setup options in Revenue Management.
To validate the outcome of your modelling you need to take the following actions in Revenue Management:
Configure your contract identification rules, such as by customer bill-to Party ID, customer purchase order number, and time frame.
Configure your performance obligation rules to identify if revenue for the performance obligation should be recognized over time or point in time.
For the above rules you can also configure extensible attributes to improve selection and grouping of source data into contracts and performance obligations.
Upload the SSPs into Revenue Management. Revenue Management uses SSPs in a formula for the relative method of allocation of total transaction price across performance obligations in the contract. Revenue Management uses the allocated amount for revenue recognition.
Use order management to track initial sales order as well as order fulfilment. Integrate the data to Revenue Management (RM) for point in time revenue recognition. RM combines satisfaction events received from order management with Performance Obligation Identification Rules configuration to recognize revenue.
Order management communicates coverage, duration, and periodicity upon fulfilment of the coverage item to Subscription Management for the maintenance. Subscription Management then sends updates to Revenue Management to process over time revenue recognition. RM combines data from subscription management with Performance Obligation Identification Rules configuration to recognize revenue. In this case revenue for maintenance is recognized periodically over time over a 12-month time frame.
Run relevant programs to automatically create contract and performance obligations in Revenue Management. Validate the accounting results in Manage Contracts UI or in the Revenue Contract Account Activity report in Revenue Management.
Note: Billing integration is not reflected in example above, as it won’t impact revenue recognition. It only impacts accounts receivable and contract asset balances.
Conclusion
Utilize Oracle Cloud Applications capabilities to automate and accelerate your revenue process. This minimizes manual interventions. It enables your enterprise to address the ASC 606 and IFRS 15 core principle efficiently and consistently.
Useful Webcasts
Learn about the integrations and related use case examples. Log in to Oracle Cloud Customer Connect and listen to webcasts on:
Manage Revenue to Address ASC 606 / IFRS 15 Accounting Principles
ERP – Integration of Revenue Management with Order Management and Supply Chain Cost Management with Demo of End to End Flow
CX – Subscription Management: OSS-RMCS Integration Deep Dive
Understand Setup and Processes
Review Oracle Help Center documentation on docs.oracle.com and My Oracle Support documentation for required setup steps and processes for the integrations.
You can find useful documentation related to this blog below:
Revenue Management User Guide: Overview of Revenue Management Integration
Subscription Management Implementation Guide: Integrate Revenue Management
Project Management: My Oracle Support article on FAQ – Performance Obligation Accrual Feature For New IFRS 15/ASC 606 (Doc ID 2414249.1)
My Oracle Support article on What Are The Mapping Extensible Attributes Between Revenue Management And Upstream Products? (Doc ID 2825636.1)
