Introduction
As digital architectures become more complex, ensuring continuous availability of mission-critical databases has never been more crucial—regardless of where your workloads run. As Harvard Business Review aptly highlights in “The Myth of Cloud Resilience in the Age of Intelligence,” organizations are waking up to the risks inherent in over-reliance on a single cloud service provider (CSP). This growing concentration risk, especially in highly regulated industries, has propelled multicloud from a theoretical insurance policy to a practical necessity for mitigating risk, operational continuity, and regulatory compliance.
Yet, for database architects, synchronizing data between different clouds has typically meant battling through custom scripting, inconsistent security models, and unpredictable latency—making multicloud disaster recovery more promise than reality. Today, that dynamic is rapidly shifting. Regulatory bodies like the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA), through directives such as CPS 230, are urging organizations to maintain operational resilience and manage concentration risk, driving renewed interest in robust multicloud strategies.
Resilience and Disaster Recovery:
Regulators and industry best practices emphasize robust business continuity and disaster recovery planning. Deploying across multiple clouds or regions enables rapid failover if one service experiences an outage, minimizing downtime for mission-critical applications.
Oracle is meeting this challenge head-on. With Oracle Autonomous Data Guard, enterprises can now deploy high-availability and disaster recovery (HA/DR) across both Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and Amazon Web Services (AWS). This groundbreaking capability enables you to configure standby databases between clouds, delivering seamless data protection and business continuity—even if a major cloud provider or region experiences an outage.
Key Drivers in Regulated and Enterprise Industries
Risk Management:
A principles-based regulatory approach focuses on managing concentration risk—not requiring multi-cloud as a technical requirement but expecting strategies that limit over-reliance on a single provider and ensure sustained operations in the event of a disaster.
Vendor Lock-in and Leverage:
Multicloud architectures provide organizations with greater flexibility, reducing the risk of being constrained by a single provider’s roadmap or pricing.
Compliance and Data Sovereignty:
Organizations can leverage diverse cloud providers’ region-specific options, supporting compliance with data residency, privacy, or sovereignty mandates like GDPR, HIPAA, and FedRAMP.
Best-of-Breed Services:
Adopting multiple clouds grants access to unique or advanced features not available from a single provider, enabling enterprises to drive innovation with best-in-class solutions.
Key Benefits of Cross-Cloud Autonomous Data Guard
Multicloud High Availability and Disaster Recovery:
By deploying Autonomous AI Database with Autonomous Data Guard across OCI and AWS, you can withstand cloud-specific outages and downtime. If your primary database in one cloud becomes unavailable, a fast, orchestrated failover to the standby in the other cloud keeps critical applications online.
Business Resilience and Compliance:
Distributing primary and standby databases between cloud providers facilitates alignment with stringent resilience, regulatory, and geographic requirements. This logical separation reinforces both redundancy and security.
Application Mobility and Cloud Flexibility:
With a synchronized standby database in each cloud, you gain application mobility. Entire workloads or applications can be migrated from AWS to OCI or vice versa—without interruption or loss of data integrity. This approach supports strategic migrations, cloud exit strategies, and rapid adaptation to new regulatory or business demands.
Read-Only Access with Active Data Guard:
Oracle Active Data Guard enables your standby database to be opened for read-only workloads while remaining in sync with the primary. This allows you to offload analytics or reporting to the standby, maximizing the value of your investment and maintaining protection.
Fully Managed Protection:
Autonomous Data Guard automates the configuration, monitoring, and management of disaster recovery environments. Failover operations are coordinated for speed and confidence, reducing manual effort and ensuring your recovery plan is always ready for action.
How It Works
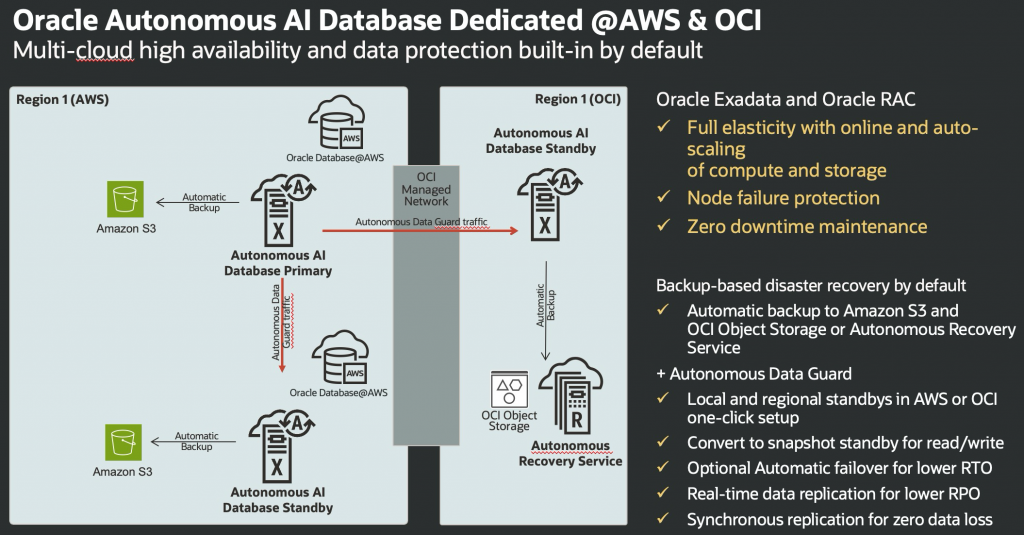
Oracle Autonomous Data Guard provides secure, encrypted, real-time data replication between Autonomous AI Database instances—whether in OCI, AWS, or both. In the event of disruption, immediate failover to the cross-cloud standby safeguards business operations, data integrity, and availability. Meanwhile, Active Data Guard enables leveraging the standby for read-only queries and analytical workloads, supporting business intelligence even before any failover is necessary.
Conclusion
With Oracle Autonomous Data Guard enabling cross-cloud disaster recovery, scalable read capabilities, and application mobility between AWS and OCI, Oracle delivers a powerful and agile solution for forward-looking enterprises. Your databases—and the critical applications they support—remain secure, highly available, accessible, and portable across clouds, empowering your organization with best-in-class resilience and flexibility to meet tomorrow’s challenges.
References and Further Reading
- Harvard Business Review: The Myth of Cloud Resilience in the Age of Intelligence
- Regulation Tomorrow: Now in force: APRA CPS 230 – operational risk management
- Oracle Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure Data Guard Documentation

