As an Autonomous Database user, you have likely been using the powerful set of cloning features available in Autonomous Database (ADB), which make it easy to create a single point-in-time clone (ie. copy) of your database, or a clone in which the data can be constantly updated from its source database using a refreshable clone. ADB’s cloning features make it easy and scalable to share copies of your data with other business units, create temporary dev-test database environments, recover older copies of the database among many other use cases.
Before I jump right into telling you about the new Cross-Region refreshable clones feature, I would like to highlight the primary cloning options available to you in ADB, to help choose the right clone option for your specific use case.
- Full Clones: These types of clones are a single & standalone point-in-time, read/write, full copies of your database (ie. both data and metadata). You may full clone from a running database or clone from any backup timestamp. Full clones are a great way to provide a user with a point-in-time snapshots of your database and some example use cases are:
- Providing point-in-time snapshots of your data to users in other business units and different regions of the world, without needing to provide user access or passwords to your source database
- Creating a dev/test sample database for your developer team to use during application development
- Cloning from specific available backup timestamps in past months for auditing data or creating reports / visualizations
- Cloning (or restoring) from an older database backup, if your current database data has gotten corrupted, as a recovery solution
- Metadata Clones: These clones are also single, standalone, read/write, point-in-time copies of your database, but as the name suggests only contain the metadata objects (ie. the table structures, views, partitions, procedures, functions etc.) from the source database, and does not copy over the data in the tables. These are usually the quickest clones to create, since they do not copy over any data and can be useful for:
- Creating independent, empty copies of databases to be populated with data from your application or ETL process, that fit the same structure as the source database (such as different years or months of a certain dataset)
- Spinning up lightweight Dev/Test environments that are agnostic of the data present in the database
- Refreshable Clones: These read-only clones stay connected to the source database that they were created from, and can be easily refreshed (ie. updated) with the latest data, or a specific data timestamp within the last week, from the source database. These clones have some powerful, high-efficiency use cases such as:
- Creating clones of larger databases for auditing or reporting purposes, since refreshing the latest data from the source is usually significantly faster than full cloning a large database
- Providing a database that can lag a day (or more) behind your source database, in situations where the most recent incoming production data is raw, erroneous and requires cleansing
- Providing up-to-date dev/test environment for data science or analytics; Refreshable clones can be disconnected from the source and made read/write for upto 24 hours to temporarily clean, transform or load additional data
- Creating billing or workload separation for your databases between business units within your organization
In addition to the use cases above, full and metadata clones had the added benefit of being able to clone across regions, making it useful for migrating point-in-time data from region to another. Today, we are introducing the ability to also create cross-region refreshable clones! This provides all the refreshable clone benefits and use cases mentioned above across regions, along with additional benefits such as being able to online migrate a database by refreshing the latest available data from one region to another as often as required. If you are an Oracle Web Logic Server (WLS) user and require a replicating cross-region clone of your database that can be disconnected and temporarily made read/write as described in this paper, you may use cross-region refreshable clones with WLS for this purpose. (Note: We are also working on a complete snapshot standby solution for ADB, coming soon)
How to create a Cross-Region Refreshable Clone
Creating a cross-region refreshable clone couldn’t be simpler – All it takes is a few clicks and scrolls!
- Navigate to your favourite database that you want a refreshable copy of and click “Create Clone” under More Actions, on your database console
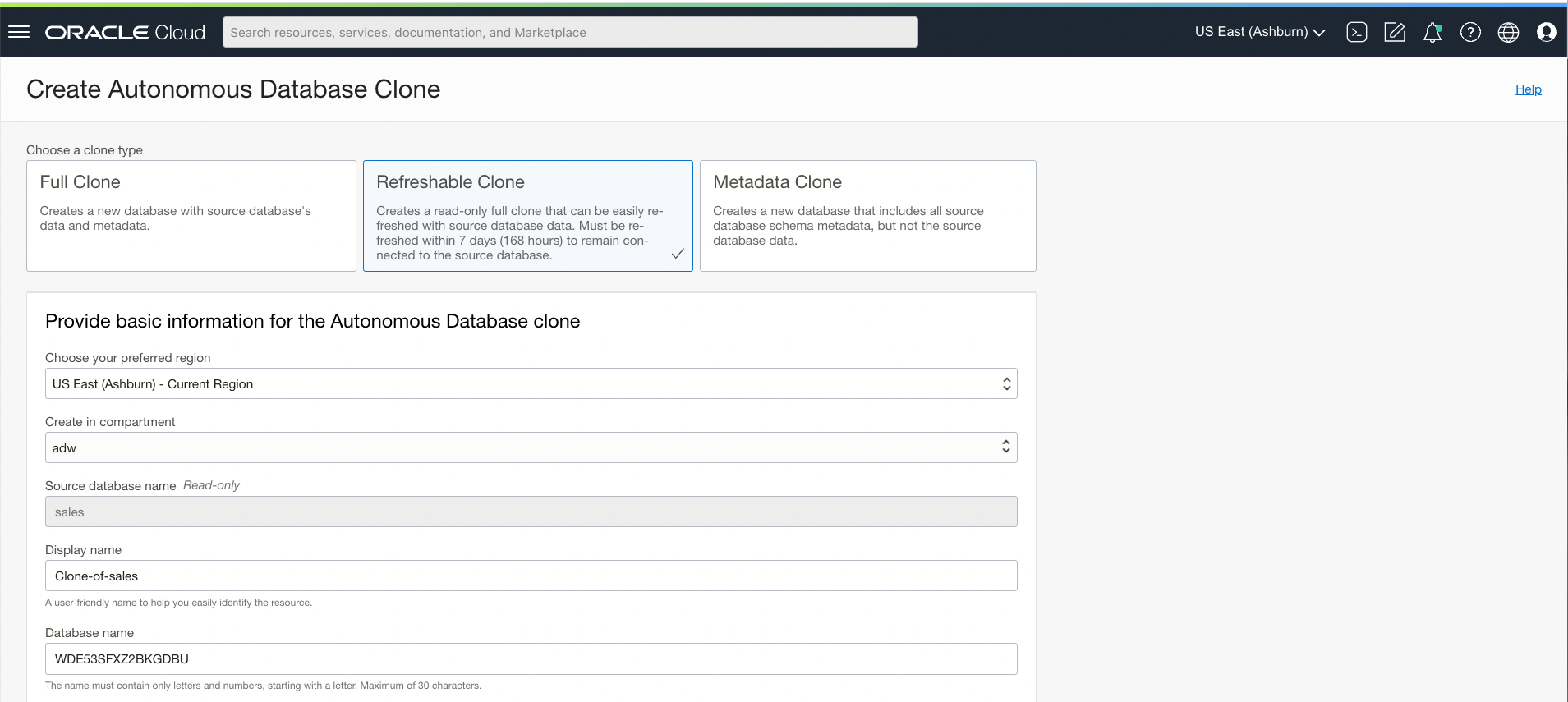
- Under the clone type options, select Refreshable Clone
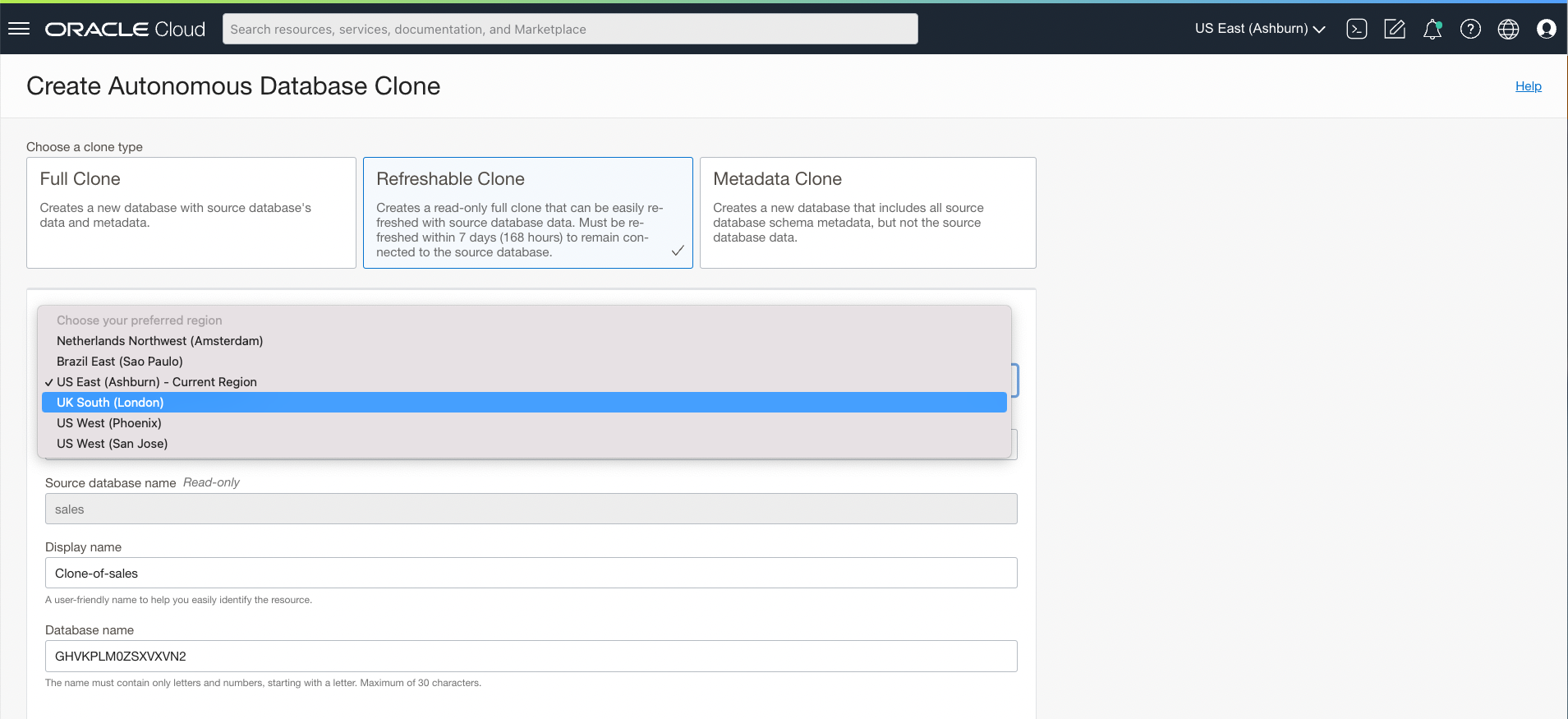
- You will now have the option to choose your preferred region for your refreshable clone. Selecting any region other than your current region creates a cross-region refreshable clone.
Note: The region options you will see is based on the region pairings available for your source’s region, and the regions your tenancy is subscribed to. Read about paired regions or requesting new region pairings to suit your needs here. - You may select your required CPU count and other networking or license preferences for the cross-region refreshable clone. The storage size in TB will follow that of the source, as will the password for the database. Changes made to these parameters on the source database will also reflect on the refreshable clone, once it is refreshed.
- Click Create Autonomous Database Clone and you are done!
Once available, you may now connect to and query your refreshable clone as you would any of your Autonomous Databases. When you need to refresh the clone’s data from the source database in the remote region, simply hit Refresh Clone and select any timestamp that lies within 1 week of the source data. The refreshable clone will then automatically pull in all the data from the source database as of your selected timestamp. To keep refreshable clones active, refresh your clone at least once every 7 days. Since the clone is connected to the source it is read-only but, as mentioned above, you may also disconnect the clone from the source db for upto 24 hours, if you need to temporarily write data into or update the clone.
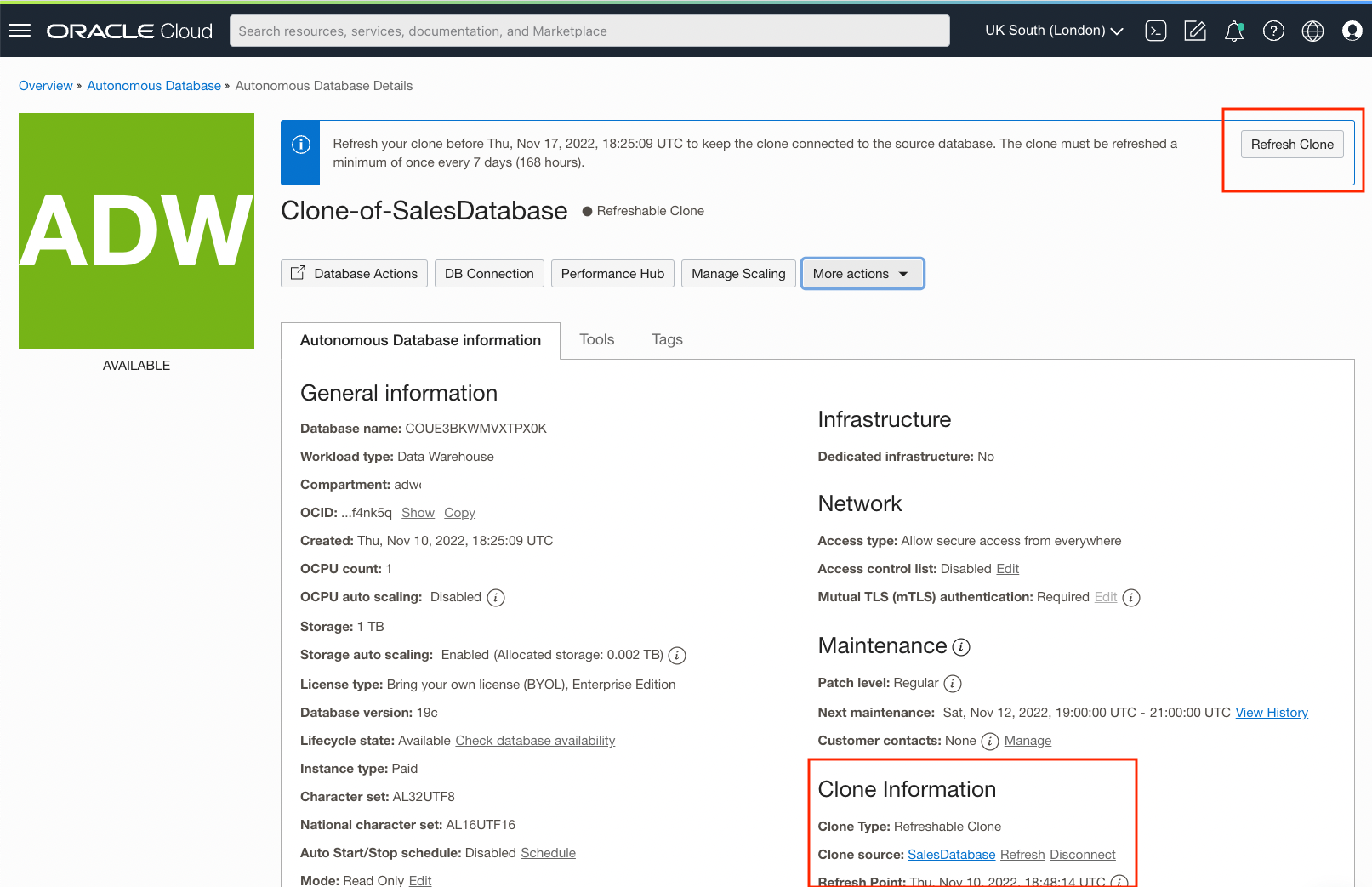
While the simplest way to create a single refreshable clone is via the UI above, ADB also provides easily scriptable APIs and SDKs to automate the calling of any feature available on the database console. A cross-region or local refreshable clone, can be managed, refreshed or disconnected from its source via the UI console or by calling the API. For more content on refreshable clones refer to the official documentation, and to learn more about how cross-region refreshable clones are billed refer to the Oracle Cloud service description.
Go ahead, try out cross-region refreshable clones on your database right away. Tweet us your interesting use cases for clones on ADB and how your team is deriving business value out of them, we’d love to know!
Like what I write? Follow me on the Twitter!
