The Spatial features included in Oracle Autonomous Database allwo you to incorporate location intelligence into business processes and applications. Location is a key attribute in a dataset, and virtually all business data contains location information since everything happens somewhere.
We can easily incorporate location and location relationships into business operations, answering questions such as:
- Do we have assets located in a flood zone?
- Where are our nearest competitors?
- Are health services located where they are needed the most?
Historically many organizations have managed geospatial data with specialized proprietary data structures, outside of their central enterprise data stores and accessible only through a special toolset. With Oracle Autonomous Database, geospatial data like geocoded addresses and regions are first class data elements and can be accessed with standard SQL to perform native spatial operations such as proximity search and distance calculations.
Oracle Autonomous Database tools provide low code data preparation and application development that supports natively managed geospatial data. The ecosystem of specialized software (i.e., GIS software and developer toolkits) supports Oracle’s spatial platform so you have the flexibility to mix and match other tools to best fit your organization’s needs. By maintaining geospatial data natively in Oracle Autonomous Database, a wide array of analytics and data warehousing, transaction processing, and mixed workload use cases are enabled, and efficiencies are gained while preserving existing investments in other tools and development.
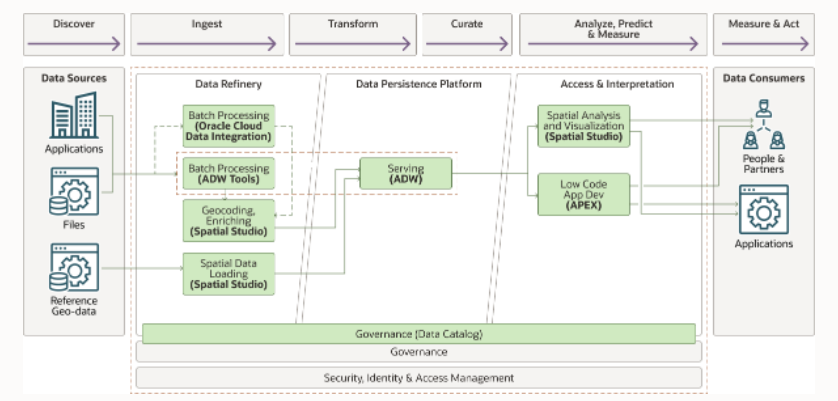
Fig1: Illustration showing the functional layers of the reference arcitecture to build a geospatial platform
This reference architecture uses Oracle Autonomous Database for analytics and warehousing where the location components of business data like place names, addresses, co-ordinates, and so on are converted to a native spatial data type and combined with geospatial reference data to enable location-based insights. The architecture also includes Oracle Spatial Studio and Oracle Application Express (APEX), both no-cost features of Oracle Autonomous Database, for low-code spatial data preparation, analysis, visualization, and application development. The architecture focuses on logical divisions like data refinery, data curation, access, and integration.
The reference architecture has step-by-step deployment guidance using Terraform code in GitHub, and deploys the sample stack in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Resource Manager.
Learn more…
- Reference architecture: Build a geospatial platform on Oracle Autonomous Database
- Geospatial 101: What is a geospatial database?
- Workshop: Get started on using Oracle Spatial Studio
