Overview
Storage Gateway is a cloud storage gateway that lets you connect your on-premises applications with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Applications that can write data to an NFS target can also write data to the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage, without requiring application modification to uptake the REST APIs.
To Make it simpler, now you can sync your On-Premises application data to Oracle Cloud Object Storage. How It Works, the idea is simple. install the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Storage Gateway in a compute instance or on-premises host. After a little configuration, when a file is written or modified in a Storage Gateway backed share, that file is automatically uploaded to a connected Object Storage bucket.
Prerequisites
- Two dual-core CPUs or better. Oracle recommends 4-core CPUs.
- The recommended local storage disk size is 600 GB, which includes 500 GB for the file system cache, 80 GB for metadata storage, and 20 GB for log storage.
- Oracle Linux 7, Docker 1.12.6 or newer and NFSv4.
- Storage Gateway installation software automatically installs Docker and the NFS protocol.
- Familiarity with the administration and configuration commands of the operating system on the host machine.
How Storage Gateway Works
Storage Gateway is installed in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure compute instance or as a Linux Docker instance on one or more hosts in your on-premises data center. Applications store and retrieve objects from Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage through file systems that you create in Storage Gateway.
Storage Gateway exposes an NFS mount point that can be mounted to any host that supports an NFSv4 client. The Storage Gateway mount point maps to an Object Storage bucket.
Installation and configuration of Storage Gateway
You install Storage Gateway by first going to the Storage Gateway Download page. Click the Download link for all supported platforms.
Create a directory in host and move the downloaded file – ocisg-1.4.tar.gz to the newly created directory.
Unzip the ocisg-1.4.tar.gz file using command — tar -xf ocisg-1.4.tar.gz
Create 3 folders for Cache, Metadata and Log which will be pointed during the installation.
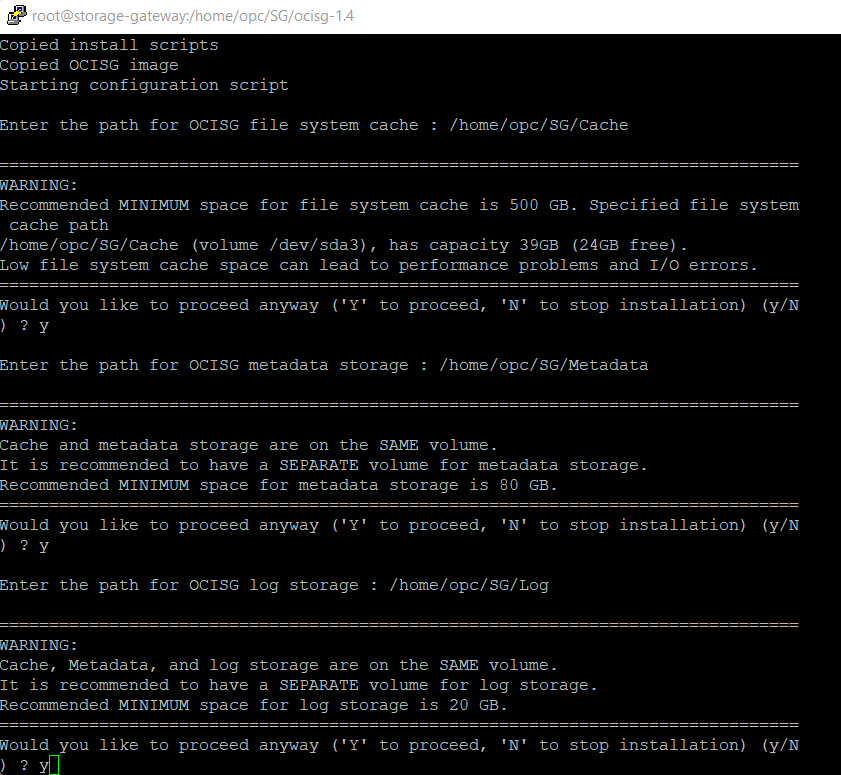
Invoke the installer ./ocisg-install.sh
The script guides you through the Storage Gateway installation. Depending on your host machine configuration, your prompted to install Docker and XFS.
Point the newly created folder location when prompted during installation
After a successful installation, the script provides the following information:
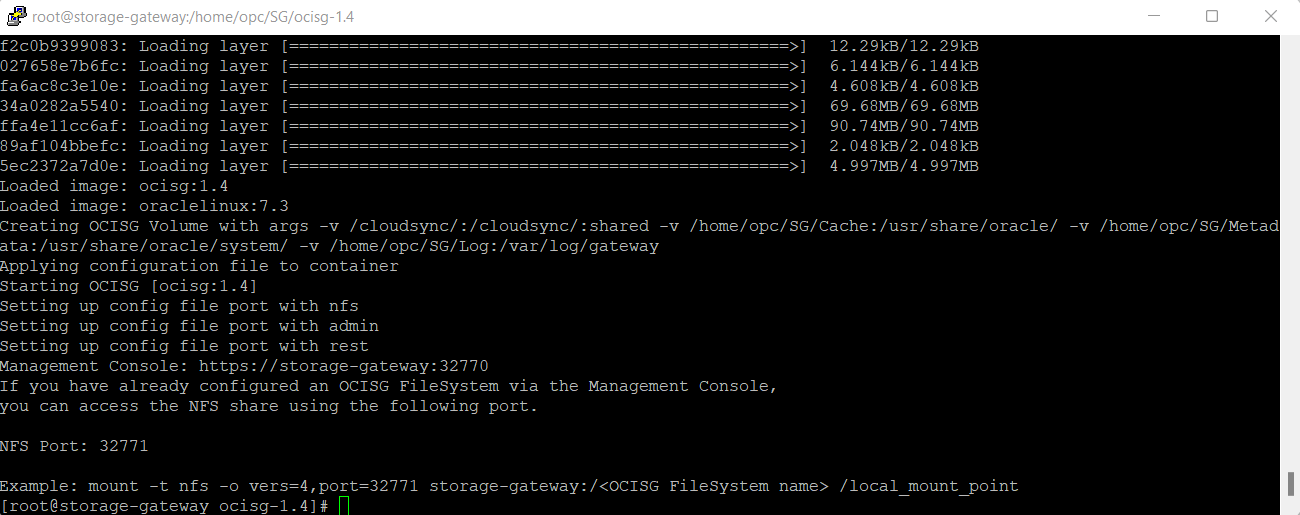
Note: Make sure the port is open in the system where you have installed the storage gateway
You can access the Management Console — https://<storagegateway_hostname>:<port_number>
E.g.: https://myStorageGatewayHost:33770
Enter the New Password twice and save.
The User Interface looks as below
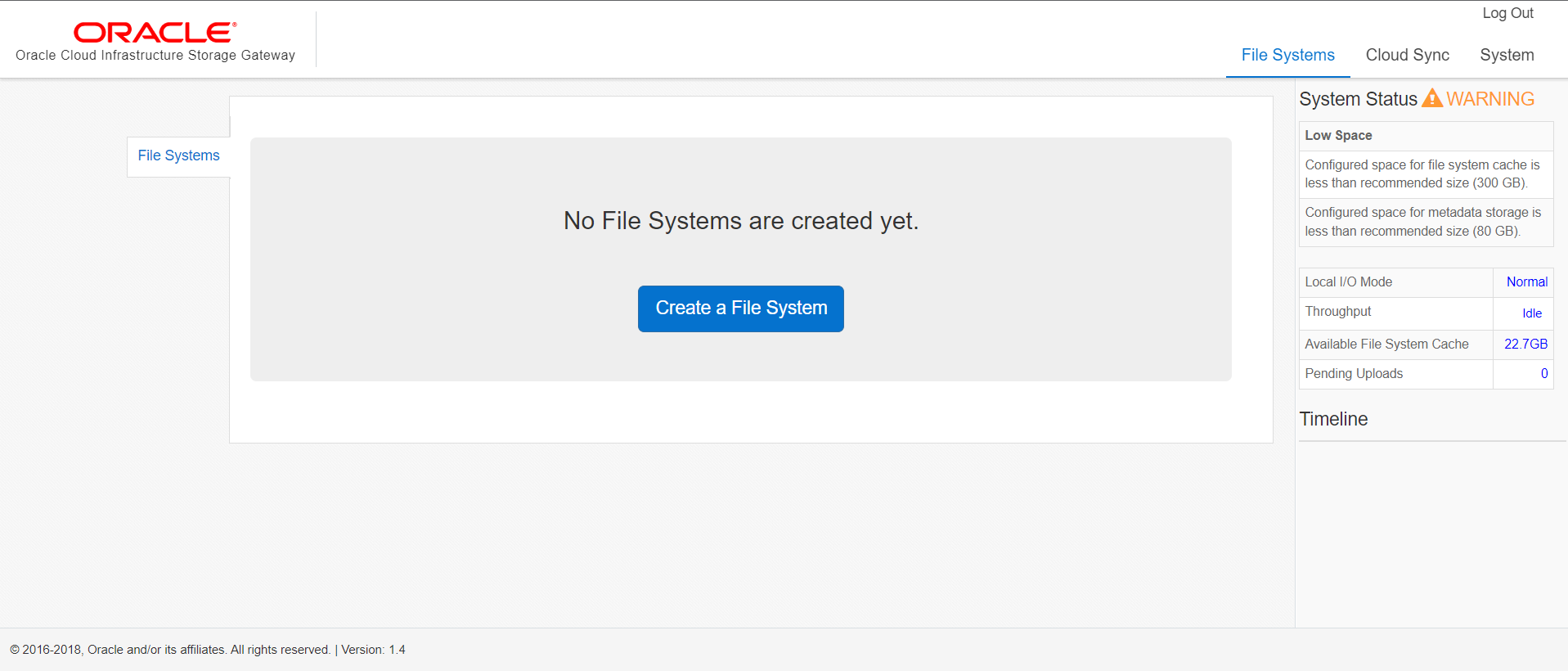
Click on Create a file system, here you will be giving all the details of the cloud storage that you will be used for data sync which includes:
- Object Storage Endpoint URL.
- OCID Of User, Compartment & Tenancy.
- Fingerprint of User
- Object Storage Tier (Standard or Archive)
- Private Key
- Private Key Passphrase
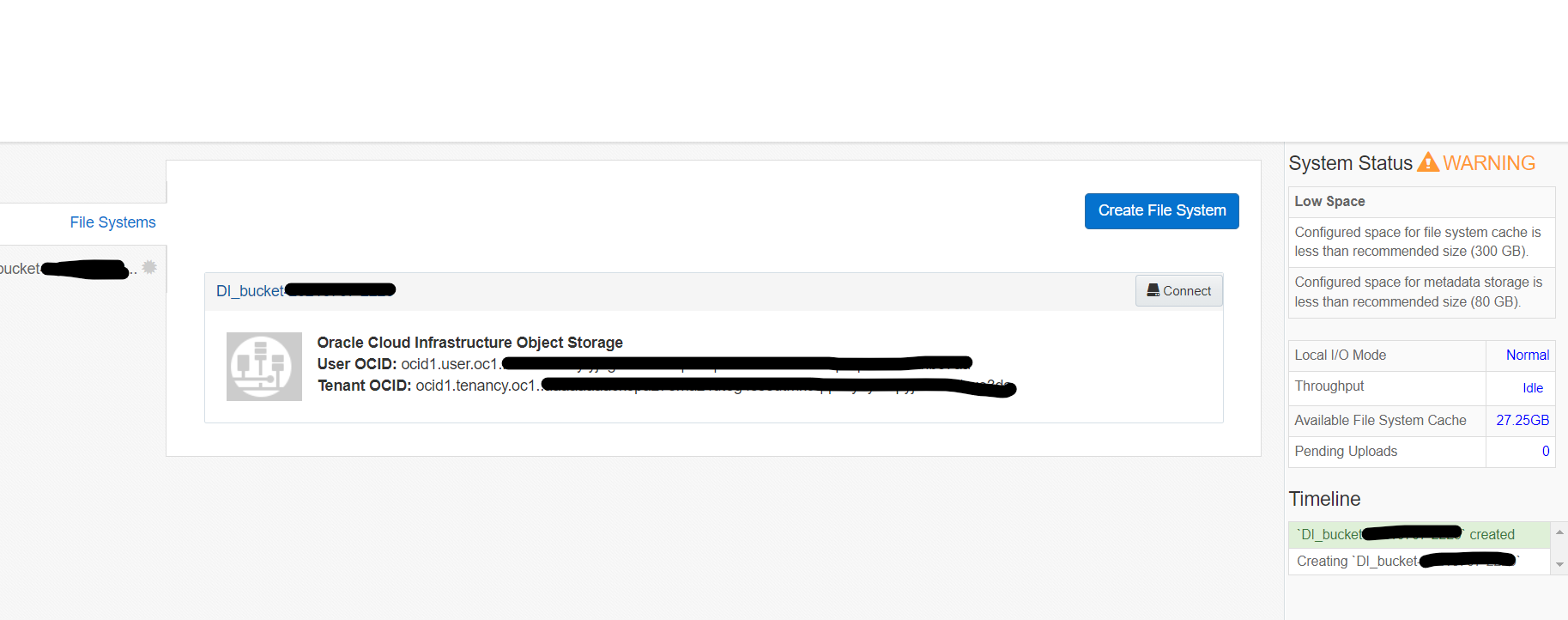
After all the details were given, you can see the new filesystem created pointed to OCI Object Storage
Use NFS Client Mount Command to mount the host machine to object storage
sudo mount -t nfs -o vers=4,port=<NFS_port_number> <storage_gateway_host_name>:/<ocisg_file system_name> /<local_mount_point>
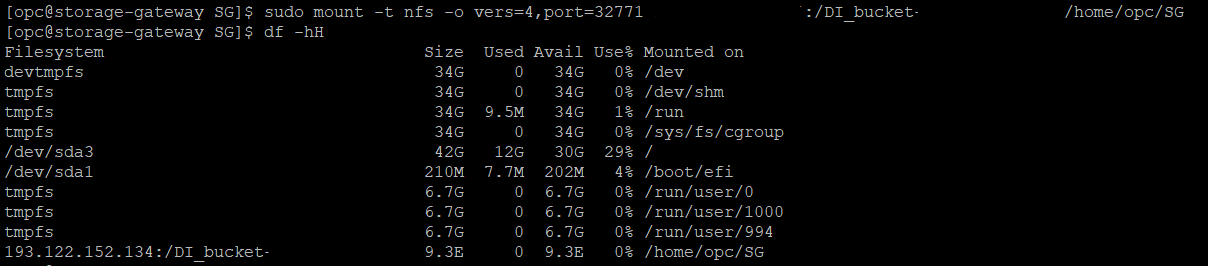
As captured in above image, df command shows Avail space 9.3E
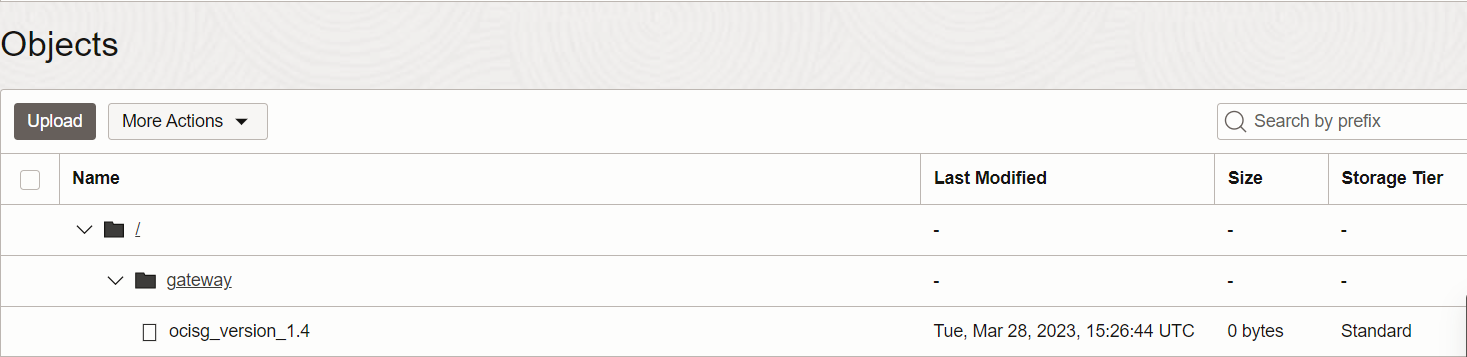
Once the above steps are done create dummy files/folders in the local_mount_point which will be reflected in the OCI Object Storage
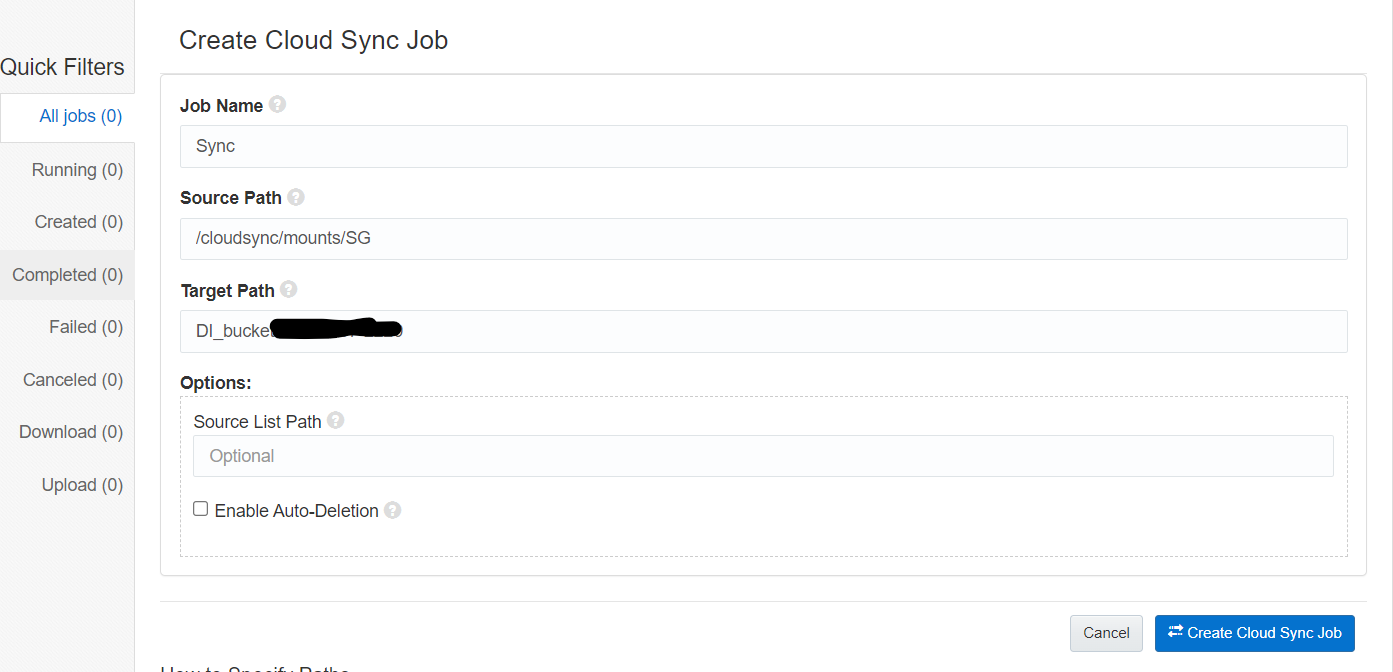
You can also create a cloud sync job to keep Host Machine and Object Storage in sync.
From the console go to Cloud Sync job page and enter below details and create cloud Sync. You can enable Auto-Deletion as well.
After the cloud sync job is created you can run through console or schedule it to run at specific intervals.
Using Storage gateway cloud sync we can easily synchronize on-premises data to cloud with out any manual intervention. This not only saves your time but also protects your data integrity and consistency.
Conclusion
With Storage Gateway, you can support below use cases
- Backup and archive with Cloud Sync
- Migrating data to the cloud
- Hybrid Cloud Workloads and Data Processing
- Nearline Content Repositories and Data Distribution
- Tiered Storage and NAS Capacity Expansion
I hope that this blog helps you understand Storage Gateway concepts in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. If you have any questions regarding Storage Gateway, post them in the comments. For more information, see the following resources:
https://www.oracle.com/cloud/storage/storage-gateway
https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/StorageGateway/Concepts/storagegatewayoverview.htm
https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/StorageGateway/Tasks/installingstoragegateway.htm
