The graph features of Oracle Database enables developers to store and navigate relationships between entities. In the past these updates have focused Oracle Graph Server and Client, in this blog post we change the structure so that we present updates from all the ways we release Oracle Graph features.
SQL Property Graph (Oracle Database 23ai, Release Update 23.6)
SQL support for property graphs in Oracle Database 23ai is now widely available in Oracle Cloud and in partner cloud services Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services, giving you many options to use Oracle Graph. Graphs are a native object in Oracle Database 23ai and can be created and queried using any SQL tool.
The newest version of Oracle Database 23ai (23.6) includes a new aggregate which can be used inside the GRAPH_TABLE clause for SQL Property Graph queries. This new syntax is BINDING_COUNT, which can count the number of bindings to an element variable.
For example, the third column returned from the GRAPH_TABLE below will return path_length values 1, 2 and 3.
SELECT * FROM GRAPH_TABLE ( g
MATCH (a) -[e]->{1,3}(b)
COLUMNS (a.id AS a_id, b.id AS b_id, BINDING_COUNT(e) AS path_length)
)
Note: this is equivalent to, but more direct than COUNT(EDGE_ID(e)) AS path_length.
Graph Server and Graph Client Tools
Graph Server is used to run graph algorithms, and client libraries are used for visualization and as plugins for development tools.
- Graph Studio in Autonomous Database Serverless integrates these components and makes them available when an Autonomous Database instance is provisioned. This simplifies setup and management so that developers can get started using graph features in minutes. Graph Studio now includes comprehensive support for SQL property graphs.
- Graph Server and Client packages these components as a separate download for use with other database deployments. Every release of Graph Server and Client includes an OCI Marketplace image for easy deployment with databases in Oracle Cloud. Graph Server and Client supports Oracle Database 23ai and Oracle Database 19c, and is released quarterly. The latest release of Graph Server and Client is 24.4.
Graph Studio and Graph Server and Client include several updates described below.
Network Evolution in Graph Dashboard
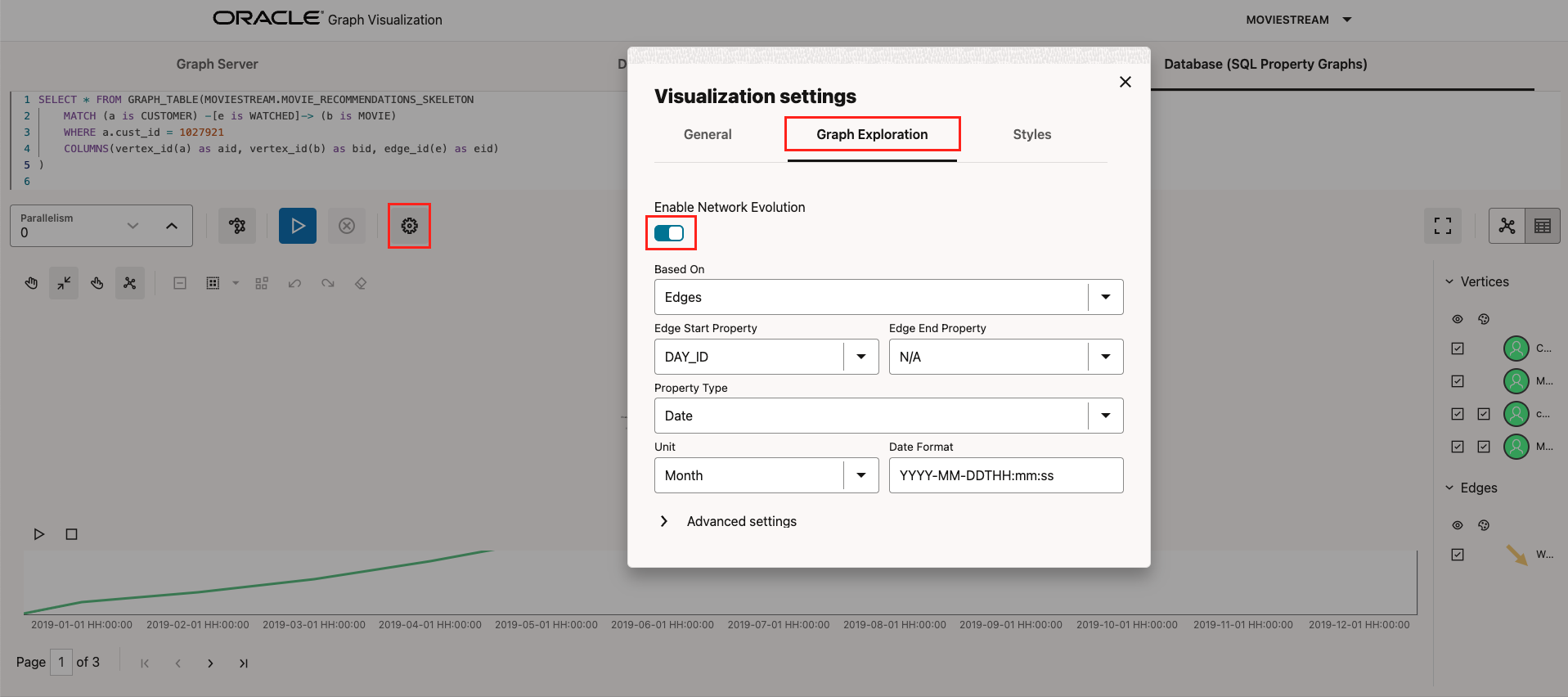
This release includes support for network evolution in the graph visualization application, which comes as a part of the Graph Server download. Network evolution allows you to visualize how your graphs change over time, or by sequence. This feature can help you track changes in your graph, identify trends, and understand relationships as they evolve, providing deeper insights into the development of your data over time.
To use this feature, select visualization settings, Graph Exploration, and then Enable Network Evolution. Provide the vertex or edge property you want to use and select the data type as integer or date.
PGQL Property Graph Update
When creating PGQL property graphs in the database source/destination keys can now reference any columns of the vertex table. This feature adds additional flexibility to graph modeling so you can easily reference columns other than the primary key of the vertex table as a source or destination key for the edge.
Example
CREATE PROPERTY GRAPH LIVES_IN_GRAPH
VERTEX TABLES (
PERSON
KEY (pid)
PROPERTIES(name, address, state, zip),
TOWN
KEY(tid)
PROPERTIES(name, state, zip)
)
EDGE TABLES (
PERSON AS LIVES_IN
KEY(pid)
SOURCE KEY(pid) REFERENCES PERSON (pid)
DESTINATION KEY(state,zip) REFERENCES TOWN(state,zip)
) OPTIONS (PG_PGQL)
As a reminder Oracle Database 23ai supports SQL property graphs and PGQL property graphs. Oracle Database 19c supports only PGQL property graphs.
Multi-Destination Dijkstra’s Algorithm
Dijkstra’s algorithm is a fast algorithm for finding a shortest path in a graph. It is especially useful when dealing with non-negative weights, such as distances, costs, etc. Usually, Dijkstra’s algorithm finds the shortest path between a given source and destination node. This new variant of the algorithm tries to find the shortest path between the source and all vertices of the graph.
This new algorithm can be useful for several use cases, such as network routing, supply chains, transportation, recommendation systems, cyber-attack path analysis, finding cost-efficient transaction chains, contact tracing, and more.
Both PGQL property graphs and SQL property graphs can be loaded into Graph Server for use with this new algorithm and any other existing graph algorithm.
Other notable updates
– Graphs with CLOB properties can now be loaded into Graph Server memory
– Graphs with unbound (or null) vertex and edge variables can now be loaded into Graph Server memory
Graph Size Estimator
Graph Size Estimator, used to calculate the amount of memory a graph requires when loaded into Graph Server for analysis with algorithms, has several new updates. You can try them here.
APEX Graph Visualization Plug-in
The APEX Graph visualization Plug-in 24.1 has been released with the following features
- Improved default exploration modes
- Option for a cluster-based layout
- Improved UI for the Attributes section to use input fields and check boxes, instead of setting objects in JSON text
This plugin is available here and documented here.
For more information, please visit our Property Graph documentation and RDF Graph documentation.
