SQL Property Graph (Oracle Database 23ai, Release Update 23.8)
SQL support for property graphs in Oracle Database 23ai is now widely available in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and through solutions offered in partner cloud services at Oracle Database@Azure, Oracle Database@Google Cloud, and Oracle Database@AWS (currently in preview), giving you many options to use Oracle Graph. Graphs are a native object in Oracle Database 23ai and can be created and queried using any SQL tool.
ONE ROW PER VERTEX/STEP Support for Arbitrary Path Patterns
Previously, ONE ROW PER VERTEX/STEP only worked for a path pattern containing a single quantified edge pattern. This has been enhanced to now work for path patterns containing any number of edge patterns (quantified or not).
Example
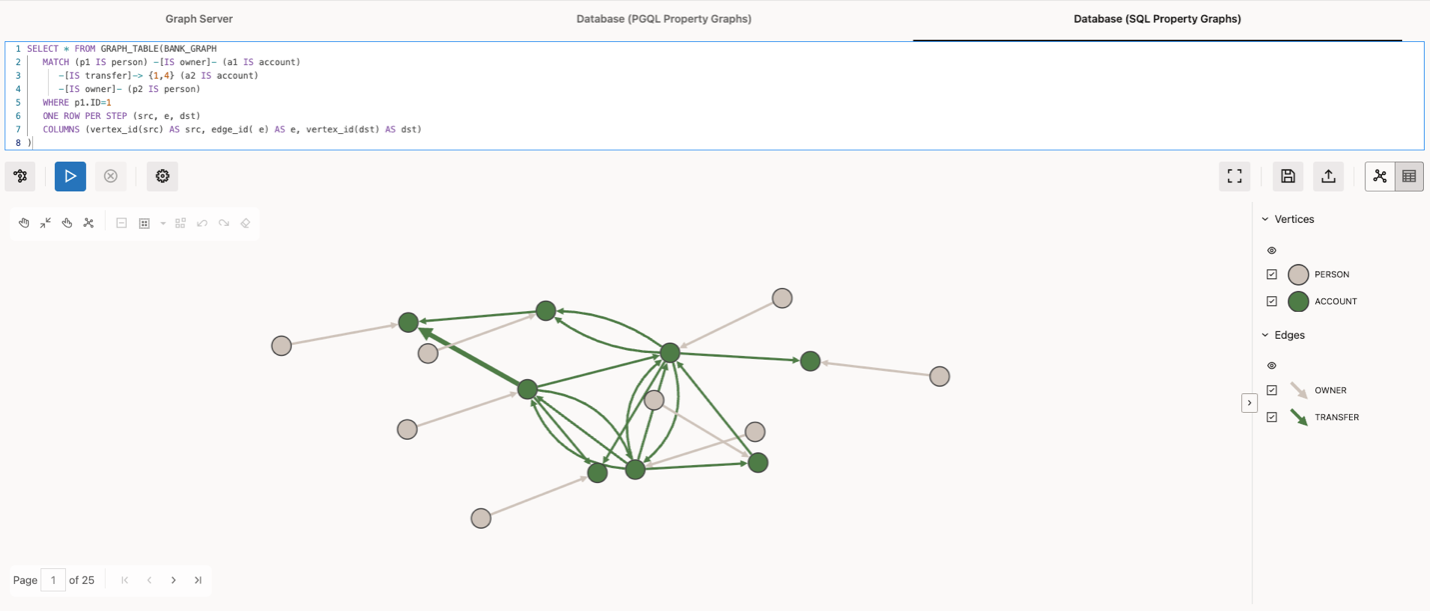
MATCH (p1 IS person) -[IS owner]- (a1 IS account) -[IS transfer]-> {1,4} (a2 IS account) -[IS owner]- (p2 IS person)
WHERE p1.ID=1 ONE ROW PER STEP (src, e, dst)
COLUMNS (vertex_id(src) AS src, edge_id( e) AS e, vertex_id(dst) AS dst)
)
Note: Currently, ONE ROW PER VERTEX/STEP only works with single path patterns
Support for MATCHNUM and ELEMENT_NUMBER Functions
MATCHNUM and ELEMENT_NUMBER functions are now supported for SQL Property Graphs, which can be useful in combination with ONE ROW PER VERTEX/STEP. MATCHNUM returns a number that uniquely identifies a match in a set of matches. ELEMENT_NUMBER returns the sequential number of the graph element that an iterator variable currently binds to.
Example
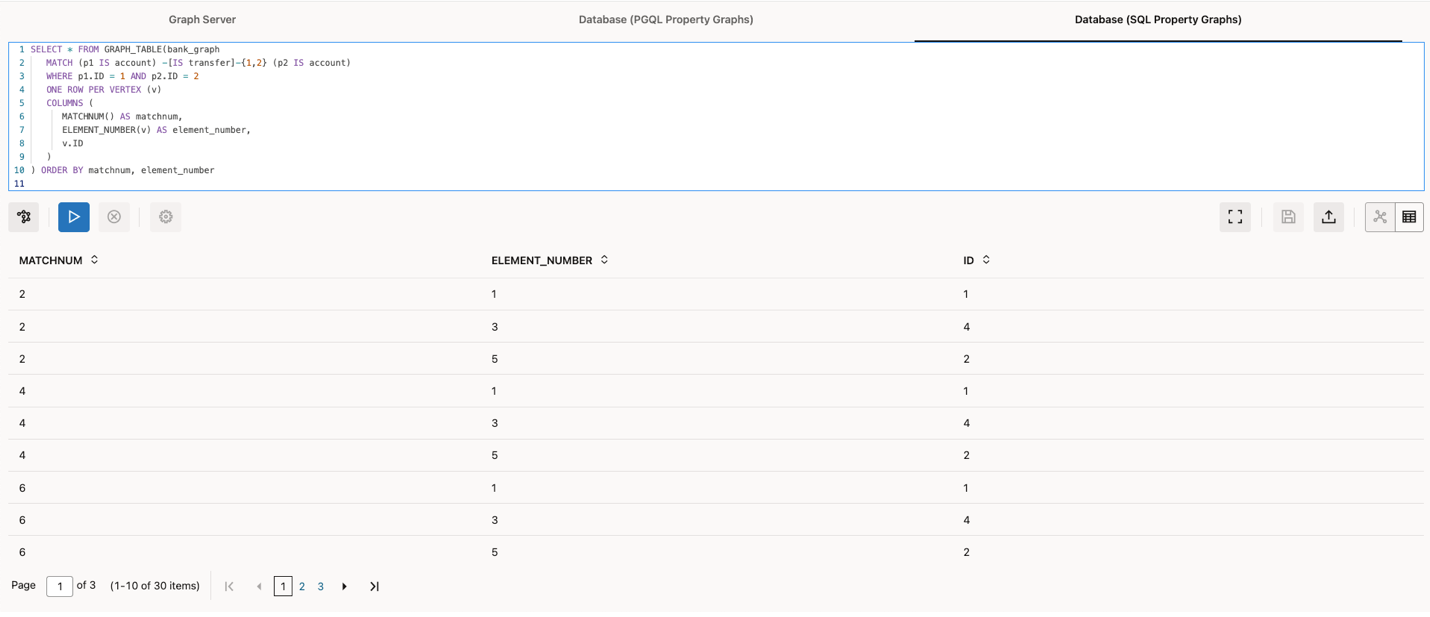
SELECT * FROM GRAPH_TABLE(bank_graph
MATCH (p1 IS account) -[IS transfer]-{1,2} (p2 IS account)
WHERE p1.ID = 1 AND p2.ID = 2
ONE ROW PER VERTEX (v)
COLUMNS (
MATCHNUM() AS matchnum,
ELEMENT_NUMBER(v) AS element_number,
v.ID
)
) ORDER BY matchnum, element_number
Graph Tools
Quickstart Container Image
This release includes the ability to launch a quickstart container image for working with graphs. This container includes Graph Server 25.2 and Oracle Database Free 23ai (23.7.0.0-lite), with PDBADMIN and GRAPHUSER preconfigured. It also includes a pre-created SQL Property Graph, named BANK_GRAPH, which models transactions between bank accounts. So, you can easily start this container image and start running graph queries.
Using this image, developers can gain hands on experience creating and querying graphs in a free standalone environment. To install the image, run the following command:
Podman run –name oraclegraph -p 7007:7007 -d \
container-registry.oracle.com/database/graph-quickstart:latest
Graph Server and Client Tools
Geographical Layout
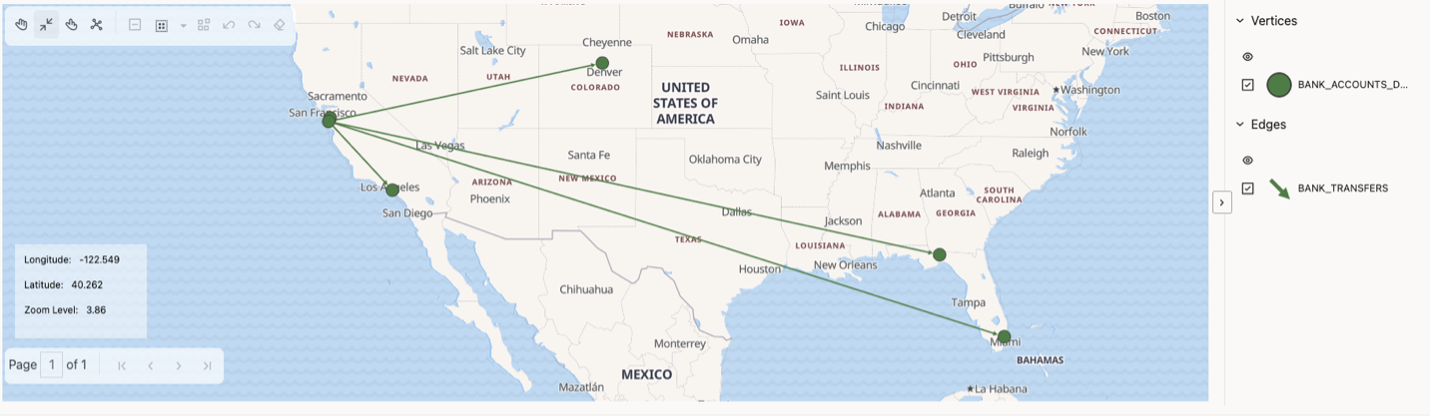
This release includes support for geographical layout with the ability to choose properties to use for placement.
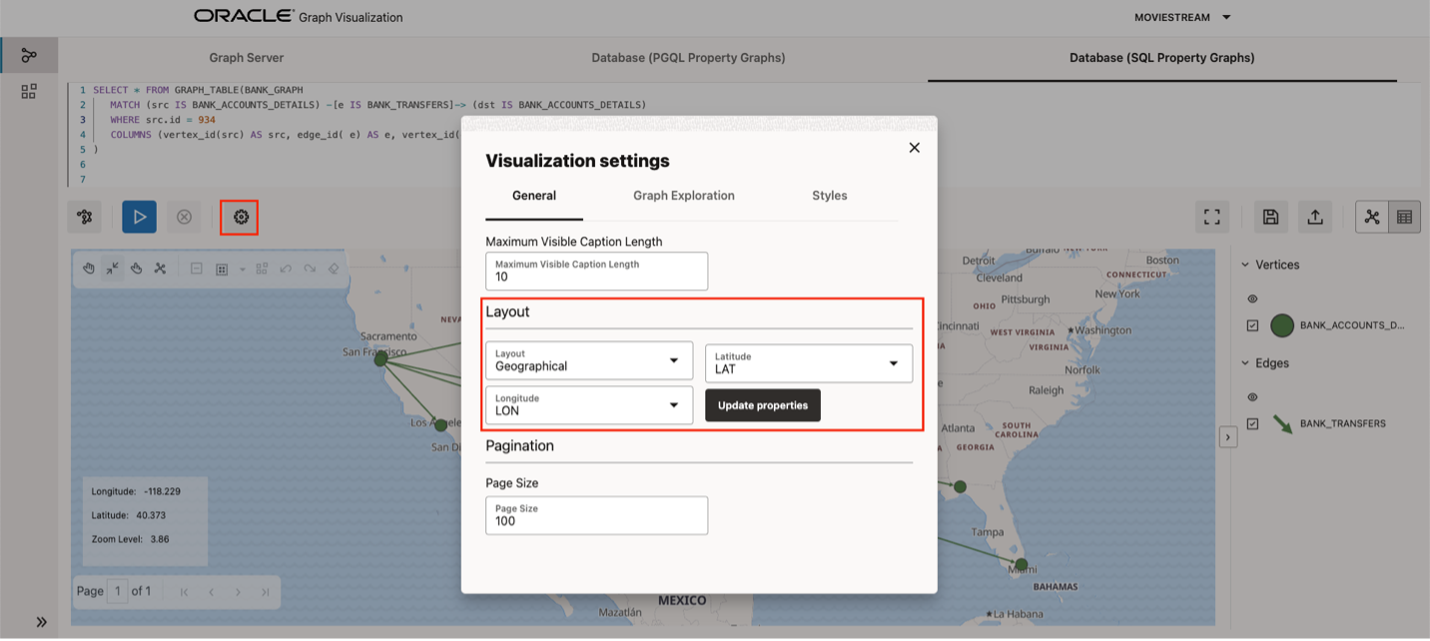
This allows developers to choose which properties they want to use to position the nodes on a map in the form of latitude and longitude coordinates. The graph will then render on a dynamic map of the globe to easily visualize the geospatial coordinates and their relationship in the graph.
Enhanced Styles for Multiple Conditions
In previous version of the graph visualization applications, multiple styles couple only be applied in a Match All context, meaning all conditions must be true for a style to be applied. This release includes support for Match All and Match Any, so when developers add multiple conditions, they will have the option to select Match All or Match Any.
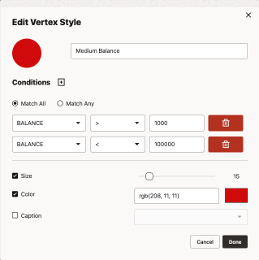
Match All is aligned with previous support for multiple conditions, meaning all conditions must be true for the style to be applied. For example, the style created in the image below will find all vertices where the balance is greater than 1000 and the balance is less than 100,000.
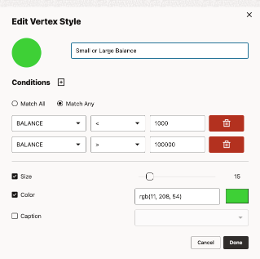
Match Any allows any condition to be true for the style to be applied. For example, the style created in the image below will find all vertices where the balance is less than 1000 or the balance is greater than 100,000.
Graph Server
Loading a SQL Property Graph with Composite Keys into Graph Server Memory
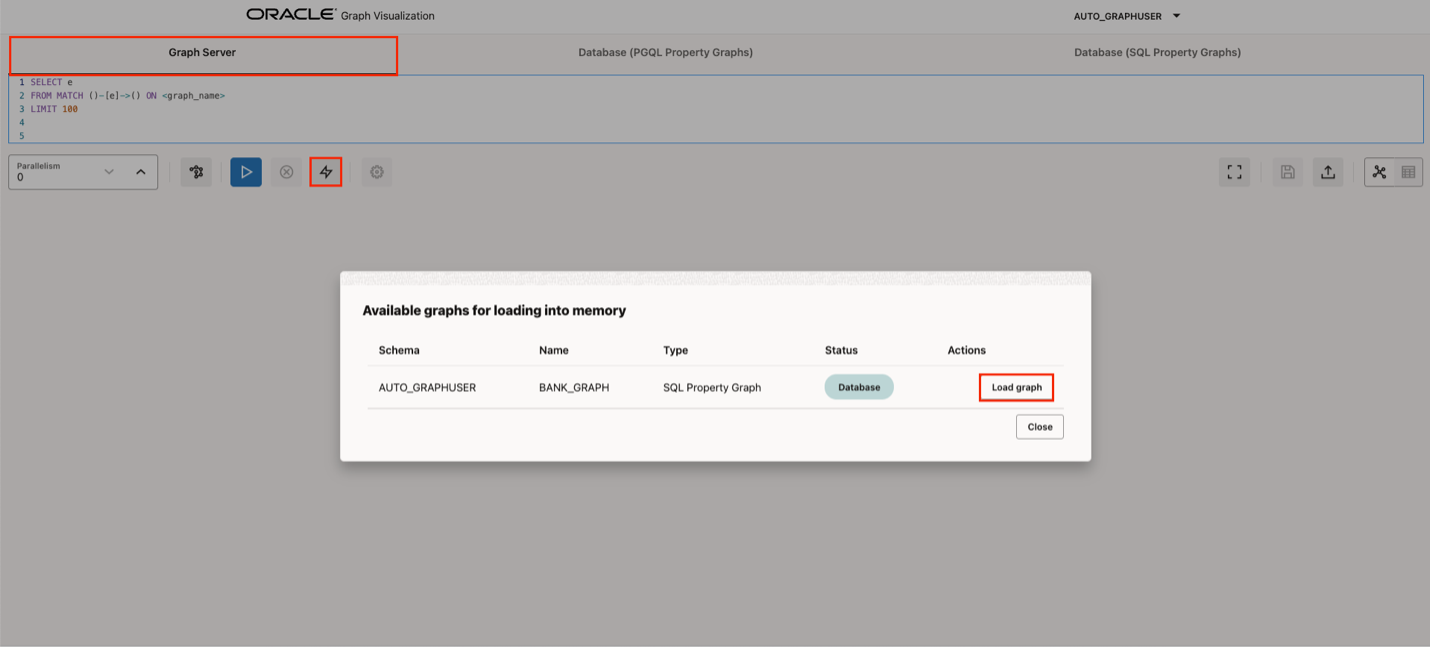
Previously, Graph Server supported loading graphs with composite keys on edge tables only, and supported only keys of type int, long or string. This release includes support for loading a SQL Graph into Graph Server memory when there are composite keys on vertex and/or edge tables, and also supports keys of any SQL Graph key type.
This allows developers more flexibility in how they model their graph, when they need to run graph algorithms in Graph Server. For existing users, there are no changes required in their application to support graphs created from tables with composite keys. Developers can still load their graph into memory using the session.readGraphByName(“GRAPH_NAME”, PG_SQL) function in Python, the session.readGraphByName(“GRAPH_NAME”, GraphSource.PG_SQL); function in Java, or by loading the graph directly through the UI.
Note: Flashback Synchronizer, Expand APIs and subgraph queries with composite keys in the WHERE clause are not currently supported.
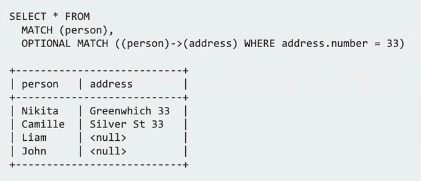
Support for OPTIONAL MATCH in Graph Server
Graph Server now supports OPTIONAL MATCH. This enabled developers to search for connections that may or may not exist. If they do exist, the values queried will be returned, otherwise they will return null. This can be extremely useful for scenarios where a path exists for some vertices but not for all. Using this syntax, developers will still be returned a result set using OPTIONAL MATCH, where as the result set would be empty without it.
Example:
SELECT * FROM SOCIAL_GRAPH
MATCH (person),
OPTIONAL MATCH ((person)->(address) WHERE address.number = 33)
Other Notable Updates
- Graph Studio: Added –skip-if-exists flag to the conda interpreter.
- Checks if the environment already exists locally and only downloads if not.
- Graph Visualization App
- Added ability to change label caption size.
- Renamed caption legend entries for captions.
- Now shows the label and property the caption is applied to.
- Restore to Defaults button – removes any custom styles and resets to the default visualization settings.
For more information, please visit our Property Graph documentation and RDF Graph documentation.
