Azure Storage provides a layered security model. This model enables you to secure and control the level of access to your storage accounts. You can create Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) GoldenGate ADLS connections through public endpoints or private endpoints.
Either you use public or private access, OCI GoldenGate supports Shared Key, Shared Access Signature and Azure Active Directory authentication types.
If you configured your Azure Storage Account with public network access enabled from all networks, OCI GoldenGate will create the connection using the public internet. You can just provide your Azure Storage Account name and authentication details to create the connection.
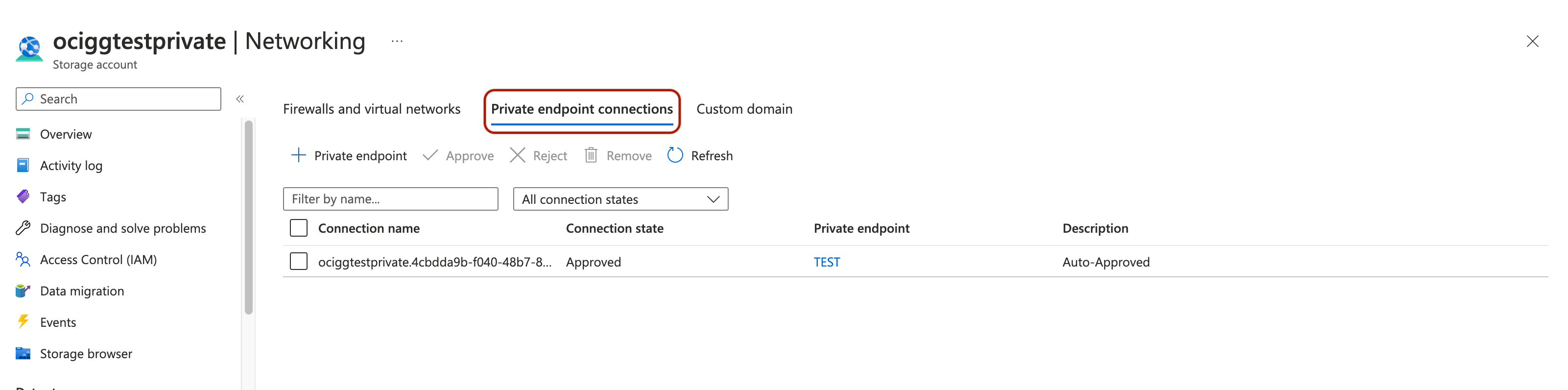
You can also use Private Endpoints for Azure Storage Account which assigns a private IP address from your VNet to the storage account and secures all traffic between your network and the storage account over a private link. You can also create an OCI GoldenGate ADLS connection for Azure Storage Accounts running with Private Endpoints.
First, you need to create an interconnect between your OCI and Azure accounts. Arun and Andrei covered a step-by-step process for interconnecting OCI and Azure. You can also refer to Regional Availibility document to see in which regions you can create OCI and Azure interconnects.
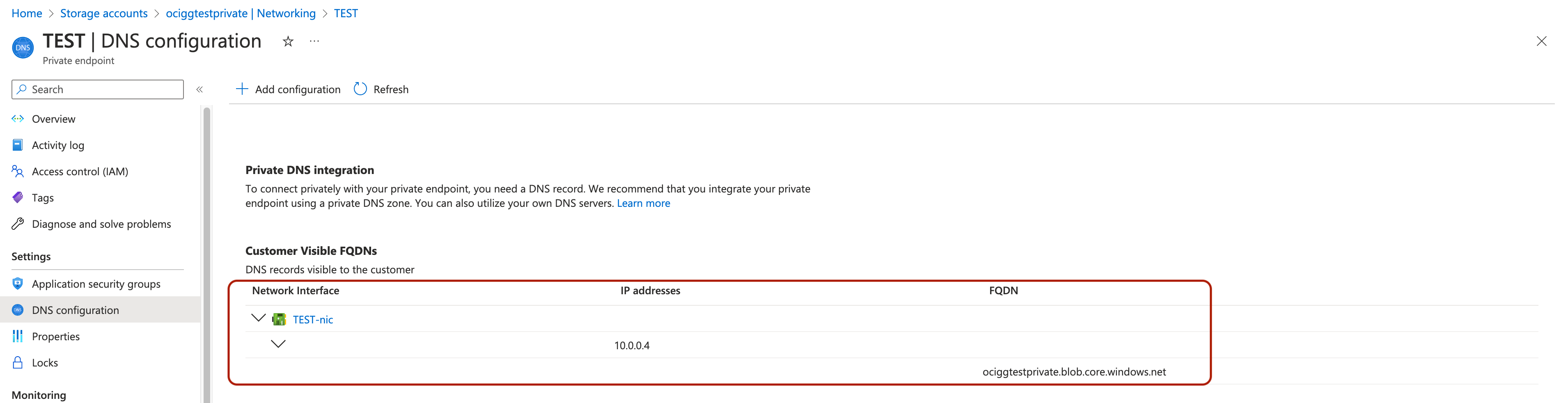
Then, you need to set up an Azure Storage Account with a private endpoint. You can refer to Azure documentation for more details.
Create OCI GoldenGate Azure Data Lake Storage Connection:
ADLS connection can be created using one of the 3 Azure Storage authentication methods:
- Shared Access Key
- Shared Access Signature
- Azure Active Directory
Depending on the authentication type, you’ll need to provide different details.
For Shared Access Key, you’ll need to provide Storage Account Access Key. You can refer to Azure Documentation to get the details about how to create and obtain storage account access keys.
For Shared Access Signature, you’ll need to provide SAS Token. You can refer to Azure Documentation to get the details about how to create a SAS Token.
For Azure Active Directory, you’ll need to provide Azure Tenant ID, Azure Client ID and Azure Client Secret. For Azure Active Directory authentication, you need to register an application in Azure AD App Registrations and assign needed roles to the application. For example, Storage BLOB Data Owner. You can refer to Azure Documentation to get details about Azure AD App Registrations and roles.
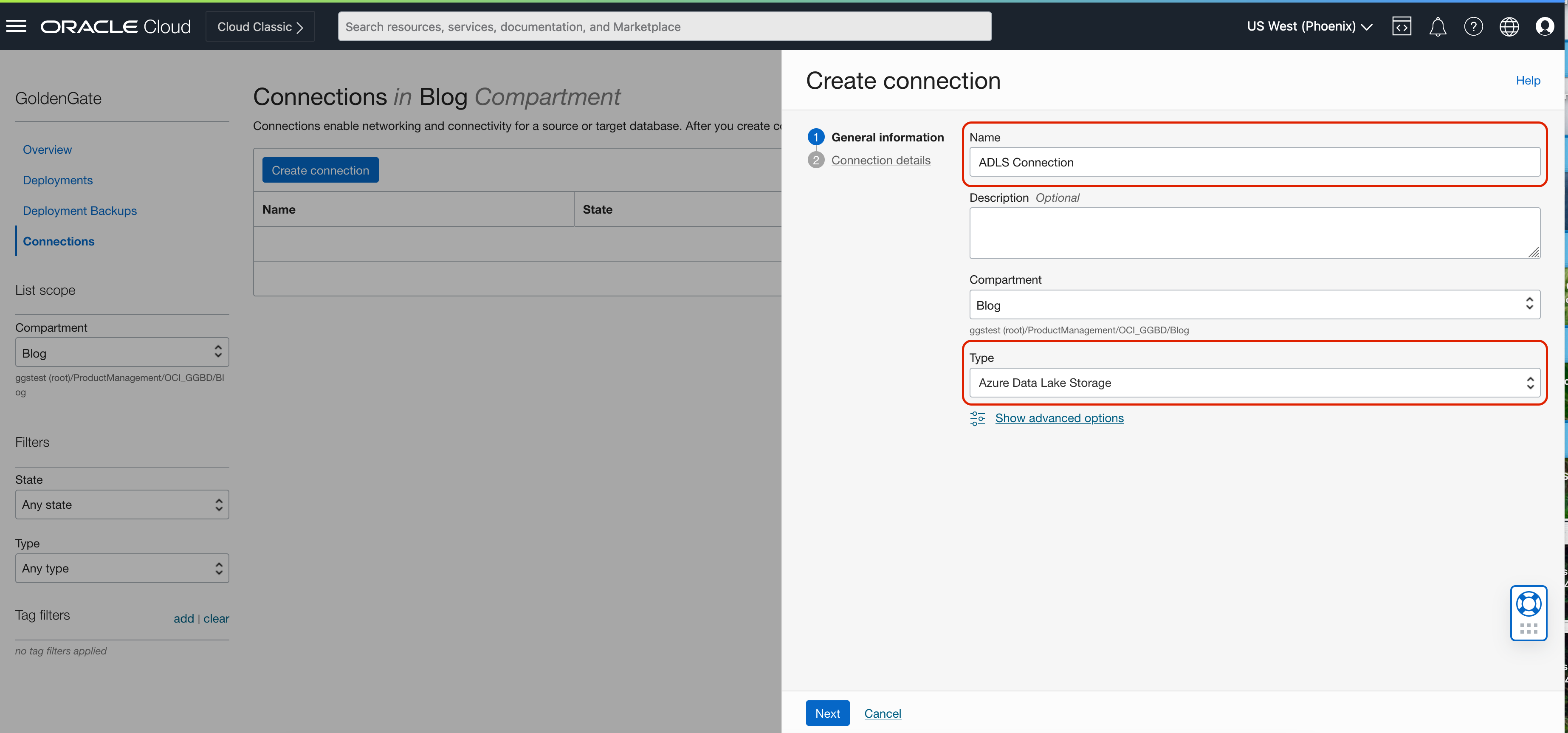
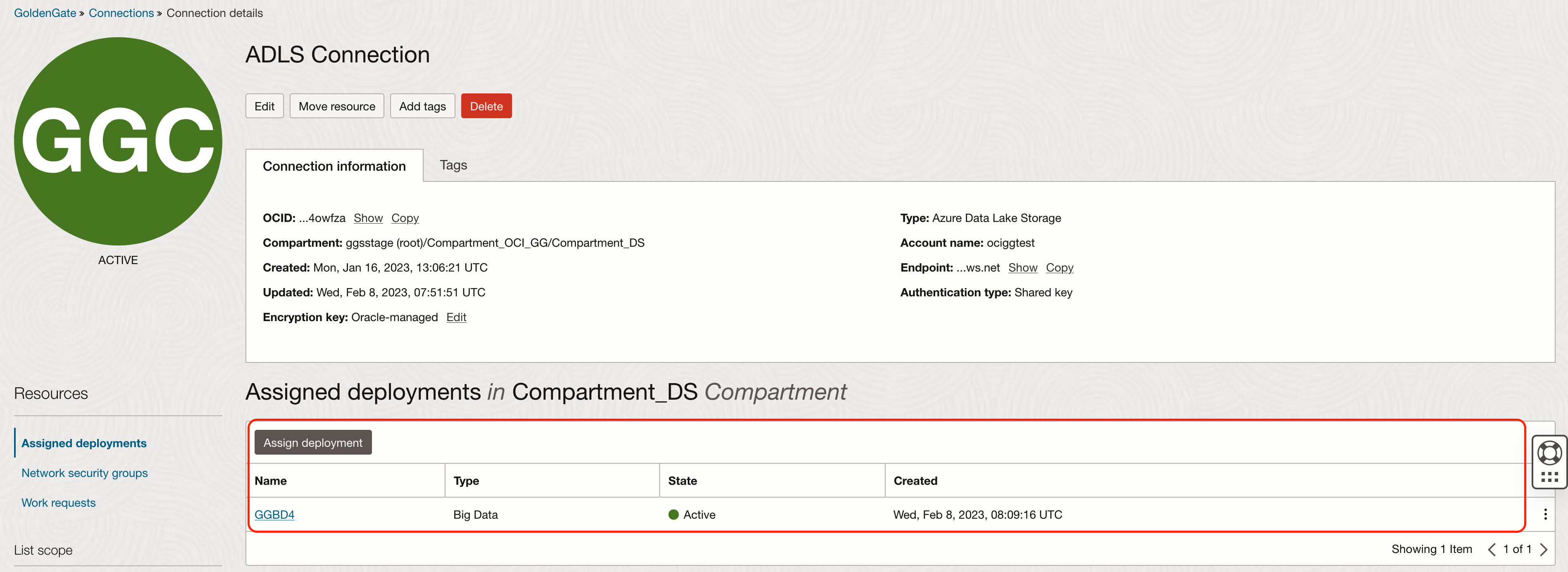
To create an OCI GoldenGate Connection for ADLS, click Create connection button. Provide a Name for the connection and select the Type as Azure Data Lake Storage. Click Next.
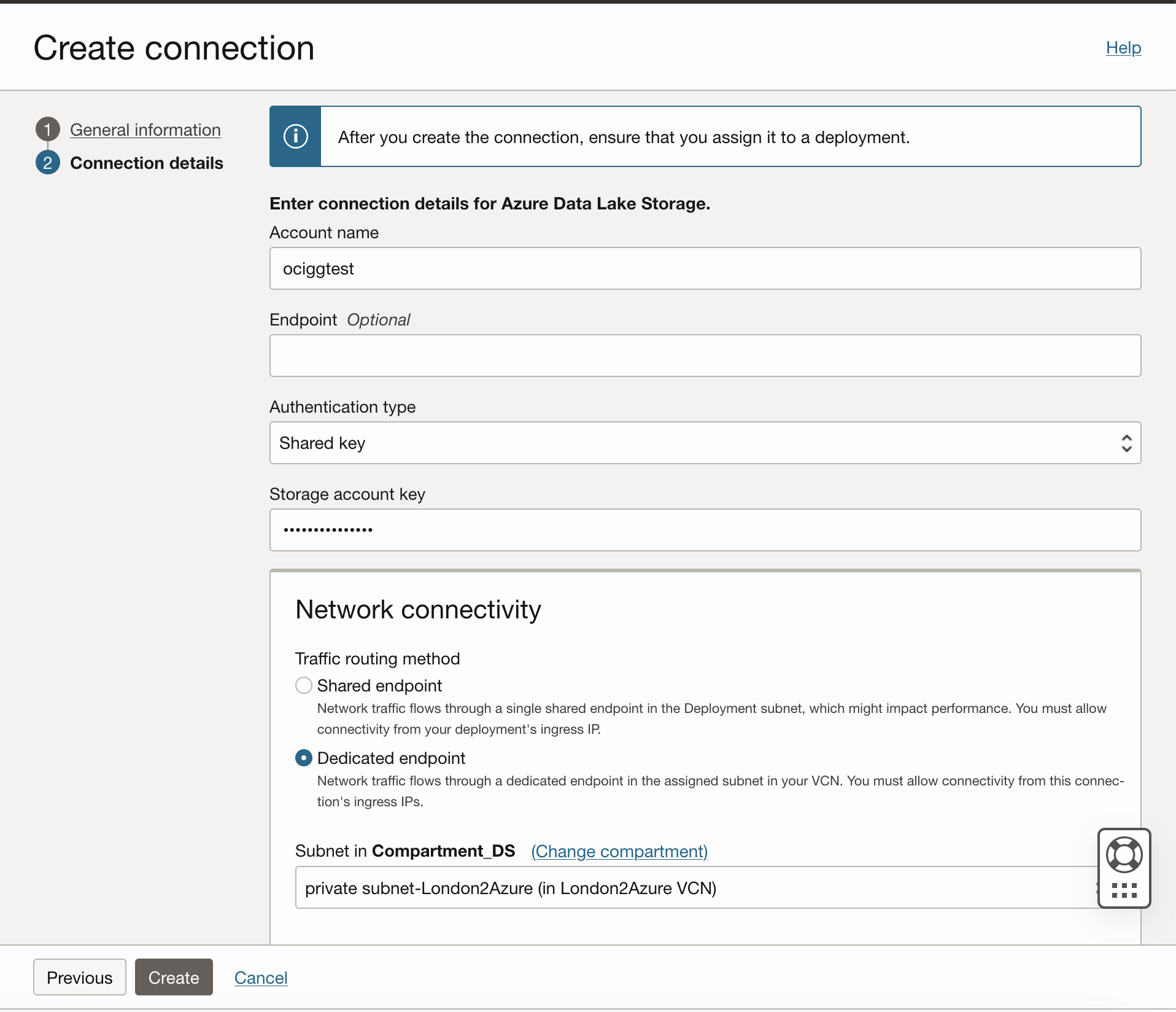
Provide your Azure Storage Account Name, select the authentication type, select Traffic Routing Method as Dedicated Endpoint and click Create. With Dedicated Endpoint, select the subnet which is also used by your Azure-OCI interconnect.
Once connection is created, assign connection to the OCI GoldenGate Big Data deployment.
Before creating the replicat, we need to do some changes in OCI DNS Management as well:
- In OCI Networking/ DNS Management/ Private Views, select the private view that has the same as the VCN where the subnet is step 1 is created.
- Click Create Zone and provide the zone name as blob.core.windows.net
- Select the zone created in step 3 and click Manage Records.
- Click Add Records.
- For Name, provide the target storage account name. Select Type as IPV4. In RDATA/Answers, provide the private endpoint ip address of the target Azure Storage Account and click Add Record.
- Click Publish Changes and Confirm Publish Changes.
Now, you can go to OCI GoldenGate console and configure the replicat. You can refer to OCI GoldenGate documentation for details. To ingest parquet format in real-time into Azure Data Lake Storage, you can refer to OCI GoldenGate Real-Time Ingestion for Azure Data Lake Storage blog.
