Oracle Database@AWS is a strategic partnership between Oracle and AWS that enables applications running in Amazon Web Services (AWS) Regions to use Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure and Oracle Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure running on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) in AWS. With Oracle Database@AWS, you can simplify management and operations with streamlined purchasing through the AWS Marketplace using existing AWS commitments. AWS applications deployed on EC2 and services such as Amazon Redshift, Glue, Athena and more can now have low-latency, native access to Oracle databases running on Exadata Cloud Infrastructure and take advantage of Oracle Database 23ai features like AI Vector Search. Tight integration between the AWS Management Console and OCI lets you get started faster and with the fully managed Autonomous Database.
Benefits of Autonomous AI Database:
Autonomous AI Database is a fully managed Oracle Database experience with service automation that makes it simple and cost effective to build database applications, whether those applications are non-critical or super critical in nature.
Autonomous AI Database embodies the automation of all Oracle Database best practices to provide an always online, high performance, secure and cost-effective solution through innovative pay-per-use automation. With the fully managed Autonomous AI Database, you delegate the health and availability of not just the hardware and virtualization, but the database itself to Oracle eliminating DBA repetitive administrative tasks.
Autonomous AI Database makes it simple to deal with transactions and analytics in a single solution while transparently handling traditionally hard architectural and operational challenges like availability, scalability, extreme Performance and security.
You can use Oracle Zero Downtime Migration (Oracle ZDM) to migrate Oracle databases to Oracle Database@AWS and leverage full compatibility with Oracle Database and Exadata – including Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC). In addition to running production workloads, developers can also build new cloud native applications using industry-leading generative AI capabilities included with Amazon Q, Amazon Bedrock foundation models, and Oracle AI Database 26ai.
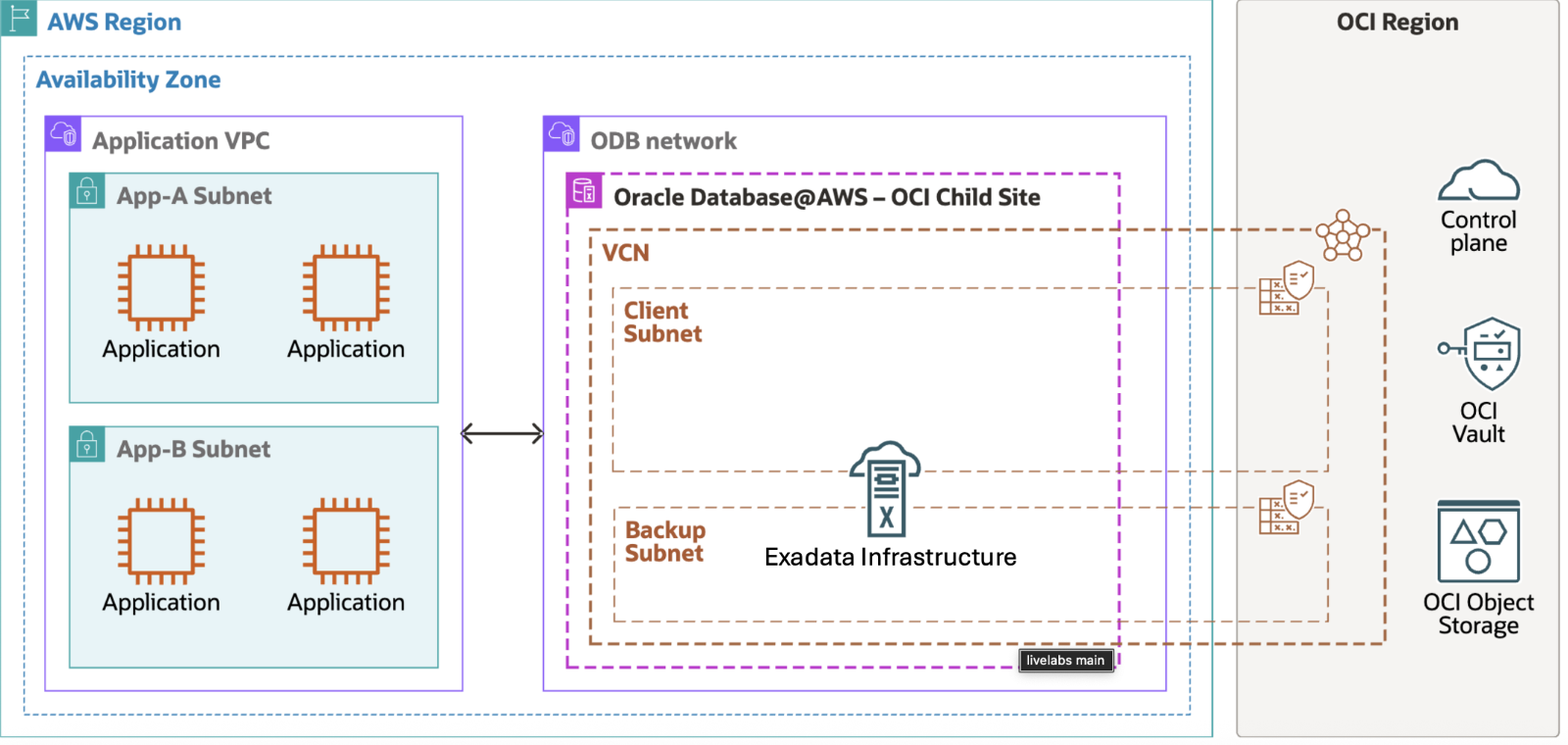
Architecture and set up for Oracle Database@AWS:
Using a Private Offer on AWS Marketplace, your journey to Oracle Database@AWS is activated with an Oracle Database@AWS subscription configured from an AWS account where you can provision resources to a new or existing OCI tenancy.
Native AWS automation makes it’s easy to start running Autonomous AI Database in Oracle Database@AWS with the following five steps:
Infrastructure Admin Provisioning Steps:
- Create the ODB network
- Create the Exadata Infrastructure
- Create an Autonomous VM Cluster in the Exadata Infrastructure
- Create an Autonomous Container Database in the Autonomous VM Cluster
Developer, Application DBA Step:
5. Create an Autonomous AI Database in the Autonomous Container Database
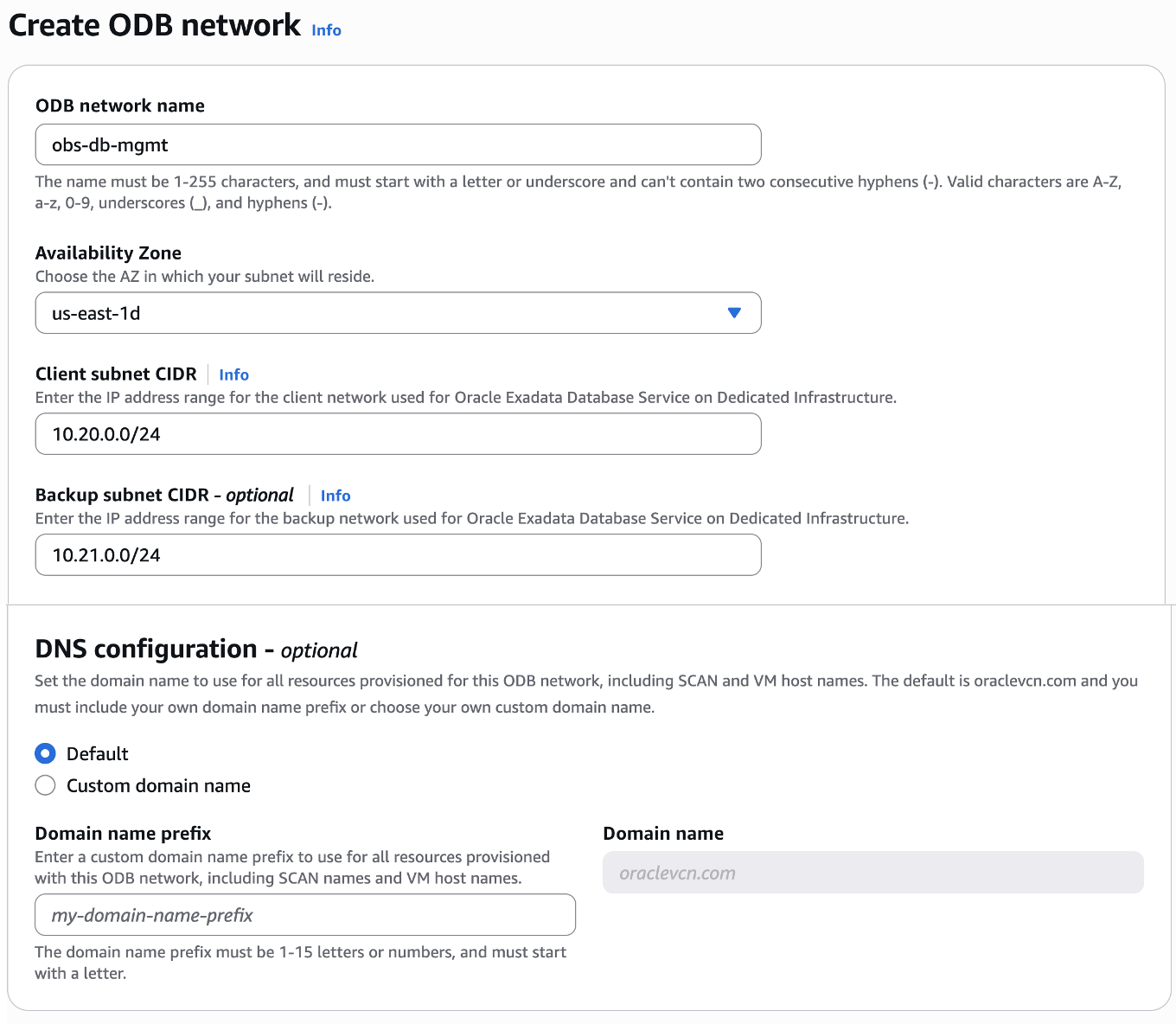
Step 1 – Create the ODB network
An ODB network is a private isolated VPC network that hosts OCI infrastructure in an AWS Availability Zone (AZ) – an OCI child site. The ODB network consists of a CIDR range of IP addresses that will identify VM Cluster nodes where databases are hosted, and a few reserved IPs for service management. The ODB network peers directly to the service network that exists within the OCI child site and application specific VPCs, thus serving as the means of communication between AWS and OCI. Separately, the service allows you to select and peer a VPC where your applications are running, thus providing a network path for your applications to connect with the Oracle Databases. The Backup subnet is not required for the Autonomous AI Database service as backups are completely managed by service automation.
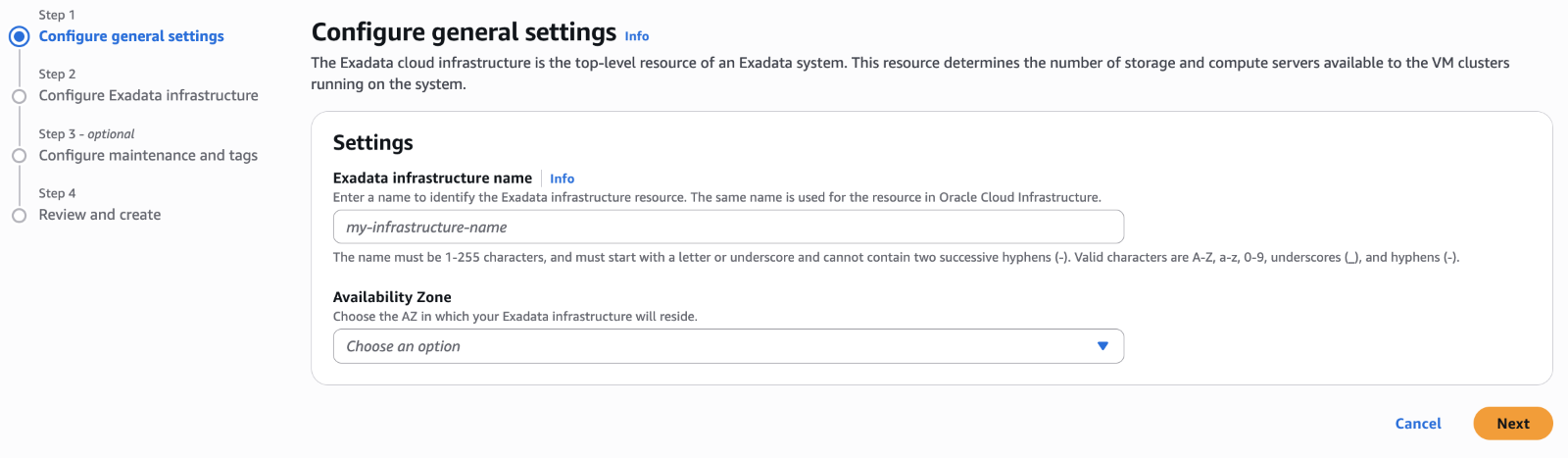
Step 2 – Create Exadata Infrastructure
Autonomous AI Database collocated in AWS supports Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure with a minimum configuration of 2 database and 3 storage servers that are internally connected by a high-speed, low-latency internal Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) network fabric that requires no configuration. Additional database and/or storage servers can be added online as needed to scale up the physical infrastructure compute and storage. Exadata Infrastructure within an AWS data center integrates the hardware with the networking resources needed to securely connect to other services in the cloud. With Oracle Database@AWS, Oracle automation fully manages the infrastructure though customers have scheduling control for monthly OS security and quarterly Exadata software maintenance. A dedicated Exadata Infrastructure subscription has a nominal cost that not only secures the hardware reservation, but provides access to the storage and memory on the respective servers. The services you run on the infrastructure reservation are then paid for in a pay-per-use model based on the type of service deployed.
From the Oracle Database@AWS left side main menu, select Exadata Infrastructure and then click the Create Exadata Infrastructure button to launch the configuration workflow.
Step 3 – Create an Autonomous VM Cluster
After you create your Exadata Infrastructure, you are ready to create VM Clusters and Oracle Database@AWS allows to create both Non-Autonomous and Autonomous VM Clusters (AVMC) on a single infrastructure. You can create multiple AVMCs to provide isolation for the Oracle Database workloads you consolidate on the Exadata Infrastructure. Creation of an AVMC does not result in any billing, so these can be pre-created for different purposes without cost. When you create an AVMC, you specify the subset of database servers from your Exadata Infrastructure where the cluster will run, the compute, memory, database storage allocations, expected Autonomous Container count that will run in the AVMC, and the ODB network to provide access to your AVMC and databases. To create your first AVMC, select Autonomous VM Cluster on the left side main menu, and then click the Create Autonomous VM Cluster button to launch the configuration workflow.
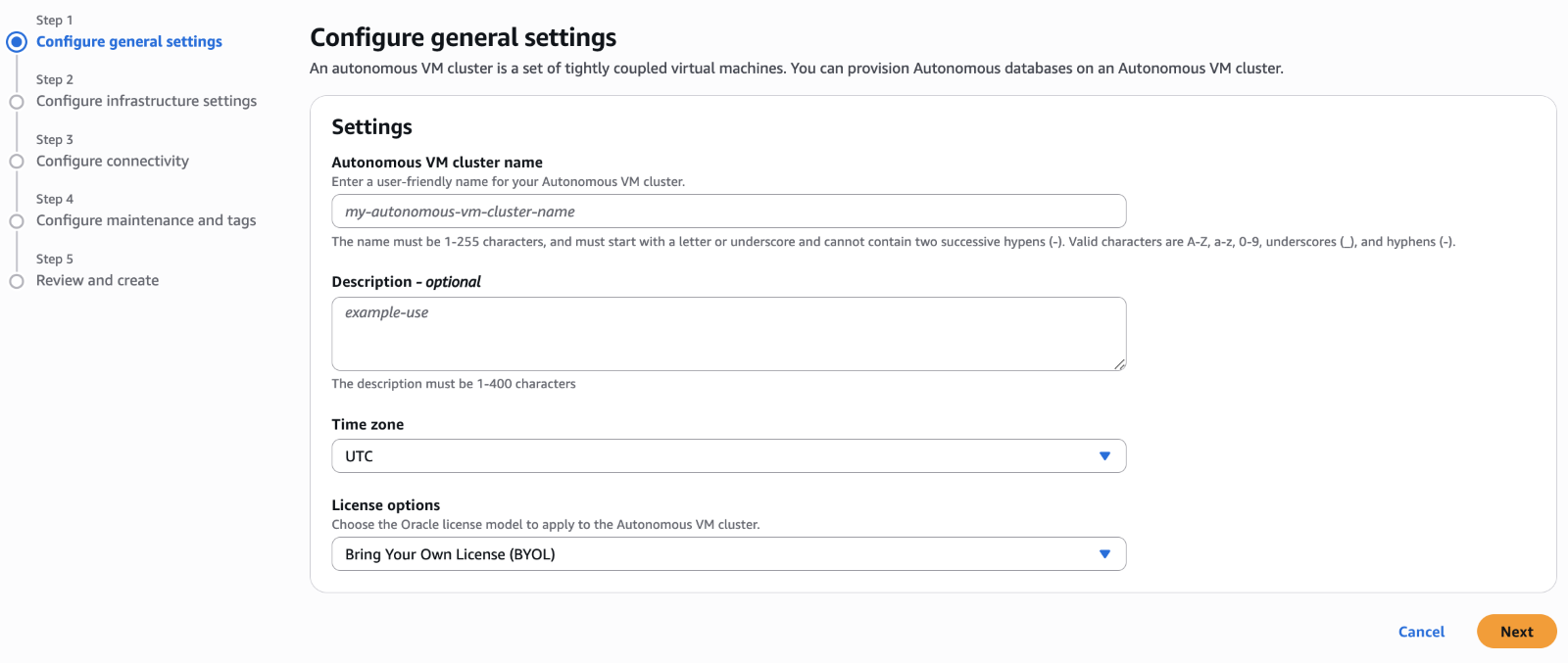
Step 4 – Create an Autonomous Container Database
After you create your Autonomous VM Cluster, you are ready to create an Autonomous Container Database (ACD). You can create multiple ACDs to provide isolation for Oracle Databases requiring different software versions, maintenance schedules and high availability configurations. To create an ACD, you must navigate (by clicking the AVMC resource hyperlink) to the details page of the desired Autonomous VM Cluster and then click the ‘Manage in OCI’ deep link, which takes you to the Autonomous AI Database service in OCI where advanced operations can be performed.
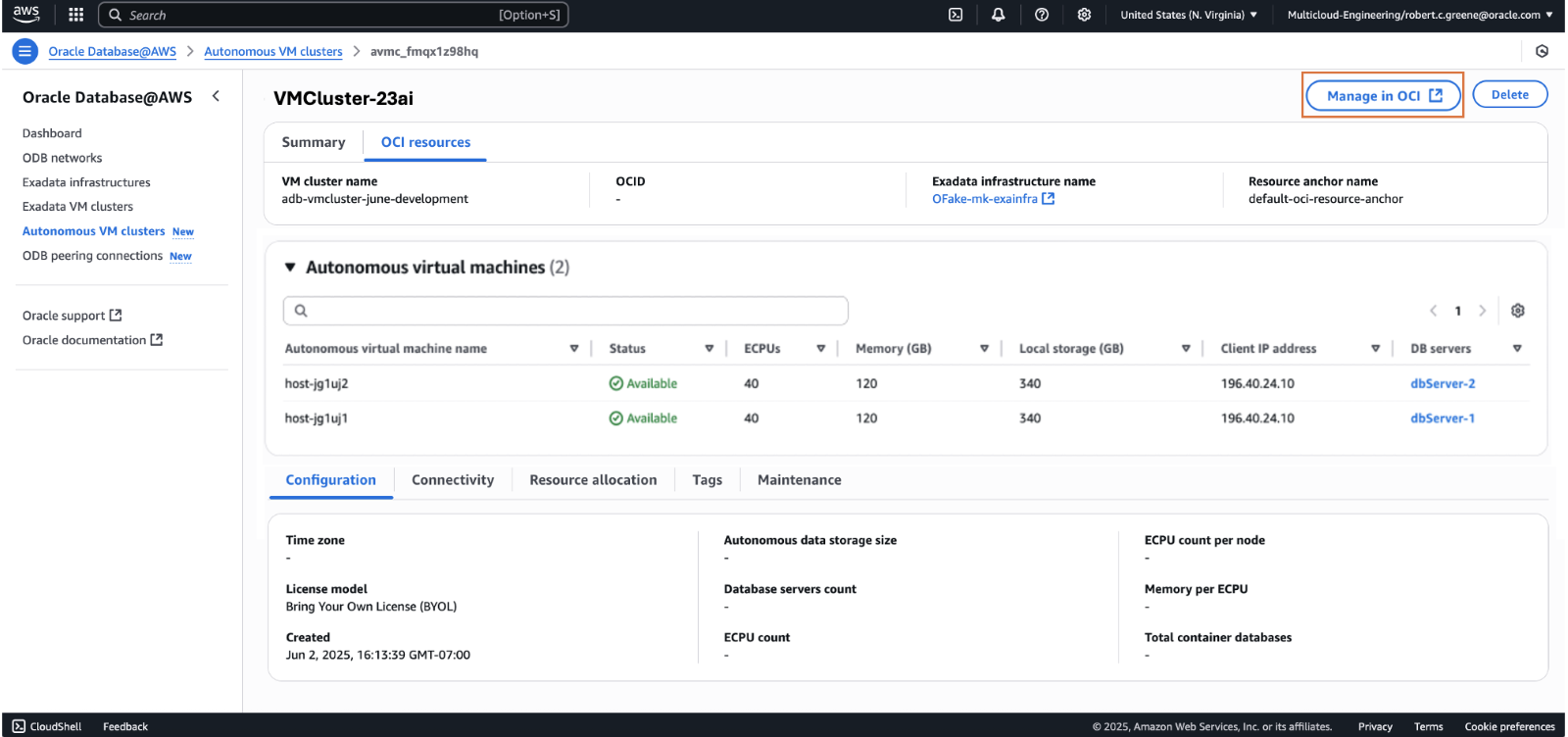
When you land on the Autonomous VM Cluster details page, select the Autonomous Container Database (ACD) tab and then click on Create Autonomous Container Database.
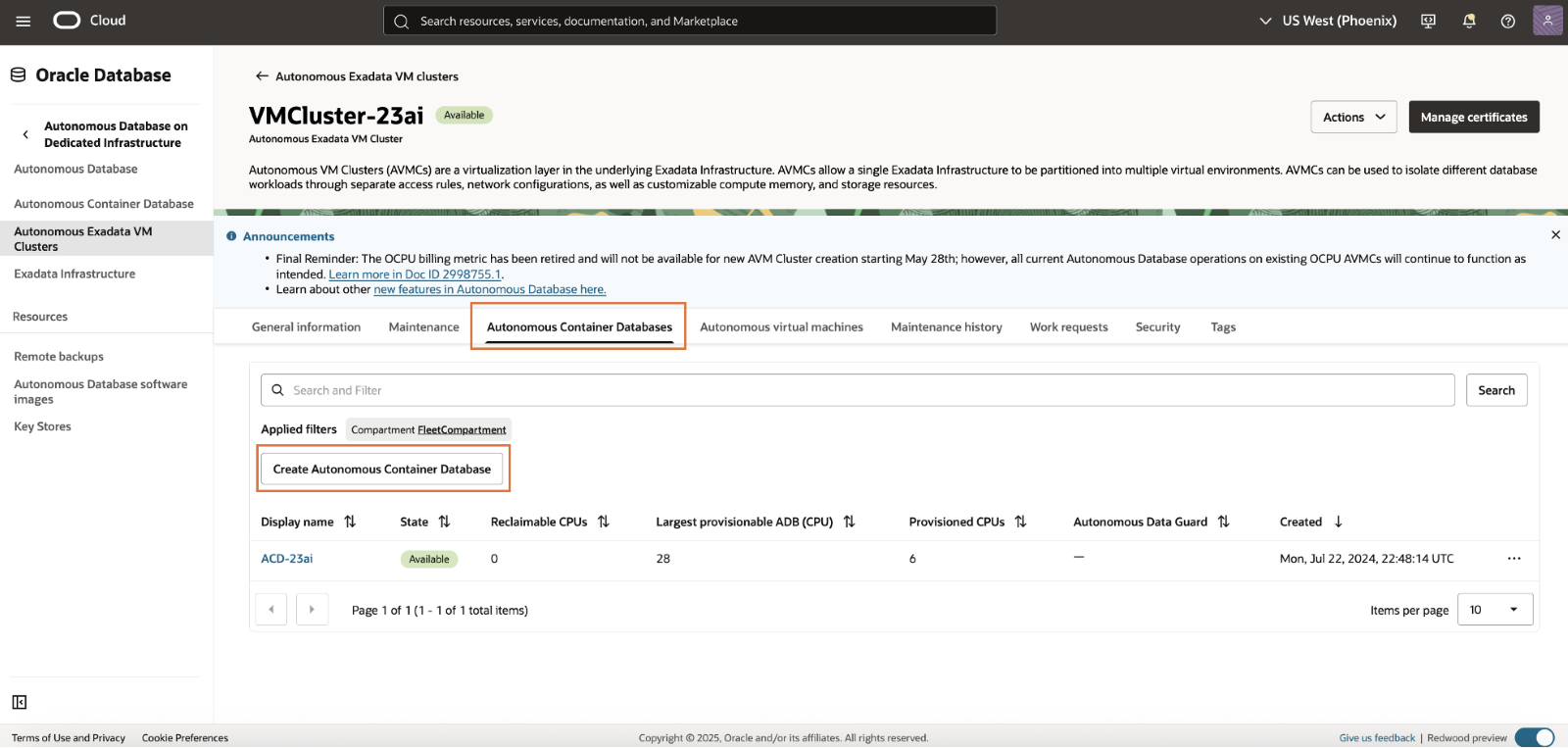
When creating the Autonomous Container Database (ACD), you have the ability to select a 19c or 26ai based image. The ACD can fully delegate all maintenance decisions to Oracle automation or can declare patterns like skipping every other quarter and always applying a version that has been previously validated in a stage environment. Like the AVMC, the ACD does not incur any billing costs and will dynamically grow as Autonomous AI Databases are added to or scaled within the container. The ACD is where you configure backup retention policies, encryption key strategy, HA and DR architecture and apply advanced database clustering controls. The default backup location is set to AWS S3, but you can change it if desired.
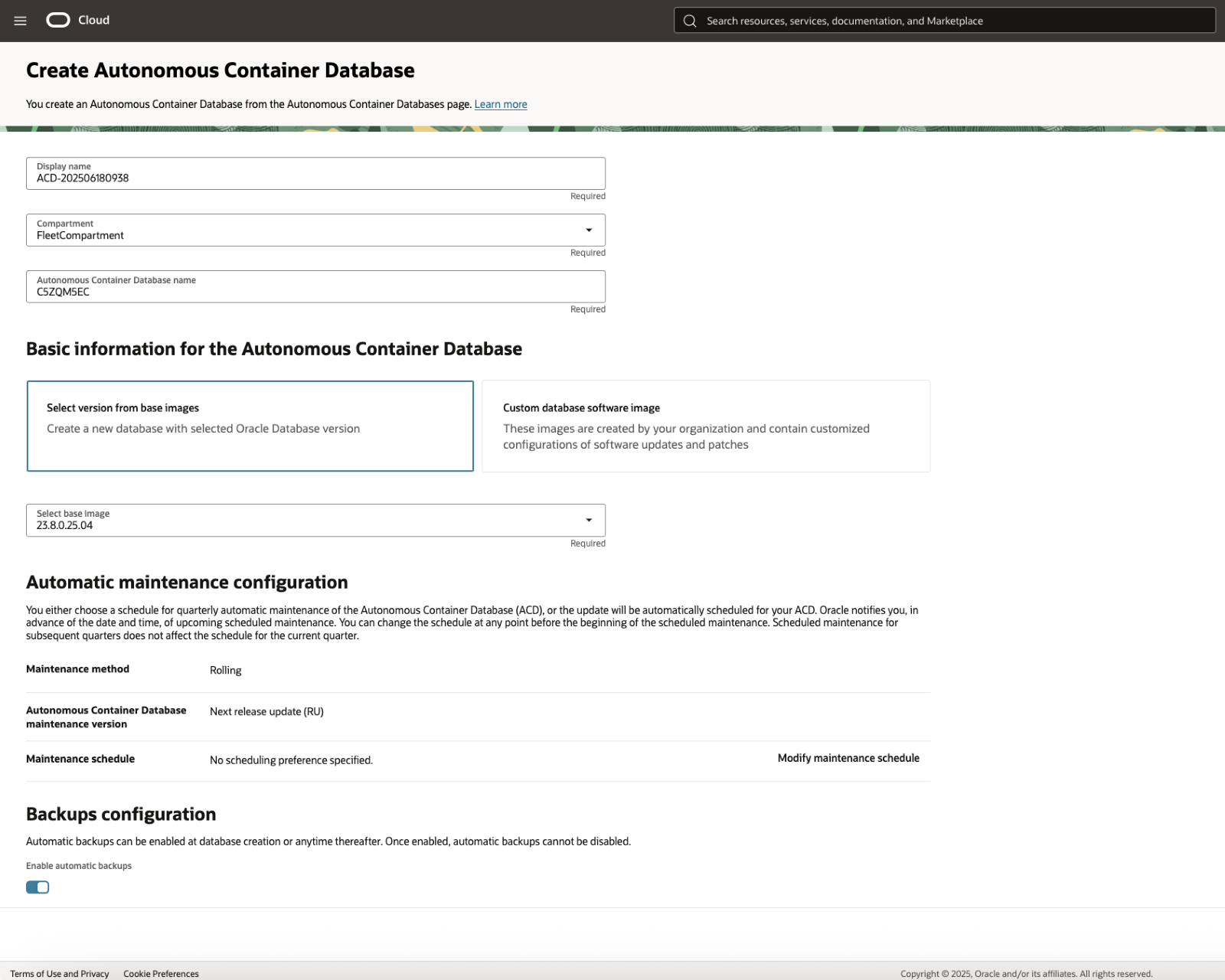
Step 5 – Create and Manage an Autonomous AI Database
To create your first Oracle Autonomous AI Database, navigate to your Autonomous Container Database details page and click on the Autonomous AI Database tab, then click on the Create Autonomous AI Database button.
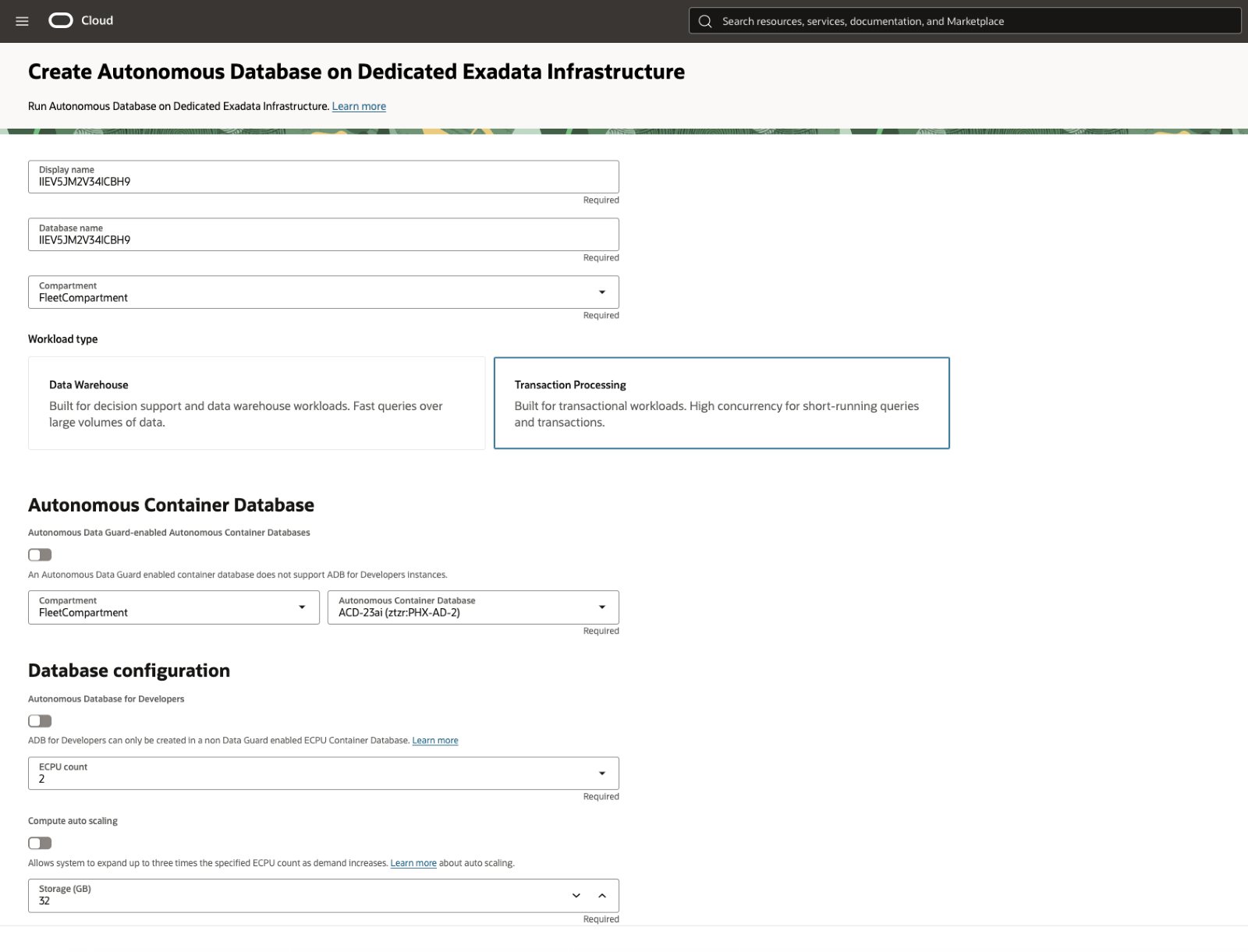
When creating an Autonomous AI Database, you can choose the type of workload as Lakehouse or Transaction Processing (mixed workloads), and the Autonomous AI Database will automatically set the optimal underlying Oracle configuration. There is an option to create Developer Database instances, which are completely free of charge, but have sizing and availability restrictions. It is highly recommended that you select Compute Auto-Scaling as this provides the best performance when workloads spike but lowest cost for steady state workload. Set the amount of initial database storage and other advanced options. Set your administrator credentials and click Create. You can learn more about the advanced features of the Autonomous AI Database by using the provided documentation links below.
Migrate an Oracle Database
Once your Oracle Autonomous AI Database is created, Oracle ZDM can be used to migrate your data from an existing Oracle Database in either an offline or online manner. Details on how to migrate to Autonomous AI Database can be found in the ZDM Live Lab.
Summary
With Oracle Database@AWS, your organization can now run mission-critical Oracle Database applications in AWS while fully delegating management tasks to Oracle Autonomous AI Database. You can easily migrate Oracle databases to the service running within AWS with minimal changes while maintaining full feature and architecture compatibility, performance, and availability you’ve come to expect from the Oracle Database. With this new deployment option for Oracle Database, you can now easily combine applications and services running in AWS with the advantages of Oracle Autonomous AI Database.
For more information:
Documentation to deploy Oracle Database@AWS
Learn about network topologies for Oracle Database@AWS
Tutorial: Provision Oracle Autonomous AI Database in Oracle Database@AWS
Oracle Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure Documentation
Zero Downtime Migration (ZDM) Logical Migration to Autonomous AI Database
