GoldenGate 23ai vector replication
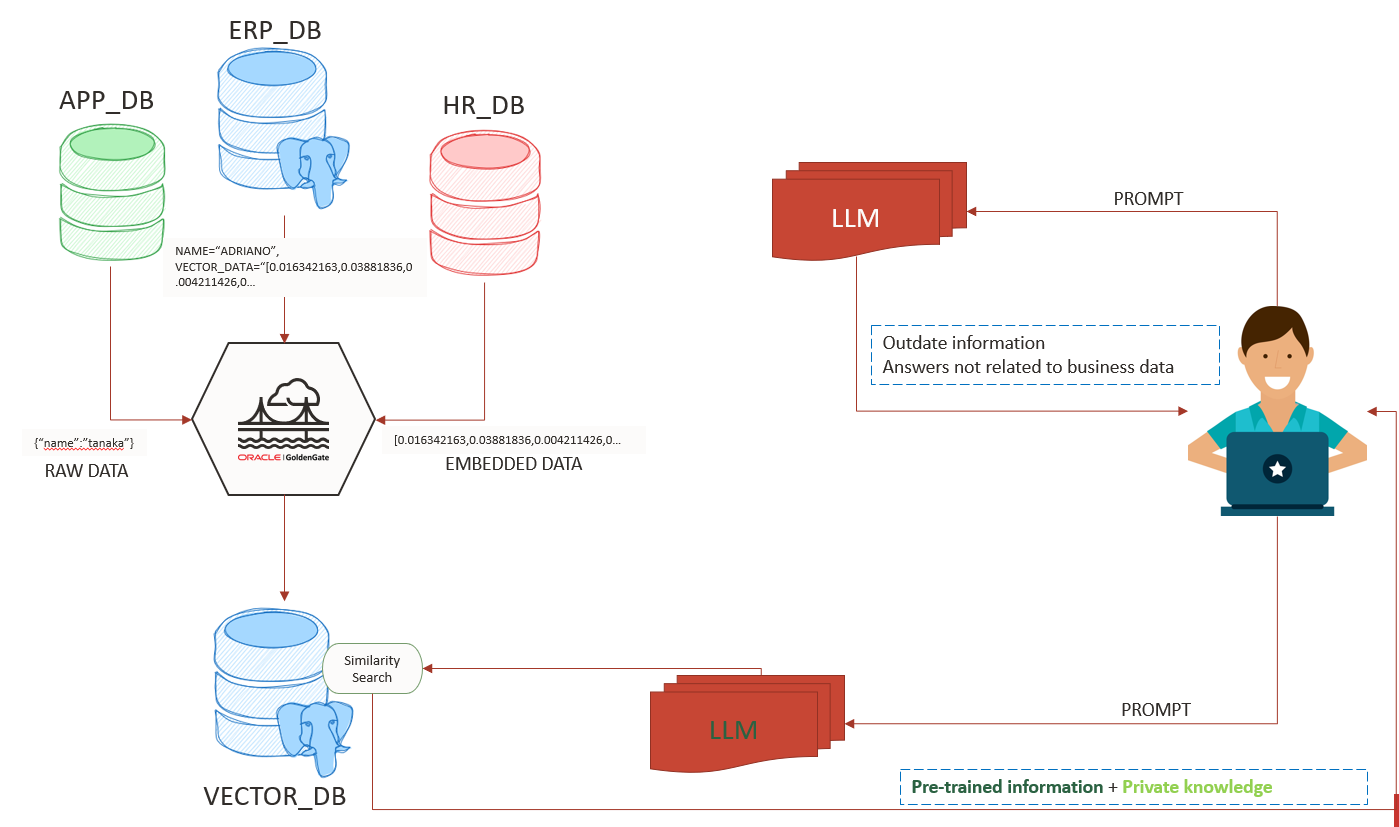
Vectors and embeddings are essential components of LLM and RAG solutions. They enhance the knowledge trained in the LLM with your proprietary data. In this post, you’ll learn how to use Oracle GoldenGate to capture and replicate vectorized data, or even generate vector data on-the-fly using OCI Gen AI Services.
Our topology has:
- Oracle Database 23ai as source
- PostgreSQL 16 as target with pgvector extension
- OCI Gen AI to create embeds.
- GoldenGate 23ai for Oracle and GoldenGate 23ai for PostgreSQL
Source:
We’re using the Oracle 23ai Free Edition as our source, which includes Vector capabilities such as the Vector Data Type and the VECTOR_DISTANCE function to calculate the distance between two vectors (for similarity checks). Create a table like this:
create table postgresday.vector_example( id number generated always as identity(start with 1 increment by 1), metadata varchar(256), vector_data vector);
The id could be used to unique identify the row, the metadata can host the piece of text (in our case) and the VECTOR_DATA column will store the vectorized version of metadata.
To insert data, you can use this example:
DECLARE
vector CLOB;
BEGIN
vector:= '[0.017242432,0.03390503,..........]';
insert into postgresday.vector_example (metadata,vector_data) values ('Your text chunk', vector);
COMMIT;
END;
/
For the extract we can have a very basic one:
EXTRACT E_PDAY USERIDALIAS free DOMAIN OracleGoldenGate EXTTRAIL postgresday/ps sourcecatalog freepdb1 table postgresday.vector_example;
Use OCI GenAI to generate the vectors
To generate vectors on-the-fly, we’ll use the OCI GenAI service. Ensure you have the OCI Python package installed and configured on your system. The setup is straightforward; details can be found here. Remember to configure it with the postgres (OS) user.
Postgres
For our target we need pgvector and plpython3u extensions, here I’m using Postgres 16 in Oracle Linux 9 and I’ve ran these commands (it could be different in your system):
yum install postgresql16-devel yum install postgresql16-plpython3 yum install pgvector_16 yum install python3 pip install oci CREATE EXTENSION vector;
Because I’m planning to use the Postgres DB as my repository, I will be doing a mapping to a table with a different structure from source:
CREATE TABLE public.vector_repo (id serial primary key,METADATA VARCHAR(1000),VECTOR_DATA VECTOR,DB_FROM VARCHAR(1000),EMBEDDED_POSTGRES VECTOR);
The DB_FROM column will contain a string to specify the source database. The VECTOR_DATA column will store the original vectorized data, while the EMBEDDED_POSTGRES column will hold the metadata value that has been vectorized by a function.
Create this function in your postgres database:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION oggadmin.oci_embed(
_model text DEFAULT NULL::text,
_input text DEFAULT NULL::text,
_input_type text DEFAULT NULL::text,
_truncate text DEFAULT 'NONE'::text,
_profile text DEFAULT 'DEFAULT'::text,
_region text DEFAULT 'us-chicago-1'::text,
_compartment text DEFAULT NULL::text)
RETURNS vector
LANGUAGE 'plpython3u'
COST 100
VOLATILE PARALLEL SAFE
SET search_path=pg_catalog, pg_temp
AS $BODY$
import oci
CONFIG_PROFILE = _profile
config = oci.config.from_file('~/.oci/config', CONFIG_PROFILE)
endpoint = "https://inference.generativeai."+_region+".oci.oraclecloud.com"
generative_ai_inference_client = oci.generative_ai_inference.GenerativeAiInferenceClient(config=config, service_endpoint=endpoint, retry_strategy=oci.retry.NoneRetryStrategy(), timeout=(10,240))
embed_text_detail = oci.generative_ai_inference.models.EmbedTextDetails()
embed_text_detail.serving_mode = oci.generative_ai_inference.models.OnDemandServingMode(model_id=_model)
embed_text_detail.inputs = [_input]
embed_text_detail.truncate = _truncate
embed_text_detail.compartment_id = _compartment
embed_text_response = generative_ai_inference_client.embed_text(embed_text_detail)
embed_text_response.data
return embed_text_response.data.embeddings[0]
$BODY$;
This function receives an text parameter, in this case the second column referenced by $2, send this text to our OCI Gen AI Service and receive a Vector as return, GoldenGate 23ai has te capability of wait for this call and insert the return in our target table.
You can test the function running:
select oci_embed(_model=>'cohere.embed-english-light-v2.0',_profile=>'DEFAULT',_compartment=>'ocid1.compartment.oc1..XXXXXX,_input=>'YOUR TEXT')
Replicat
Here we will use the new DBFUNCTION feature introduced in GoldenGate 23ai, within this parameter, the replicat can run a stored database function (that’s why we’ve created the oci_embed function).
MAP FREEPDB1.POSTGRESDAY.vector_example, TARGET public.vector_repo, COLMAP (USEDEFAULTS, db_from='oracle',EMBEDDED_POSTGRES=@DBFUNCTION('oci_embed(_model=>''cohere.embed-multilingual-v3.0'', _input=>$2::VARCHAR, _input_type=>''classification'',_profile=>''DEFAULT'',_compartment=>''ocid1.compartment.oc1..xxxxx)'));
In this case we are passing the second column (metadata column from Oracle table) to our function specifying the $2 and doing an conversion to varchar (::VARCHAR), if your table has a different structure change it to reflect it.
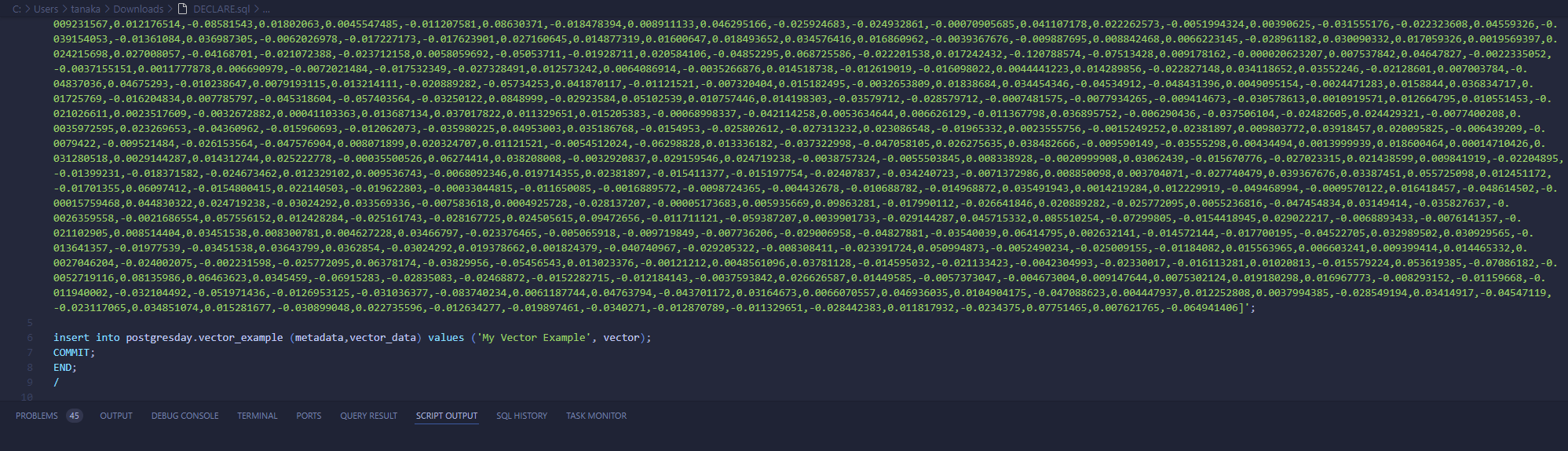
In my source I will insert this data(the vector is just an example):
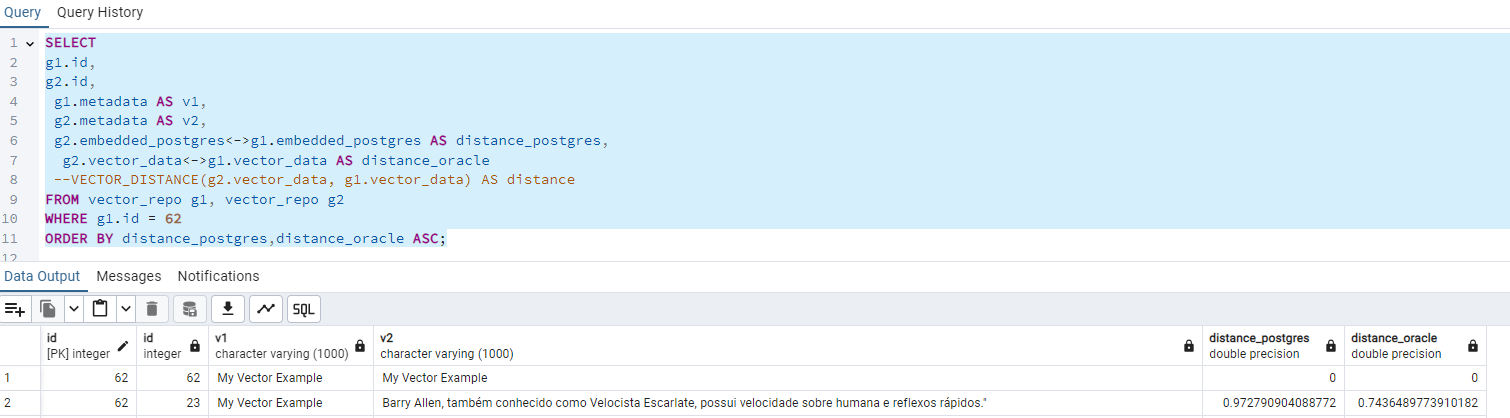
And I can check it in my postgres:
Conclusion:
This simple blog guide you on how to use some new functions of GoldenGate like the DBFUNCTION and the Vector to help you in your LLM/AI implementation, deliveryng the CDC capability to your infrastructure.

