When You Just Need a Protected Function Call
There are times when functions cannot be easily coded in PL/SQL due to logic complexity, user preferred coding language, or you may just want to offload PL/SQL CPU cycles to external compute. As you know, Oracle external procedures (EXTPROC) have been available in Autonomous Database for a while. In my case, though, I need a protected function call but don’t want the hassle of maintaining external compute with the additional expense and operational cost. I want a seamless, serverless experience with my Autonomous Database where I can define my function and securely invoke it through PL/SQL. So how to resolve this quandary?
Let’s look at the Oracle Autonomous DBMS_CLOUD_FUNCTION Package. The doc says I can invoke remote functions in multi-cloud environments – OCI, Azure, AWS and GCP, from my Autonomous Database as SQL functions. This is intriguing; so let’s put it to the test. In an earlier blog we walked through tokenization of sensitive data by invoking a PL/SQL tokenization function call to an external tokenization service provider – VGS. So how might we do this with DBMS_CLOUD_FUNCTION?
In our scenario we are a global e-commerce company. We need to pre-process customer payment card details. These transactions must be pre-processed securely to reduce our PCI DSS compliance scope before storing the data in the Oracle Autonomous Database. Using the Oracle Autonomous Database DBMS_CLOUD_FUNCTION with OCI Cloud Function, I can invoke OCI remote functions as SQL functions in my Oracle Autonomous Database. Let’s use this integration to securely pre-process and tokenize this data.
Our use case:
We receive daily transaction files in OCI Object Storage containing raw credit card numbers that must be securely stored without violating PCI standards. We need to securely tokenize these credit card numbers to comply with PCI DSS standards and store the tokenized data in our Oracle Autonomous Database for downstream processing and analytics.
Traditionally, tokenizing data using external tokenization service APIs meant increased latency due to external cloud network traffic, added complexity in configuration, and potential compliance risk. DBMS_CLOUD_FUNCTION integration with the OCI Cloud Function mitigates these issues by allowing us to
- Call a secure, external function (written in Python, Java, etc.) from PL/SQL w/in the same cloud service.
- Use modern programming language alternatives to implement logic that is too complex or inefficient in PL/SQL (e.g., encryption, tokenization, machine learning).
- Pass values from each row to the function.
- Return tokenized results as part of your SQL flow
- Stay within database boundaries and maintain PCI compliance
- Outsource Database CPU cycles to the OCI Function service
A simple workflow for our solution describes OCI Cloud Function invoked through Autonomous Database DBMS_CLOUD_FUNCTION package to tokenize credit card transition data.
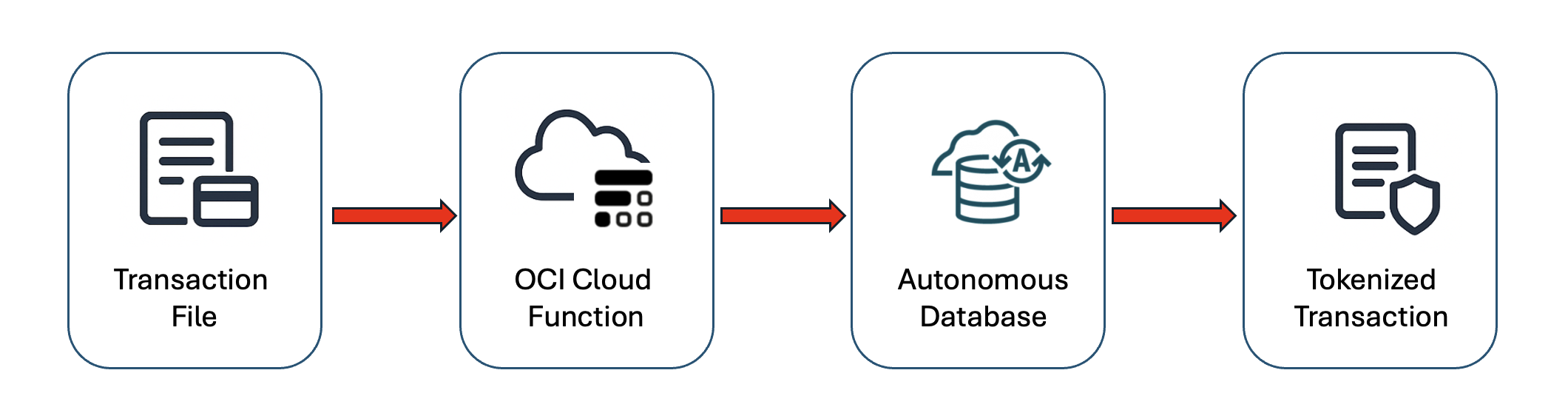
Let’s see how it works!
Create a Python OCI Function to convert credit card numbers to PCI token
import io
import json
import logging
import pyffx
from fdk import response
# Sample static key for demo; replace with OCI Vault / AWS KMS integration for production
ENCRYPTION_KEY = b"your-secure-128bit-key"
def handler(ctx, data: io.BytesIO = None):
if not data:
return response.Response(
ctx, response_data=json.dumps(
{"error": "No input received"}),
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"}
)
try:
body = json.loads(data.getvalue())
card_number = body.get("card_number")
if not card_number or not card_number.isdigit():
return json.dumps({"error": "Invalid card number"})
fpe = pyffx.String(ENCRYPTION_KEY, alphabet="0123456789", length=len(card_number))
token = fpe.encrypt(card_number)
except (Exception, ValueError) as ex:
logging.getLogger().info('error parsing json payload: ' + str(ex))
return response.Response(
ctx, response_data=json.dumps(
{"error": "{0}".format(str(ex))}),
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"}
)
logging.getLogger().info("Inside Python Tokenization function")
return response.Response(
ctx, response_data=token}),
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"}
)
Define requirements.txt
fdk>=0.1.96 pyffx
For Python-based OCI Functions, the requirements.txt file is essential for defining the external packages and dependencies required by your function code. It lists all the third-party Python libraries that your function relies on.
Create PLSQL function to invoke the OCI Cloud Function
-- A credential object in Oracle (and other cloud services like OCI or AWS) is a secure, named object that stores authentication
-- details — such as usernames, passwords, tokens, or keys — for accessing external resources or APIs without hardcoding credentials
-- in SQL or PL/SQL code.
-- Create OCI Credential
SQL> BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL (
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED',
user_ocid => 'user_ocid',
tenancy_ocid => 'tenancy_ocid',
private_key => 'private_key',
fingerprint => 'fingerprint'
);
END;
/
-- Create function catalog OCI_DEMO_CATALOG
SQL> BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_FUNCTION.CREATE_CATALOG (
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED',
catalog_name => 'OCI_DEMO_CATALOG',
service_provider => 'OCI',
cloud_params => '{"region_id":"us-phoenix-1", "compartment_id":"comp_id"}'
);
END;
/
-- Create PLSQL function to invoke the tokenization OCI Cloud Function
SQL> VAR function_args CLOB;
SQL> EXEC :function_args := TO_CLOB('{"card_number":"VARCHAR2"}');
SQL> BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_FUNCTION.CREATE_FUNCTION (
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED',
catalog_name => 'OCI_DEMO_CATALOG',
function_name => 'tokenize',
function_id => 'ocid1.fnfunc.sample',
input_args => :function_args
);
END;
/
-- Desc function
SQL> desc tokenize
FUNCTION tokenize RETURNS CLOB
Argument Name Type In/Out Default?
------------------------------ ----------------------- ------ --------
CARD_NUMBER VARCHAR2 IN
-- Test the cloud function
SQL> select tokenize(card_number => '4111111111111111') from dual;
TOKENIZE(CARD_NUMBER=>'4111111111111111')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{"STATUS":200,"RESPONSE_BODY":"3535929231211868"}
Create the table card_transactions
CREATE TABLE card_transactions ( cardholder VARCHAR2(100), cc_number VARCHAR2(20), expiry VARCHAR2(5), amount NUMBER );
View of sample credit card transactions file present in OCI object store
[
{
"cardholder": "Alice Smith",
"cc_number": "4111111111111111",
"expiry": "12/26",
"amount": 250.75
},
{
"cardholder": "Bob Jones",
"cc_number": "5555555555554444",
"expiry": "11/25",
"amount": 480.00
}
]
Insert tokenized transaction information from object store invoking the tokenize function from within PL/SQL
INSERT INTO card_transactions (cardholder, cc_number, expiry, amount)
SELECT jt.cardholder,
JSON_VALUE(tokenize(card_number => jt.cc_number), '$.RESPONSE_BODY' AS cc_number,
jt.expiry,
jt.amount
FROM JSON_TABLE(
DBMS_CLOUD.get_object(
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED',
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/mybucket/b/.../o/transactions.json'
),
'$[*]'
COLUMNS (
cardholder VARCHAR2(100) PATH '$.cardholder',
cc_number VARCHAR2(20) PATH '$.cc_number',
expiry VARCHAR2(5) PATH '$.expiry',
amount NUMBER PATH '$.amount'
)
) jt;
Conclusion
Autonomous Database integration with OCI Cloud Function using the DBMS_CLOUD_FUNCTION package is simple to implement and offers a highly secure, highly scalable solution for remote user defined function execution within PL/SQL. The combination of Autonomous Database and OCI Cloud Function offers a rich development environment for a myriad solutions extending functionality for workflow automation, data transformations, and event-driven processing, just to name a few. But it is not just for OCI! Autonomous Database is a multi-cloud solution and DBMS_CLOUD_FUNCTION integrates with other cloud vendor FaaS offerings. Let’s see what we can do with AWS Lambda!
Further reading:
https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/autonomous-database-serverless/doc/dbms-cloud-function.html
https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Functions/Concepts/functionsoverview.htm
Contributing authors:
Alekhya Manem, SMTS, Oracle Corporation
Vaibhav Khanduja, CMTS, Oracle Corporation
