For organizations running mission-critical workloads, the Oracle Exadata Database Service has long been the gold standard. It offers the performance and isolation of Exadata in the cloud. However, as business demands grow, the operational overhead of managing databases can become a bottleneck and increasingly slow innovation, even in cloud environments.
This is where Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Infrastructure transforms the equation, combining the isolation and performance of Exadata Database service with a fully managed, serverless-like operating model.
Here is why upgrading to Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Infrastructure delivers immense value compared to a traditional co-managed approach.
Co-Managed vs. Fully Managed: A Fundamental Shift
The primary difference between Exadata Database Service and Autonomous AI Database lies in the management model.
Exadata Database Service (Co-Managed): Oracle manages the underlying infrastructure and the virtualization host, while customers retain control of the virtual machines and databases. Patching, operating system updates, database tuning, and high-availability configuration remain customer responsibilities. This approach delivers maximum control, but at the cost of increased operational overhead.
Autonomous AI Database (Fully Managed): Oracle takes full control of operations, managing the complete stack from the underlying infrastructure to the database service. This includes automated patching and security updates, proactive detection and resolution, and elastic scaling to meet changing demand.
The Autonomous Value Proposition
By moving to a fully managed environment, teams can step away from day-to-day maintenance and can focus on higher-value initiatives. This approach delivers:
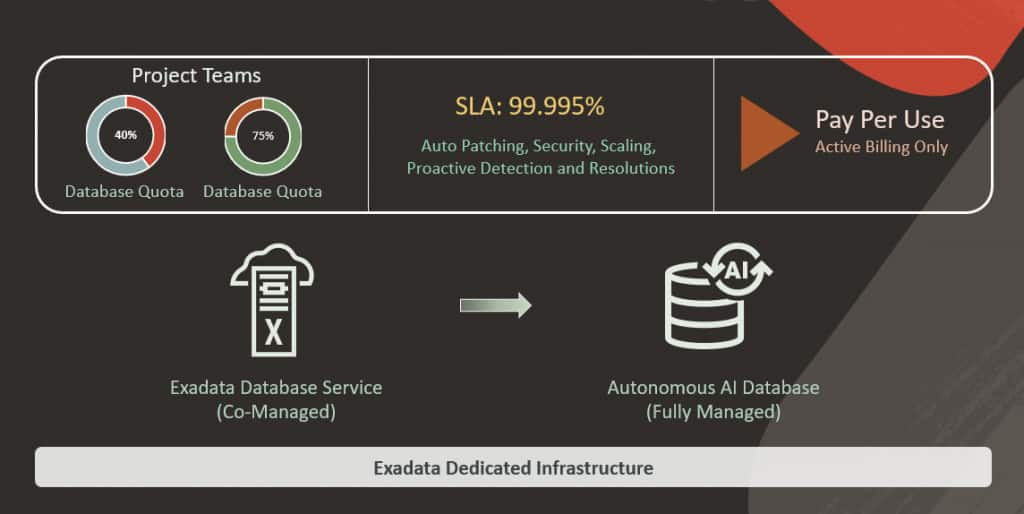
Higher SLAs: Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Infrastructure offers an industry-leading 99.95% availability SLA, which increases to 99.995% with Autonomous Data Guard. This reliability is built in, rather than something that must be manually architected and maintained.
Reduced Risk: With self-securing capabilities, the system automatically applies security patches and database fixes with zero downtime, eliminating the window of vulnerability and stability common in co-managed environments.
Automatic Scaling: Unlike static resource allocation, Autonomous AI Database can scale CPU resources instantly to meet demand, ensuring peak performance without paying for idle capacity.
The Best of Both Worlds: Running Side-by-Side
One of the core advantages of the modern Exadata Cloud ecosystem is flexibility. Exadata Database Service and Autonomous AI Database can run concurrently on the same Exadata Infrastructure, enabling a gradual transition without requiring a rip-and-replace approach.
This capability provides a seamless modernization path for existing Exadata Database Service customers:
Scale Online: Existing Exadata Infrastructure can be expanded online by adding Database or Storage servers.
Add Autonomous VM Clusters: New Autonomous VM Clusters can be provisioned alongside existing Exadata VM Clusters on the same hardware.
Migrate at a Controlled Pace: Individual workloads can be moved to Autonomous AI Database to evaluate benefits, while existing applications continue to run on the standard Exadata Database service.
Oracle fully manages the Autonomous resources once provisioned. As adoption increases, additional capacity can be requested as needed, providing a low-risk and straightforward path to modernization.
Simplified Cost Model and Self-Service Enablement
Moving to Autonomous AI Database introduces a cloud-native billing and operational efficiency that is distinct from the traditional model.
1. No Overhead Costs for Logical Resources
Unlike Exadata Database Service, where complex VM architecture can incur costs, there is no billing for Autonomous VM Clusters or Autonomous Container Databases. These resources function as logical constructs for governance, isolation, and organizational control.
2. True Pay-Per-Use for Active Workloads
Billing applies only to Autonomous AI Databases while they are running. When a database is stopped, compute charges stop as well. This model aligns costs directly with active business workload rather than pre-allocated or idle capacity.
3. Self-Service Capabilities for Business Units
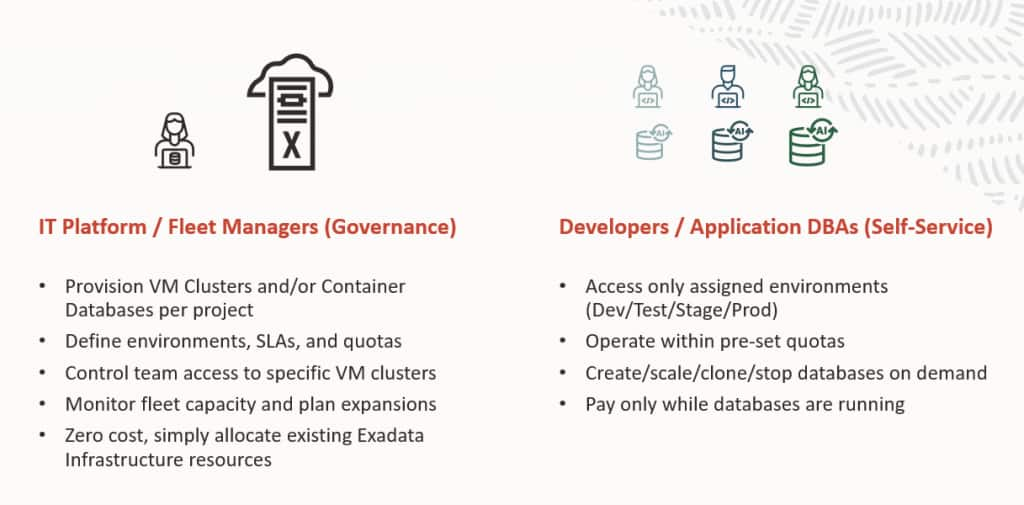
This structure enables a Private Cloud model within your organization. Central IT provisions Autonomous VM Clusters and Autonomous Container Databases and assigns quotas to control resource consumption.
Example: Defined CPU and storage quotas can be allocated to Project Team A, while separate quotas to Project Team B.
Self-Service Enablement: These teams can independently provision their own Autonomous AI Databases, perform lifecycle operations, and manage their applications, without exceeding allocated budget or impacting other tenants.
This creates an operating model very similar to Autonomous AI Database Serverless, but with the added security, isolation, and predictable performance of your own Dedicated Infrastructure.
A Clear Path to Database Modernization
Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Infrastructure represents the next evolution of the Exadata platform. It retains the strict isolation and performance required by enterprise workloads while eliminating the operational burden of database management. With the ability to run side-by-side with existing workloads and a cost-efficient consumption model, it provides a compelling and timely path to database modernization. Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated deployments are available on OCI Public Cloud, Exadata Cloud@Customer, and Oracle Database@AWS.
