Data sharing often involves balancing convenience with security, a challenge that has led many teams to compromise on one or the other. With Oracle Autonomous Database’s Pre-Authenticated Request (PAR) URL capabilities, this balance is now achievable. PAR URLs enable effortless yet secure data sharing with REST clients, providing a simple and effective solution to traditional barriers like slow, manual processes or complex permissions. With these capabilities, convenient and secure data sharing is now a reality.
Quick Recap: What Are Pre-Authenticated URLs (PAR)?
Pre-authenticated URLs (PAR URLs) provide secure, time-limited access to specific datasets in the Oracle Autonomous Database, which can be shared with external REST clients. They allow teams to easily share sensitive data without complex permissions, ensuring that access is temporary and controlled. PAR URLs can be invalidated at any time, adding another layer of security to data sharing. For more on the original introduction of this feature, you can refer to our earlier post on Secure and easy access to Oracle Autonomous Database Data via Pre-Authenticated URLs.
Introduction: Recent Major Upgrades
Over the last few months, the ADB team has worked hard to deliver a series of powerful features focused on improving user experience and functionality. These updates aim to enhance convenience for both data producers—who create and share data—and data consumers—who analyze and use that data. Each feature has been carefully crafted to provide more control, flexibility, and efficiency, all while maintaining the highest standards of data security.
For Data Producers: Enhanced Features
- Extending PAR Expiry Times: One of the most frequently requested enhancements has been the ability to extend the time a PAR URL remains valid. Previously, producers were limited in how long they could make the data accessible. This often resulted in a rush to get work done before the link expired. Now, ADB allows you to extend the PAR validity with just a few API calls. This means longer, hassle-free data-sharing periods, especially for collaborations that need more time. This feature saves producers from the hassle of regenerating URLs and offers more flexibility.
- Solving the Private VCN Problem: Sharing data from a private Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) has historically been challenging. With concerns over security and network exposure, organizations faced hurdles in making data available beyond their VCN. The new updates offer a solution by allowing users to share a carefully defined subset of their data over the public internet while keeping the remaining datasets securely hidden behind the private VCN. This selective sharing capability means you can collaborate with partners and external stakeholders without opening the entire network, effectively making secure, controlled data sharing a straightforward process.
For Data Consumers: A Smoother Experience
The enhancements to Oracle Autonomous Database aren’t just for those creating and sharing the data — they also significantly improve the experience for data consumers, making it easier for them to access and interact with the data. Key improvements include a user-friendly web interface that facilitates better data exploration.
- Web Output UI: Data consumers can now enjoy a vastly improved, user-friendly web interface for viewing and interacting with shared data. This enhanced web output UI is highly functional and designed to simplify the consumer experience.
- Grouping and Sorting: One major new feature is the ability to group and sort data directly from the web interface. For instance, if a dataset contains information on multiple product sales across different regions, consumers can easily group and sort by product, region, or time period, allowing them to derive insights more efficiently.
Provider can pick columns where GROUP BY is possible, and consumer easily can set it up. For example this original dataset:
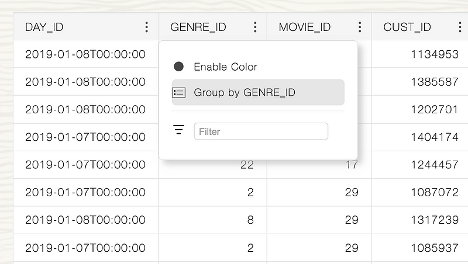
Will be shown as:
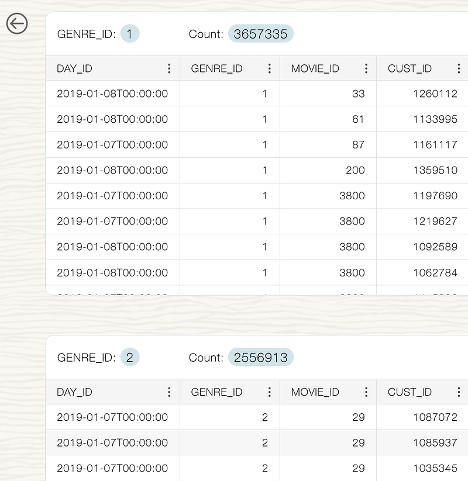
- Filtering: In addition to grouping and sorting, the improved filtering functionality makes navigating large datasets much simpler. Data consumers can filter by various fields to narrow down exactly what they are looking for. The goal is to make data exploration as intuitive as possible, allowing consumers to focus on analysis rather than struggling with the user interface.
This filter will be applied:
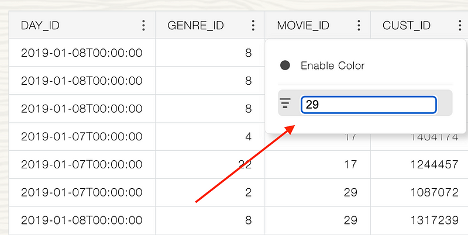
And user will see the following results:
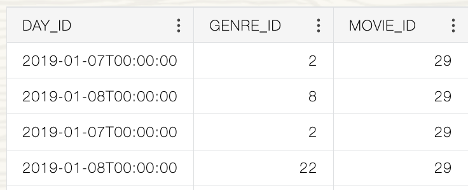
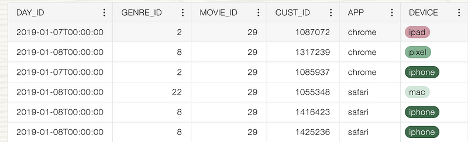
- Color Coding: Another key addition is color coding. With color-coded data, consumers can quickly identify trends, anomalies, or groupings at a glance. This visual differentiation helps in making sense of large volumes of information, allowing for a more intuitive data exploration experience and faster insights. Whether it’s highlighting top-performing sales regions or flagging data anomalies, color coding makes it easier to extract meaningful information.
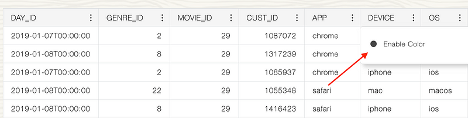
After enabling this color coding user will observe the following output:
Code in Action: Real-Life Example
To see these features in action, let’s consider a real-world scenario. Imagine a retail bank needing to share transaction summaries with a trusted partner for auditing or compliance purposes. This can be a complex task if not handled properly — security is a paramount concern, but efficiency and ease of use are also crucial. With the updated PAR capabilities, the bank can generate a secure, time-limited URL that only exposes the necessary data, keeping everything else behind closed doors.
Here’s how they might do it:
DECLARE
status CLOB;
BEGIN
DBMS_DATA_ACCESS.GET_PREAUTHENTICATED_URL(
schema_name => ‘ACCOUNTING’,
schema_object_name => ‘AUDIT_REPORT’,
expiration_minutes => 43200,
service_name => ‘MEDIUM’,
column_lists => ‘{“group_by_columns”: [“BRANCH_ID”], “order_by_columns”: [“DAY_ID”], “filter_columns”: [“CUSTOMER_ID”]}’,
result => status);
dbms_output.put_line(status);
END;
With this code, the bank can create a secure link valid for seven days, restricted to a specific group — let’s say the auditing team. This link can be shared without the fear of exposing the entire dataset or leaving it accessible indefinitely.
In case data consumer needs more time, it’s not a problem — PAR URL can be easily extended:
DECLARE
status CLOB;
begin
DBMS_DATA_ACCESS.EXTEND_URL(
id => ‘gLO4M..4V”‘,
extend_expiration_minutes_by => 1440,
result => status);
END;
Conclusion
Oracle Autonomous Database’s Pre-Authenticated Request (PAR) URL capabilities are revolutionizing the way data is shared. By offering secure, time-limited access that can be easily controlled and extended, these features empower both data producers and consumers to achieve a balance of convenience and security that was previously difficult to obtain. The recent upgrades — such as extending expiry times and solving private VCN sharing issues - have made it easier than ever to share data selectively and securely. Meanwhile, improvements for consumers, like the enhanced web output UI with grouping, sorting, filtering, and color coding, ensure that data is not only shared but also easily understood and utilized. Whether you’re in finance, telecommunications, retail, or any other industry needing controlled data sharing, Oracle Autonomous Database provides the tools to make data sharing both effective and safe. By bridging the gap between simplicity and security, Oracle is setting a new standard for data collaboration.
To learn more about how Oracle Autonomous Database can help streamline your data sharing needs, visit documentation page
