SQL Property Graph (Oracle Database 23ai, Release Update 23.7)
SQL support for property graphs in Oracle Database 23ai is now widely available in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and through solutions offered in partner cloud services at Oracle Database@Azure, Oracle Database@Google Cloud, and Oracle Database@AWS (currently in preview), giving you many options to use Oracle Graph. Graphs are a native object in Oracle Database 23ai and can be created and queried using any SQL tool.
New ONE ROW PER Clause
The newest version of Oracle Database 23ai (23.7) includes a new ROWS clause which can be used inside the GRAPH_TABLE operator for SQL Property Graph queries. This new clause can be placed directly before the COLUMNS clause to unnest/flatten path data. This syntax comes in three variations:
1. ONE ROW PER MATCH – produces one row in the result set per match returned by the MATCH clause
2. ONE ROW PER VERTEX(v) – produces row in the result set per vertex, specified by the vertex variable (in this case v)
3. ONE ROW PER STEP(v1, e, v2) – produces one row in the result set per vertex-edge-vertex triple, specified by the vertex and edge variables (in this case v1, e and v2)
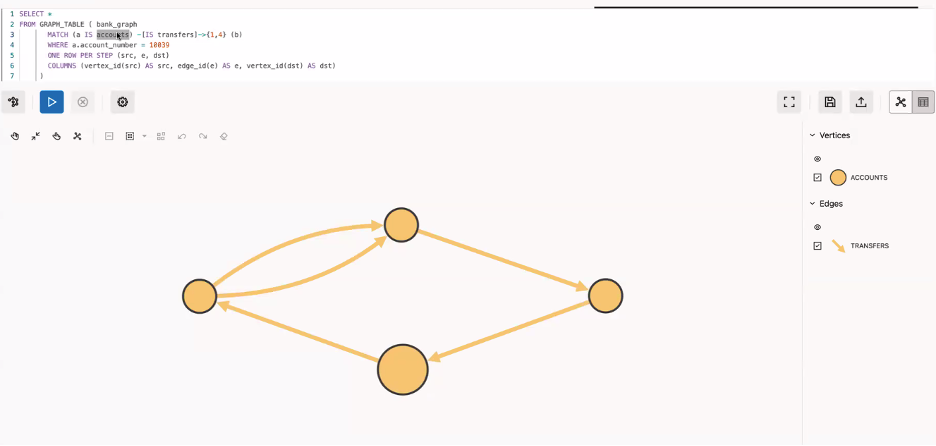
For example, we can use ONE ROW PER STEP to visualize the results of variable length paths.
FROM GRAPH_TABLE( bank_graph
MATCH (a IS ACCOUNTS) -[IS TRANSFERS]->{1,4}(a)
WHERE a.account_id = 10039
ONE ROW PER STEP (src, e, dst)
COLUMNS(vertex_id(src) as src, edge_id(e) as e, vertex(dst) as dst)
)
Note: If you use ONE ROW PER clause in a SQL graph query for graph visualization, then ensure that the underlying SQL property graph definition does not contain any vertex or edge table alias (AS clause).
Support for Vector Distance Functions and User Defined Functions Inside Aggregates
this release of Oracle Database 23ai (23.7) includes support for vector distance functions and user defined functions inside aggregates. This means you can use these functions and aggregates in the COLUMNS clause of your graph queries, creating a simpler and more flexible query writing experience for developers and DBAs. In these two examples, we are able to use aggregates with vector distance and user defined functions in a SQL graph query:
MATCH (a) ((x)-[e]-(y)){1,2} (b)
COLUMNS(LISTAGG(MY_FXN(x.name), ‘-‘) as l1));
MATCH (a) ((x)-[e]-(y)){1,2} (b)
COLUMNS(SUM(COSINE_DISTANCE(x.col, y.col)) AS m1);
Graph Tools
Graph Server is used to run graph algorithms, and client libraries are used for visualization and as plugins for development tools.
- Graph Studio in Autonomous Database Serverless integrates these components and makes them available when an Autonomous Database instance is provisioned. This simplifies setup and management so that developers can get started using graph features in minutes.
- Graph Server and Client packages these components as a separate download for use with other Oracle Database deployments. Every release of Graph Server and Client includes an OCI Marketplace image for easy deployment with Oracle Database in Oracle Cloud. Graph Server and Client supports Oracle Database 23ai and Oracle Database 19c, and is released quarterly. The latest release of Graph Server and Client is 25.1.
Graph Studio and Graph Server and Client include several updates described below.
Graph Studio (Autonomous Database Serveless only)
The latest version of Graph Studio includes a visual edge creation tool integrated into the graph modeler, to enhance the graph modeling experience. Using this tool, you can easily add an edge between your selected tables using a simple graph schema based user interface.
Graph Server and Client Tools
Import/Export Settings
This release includes the ability to export and import settings for graph visualization using the graph visualization tool that is included with Graph Server. This enables you to keep your custom styling for future use, across multiple sessions and to share your settings with other users, making graph visualisations repeatable and peristant. These settings will be backwards compatible with future releases, so the settings from this release (25.1) can be imported in future releases (25.2+).
Quicksetup Script
To improve ease of setup for Graph Server, a new script, quicksetup.sh, has been added to /opt/oracle/graph/scripts. This script can easily be run to simplify configuration tasks, such as configuring the JDBC URL and disabling/enabling TLS.

Updated Graph Visualization Library (GVT) Settings
Previously, visualization settings for the Graph Visualization JavaScript Library and APEX plugin could be applied using styles or settings.filters. The new updates to the GVT library unifies this experience by replacing settngs.filters with settings.ruleBasedStyles and replacing styles with settings.baseStyles. Rule based styles support conditions and create legends, while base styles sets the default visualizations settings for nodes and edges. So, when there is no rule based styles that apply to a set of nodes or edges, the default base style will apply. This unification simplifies the development experience by clearly defining when styles should apply and override the base styles.
The previous settings APIs (styles and settings.filters) are still supported, so there is no impact to previous application use, but these APIs are now deprecated.
Other Notable Updates
- A new API to track the progress of algorithm execution
- The GraphBuilder API in Graph Server now supports creation of the default graph model (partitioned graphs)
- New Graph Server API adds support for Single Source and Desitnation Bellman Ford Algorithm
- The earlier homogeneous graph model used in Graph Server is now deprecated
For more information, please visit our Property Graph documentation and RDF Graph documentation.
