Databases are the backbone of businesses, safeguarding everything from customer data to sensitive financial records. Although data is one of the most valuable assets for organizations, it can also turn into a major liability if not adequately protected. With the rise in high-profile data breaches and ever-increasing cybersecurity threats, safeguarding databases is more critical than ever.
Oracle Data Safe helps organizations protect their data. Through a unified console, Data Safe assesses potential risks, masks sensitive data, monitors user activity, enforces security controls, and manages the new Oracle Database 23ai SQL Firewall. Data Safe simplifies security management, ensuring continuous monitoring, secure auditing, and streamlined compliance. For Oracle Cloud databases, Data Safe is included in the database service subscription price.
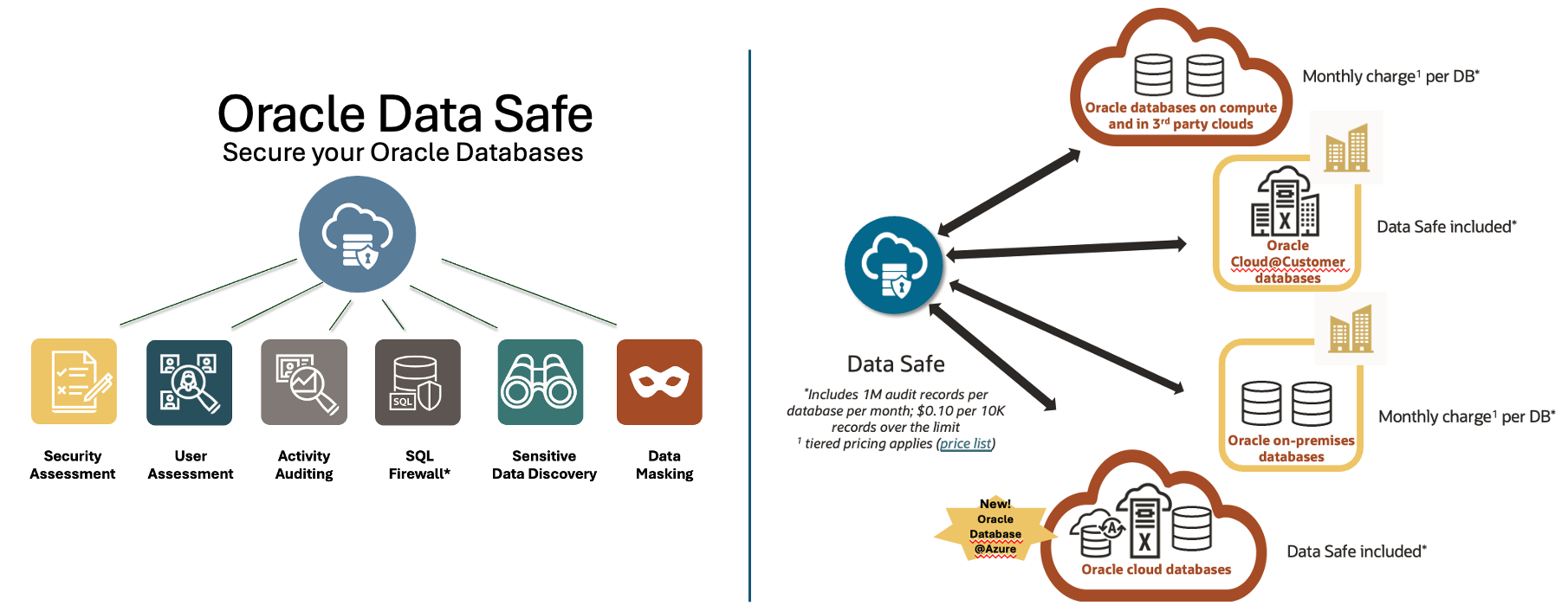
The Challenge: In organizations with large-scale environments—often including hundreds or even thousands of databases—registering each database in Oracle Data Safe manually can be a time-consuming task. Launching a registration wizard for each database, followed by configuring each database and enabling audit trails to start collecting audit records, can be a heavy lift. This is especially true for organizations operating across multiple cloud regions. It’s easy to skip a database here or there, and it only takes one misconfigured system for the bad guys to break in and steal your data.
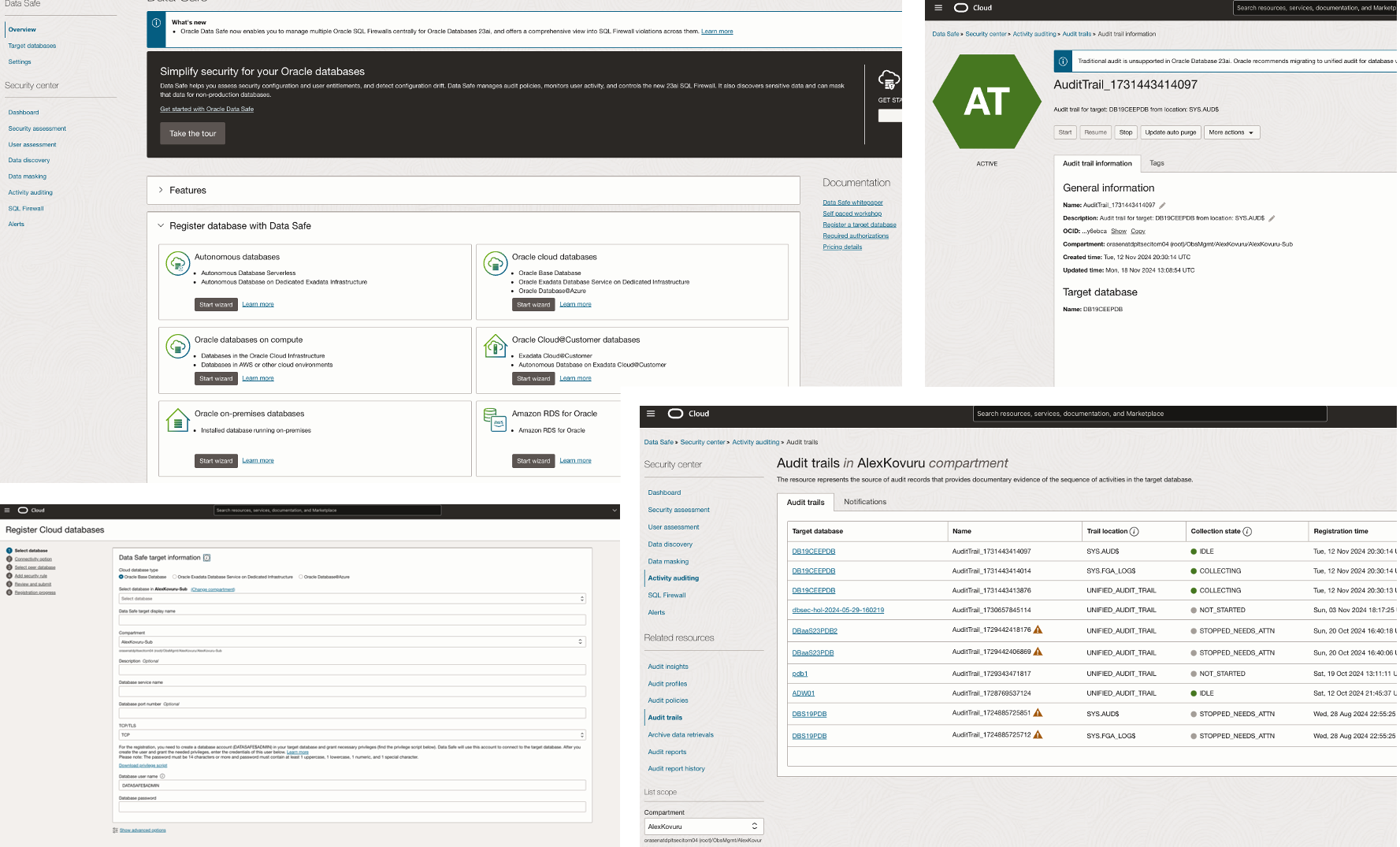
The Solution: Automating the registration process can be a game-changer! To meet this need, we developed a series of shell scripts using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Command Line Interface (OCI-CLI) commands. This script discovers unprotected databases and automates the registration process — even across regions.
Key Automation Steps
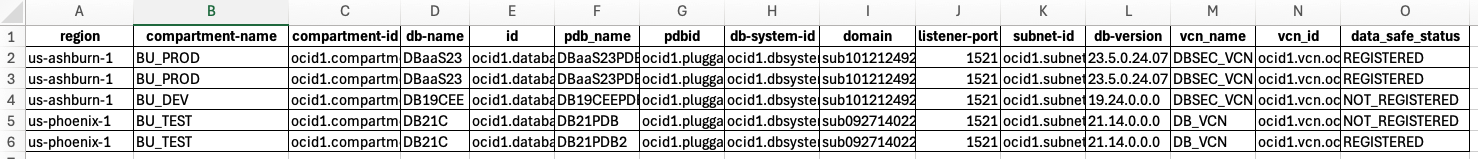
1. Discovering DBaaS Databases: The first script, OCI_DB_Inventory-DataSafe_Status.sh, automatically discovers all DBaaS databases across subscribed regions, capturing their Data Safe enablement status. It generates region-specific inventories in CSV format for easy reference:
• Cloud Base Service: All_Regions_Cloud_BaseDatabases.csv
• Cloud Exadata: All_Regions_Cloud_ExaDatabases.csv
• Cloud Autonomous: All_Regions_Cloud_AutonomousDBs.csv
Here is a sample of the output from OCI_DB_Inventory_DataSafe_Status. The script contains a status column that lets you know which databases have been registered with Data Safe, and which ones have not. The output also contains most of the information needed to register the databases.
2. Automating Database Registration: The second script, Data_safe_registration.sh, registers unmonitored databases in Oracle Data Safe.
Note: The script is compatible with both cloud and on-premises databases. For on-premises databases, administrators simply create a CSV file with the necessary connection details.
You must complete two tasks before running this script. Once completed, the script can directly initiate the registration process.
Prerequisite Tasks
• Task 1: Connectivity Options – Private endpoint / On-premises Connector
Data Safe needs to be able to connect to your databases. This is easy if your database uses a public IP address, but for obvious reasons that is a rare case. In most cases, Data Safe will connect through a private endpoint or using Data Safe’s on-premises connector.
For cloud databases, the preferred connectivity option is “Private Endpoint.” Private endpoints allow an OCI service to enter your virtual cloud network. A single private endpoint can connect Data Safe to all of the databases using a VCN. During the database discovery phase, if any unmonitored database’s VCN contains an existing private endpoint, the script automatically uses it. If not, the Connectivity_Option_Creation.sh script can be executed to establish new private endpoints and On-premise connectors as needed.
• Task 2: Data Safe Service Account Creation
The DataSafe_Service_Account_Creation.sh script sets up the required Data Safe service account in each database and grants the necessary privileges using the datasafe_privileges.sql script provided by Oracle. You can download this script from Oracle Data Safe in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.(This step is optional for Autonomous Databases, as they already include the DS$ADMIN account by default. However, it is mandatory for non-Autonomous Databases).
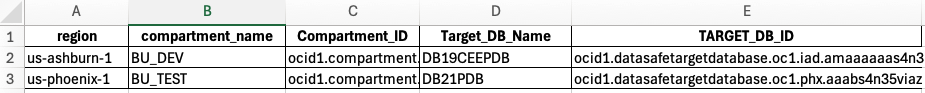
Running Data_safe_registration.sh completes the registration and generates a consolidated registration file, Datasafe_TargetDBs.csv, to facilitate ongoing management.
3. Audit Collection Activation: Once databases are registered, the script Activate_Audit_Trails.sh identifies available audit trails for each target database. Users can specify a start date for collecting audit logs, ensuring targeted audit management. Output is stored in a CSV file, All_Regions_Target_DBs_Audit_Trails_Status.csv, detailing the status of each database’s audit trails.
Automating these steps lets you save time, reduce human error, and enforce consistent security policies across regions. Detailed instructions are available in Datasafe-Reg-Automation_Instructions.pdf to guide you through each step.
Getting Started
To begin, set up the OCI-CLI and download the scripts from our GitHub repository. You’ll need appropriate permissions within your OCI tenancy to execute commands and interact with Oracle Data Safe. If OCI-CLI isn’t installed on your local machine, we recommend using Oracle Cloud Shell, accessible from the Oracle Identity Cloud Service portal. This built-in shell requires no setup, allowing you to run OCI-CLI commands directly from the browser.
Here is an example policy to grant access to Cloud Shell:
allow group <GROUP-NAME> to use cloud-shell in tenancy
for more information on installing Cloud Shell and the CLI, refer to the documentation for Cloud Shell, and for installing the CLI.
Ready to streamline your database security with Data Safe?
Download the scripts from our GitHub Repository and start automating your Oracle Data Safe registration today!
Additional Resources:
• Oracle Data Safe
• Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
• CLI for using Oracle Data Safe
• Oracle LiveLabs – Data Safe Fundamentals
