Are you looking to move data from a document database such as MongoDB to a relational database, but you are unfamiliar with relational concepts?
Are you unsure how to model JSON documents as relational tables and how to create the logical model?
Are you interested in transparent and automatic application migration from document databases to Oracle?
If the answer to any of the above questions is “Yes”, then you are at the right place.
What is JSON Relational Duality?
JSON Relational Duality unifies the benefits of the Relational and Document worlds within a single database without any of the tradeoffs of each world. The new feature in Oracle Database 23ai that enables this capability is referred to as a JSON Relational Duality View. Using Duality Views, data is still stored in relational tables in a highly efficient normalized format but is accessed by applications in the form of JSON documents. Developers can thus think in terms of JSON documents for data access while using the highly efficient relational model for data storage, without having to compromise simplicity or efficiency.
First, let’s talk about why you should migrate to Oracle JSON Relational Duality
With JSON Relational Duality, you get all the benefits of document databases and relational data model on the same data set. There is no need to enforce data integrity constraints in the application, the database does it for you! You get data integrity on any number of documents and collections. You get flexibility to access data using Document APIs, REST, or SQL to support a variety of workloads.
Next, let us talk about why you should migrate from Document databases
Document databases are great for simple use-cases. However, as use-cases become more complex, ensuring data consistency becomes more challenging. That’s because document databases duplicate shared data – so updating it and ensuring that it is consistent is very hard. Moving from document databases frees you from the burdens of denormalized storage.
Now that you have made the fantastic decision to move to Oracle, let us discuss how you can easily migrate your data and applications.
Let’s say you have an existing application running in production on a document database. If you want to move the application to Oracle duality views, how do you go about the migration?
First, you must determine the normalized relational schema that best matches your data. Next, you need to create the relational schema and create duality views on top of the relational data to match your application collections. Once this is complete, you can import data into the resulting duality views and migrate your application to use them.
But wait… How do we find the normalized relational schema that best matches your data? This seems like a hard problem, in general, especially since modern applications may have several collections with non-trivial data models.
This is where Oracle’s JSON-to-Duality Migrator comes in! The migrator addresses the challenge of preserving JSON document semantics in relational schemas. By inferring implicit relationships from document collections, it generates updatable duality views that mirror original JSON structures. This method ensures backward compatibility for applications reliant on document APIs while leveraging relational optimization, such as indexing and ACID compliance. The tool supports iterative refinement, allowing developers to adjust inferred schemas post-migration. The migrator allows you to:
- Design an effective normalized relational schema, derived from an existing set of JSON collections.
- Migrate data from document database to Oracle duality views, while automatically transforming to the target schema.
- Lift-and-Shift applications transparently with minimal to no code changes.
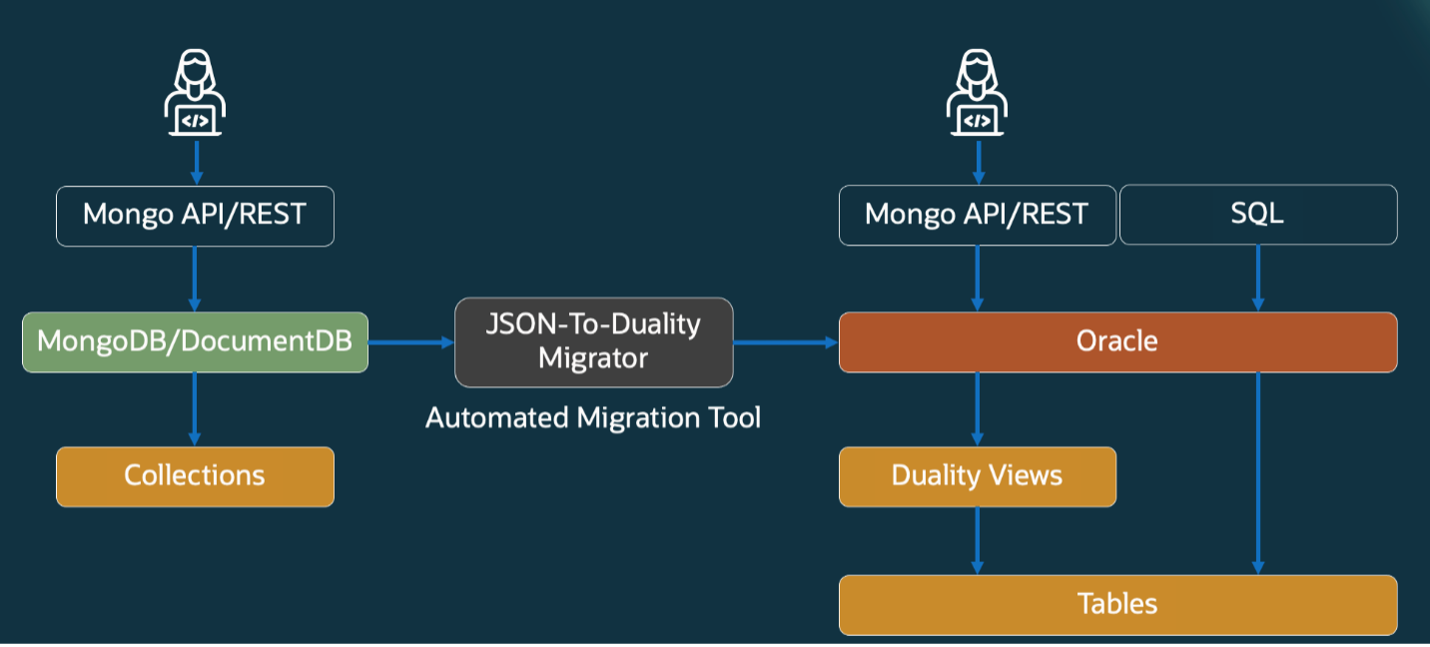
What does the JSON-to-Duality Migrator provide?
- Generates DDL scripts to create the relational schema (including tables, indexes, constraints, and sequences)
- Generates duality views that mirror the shape of the JSON documents in the input collections
- Automatically normalizes and deduplicates data
- Optionally allows users to fine-tune and optimize the generated schema
How does the JSON-to-Duality Migrator work?
- Determines normalized schema after analyzing data and structure of input JSON collections
- Uses sophisticated unsupervised machine learning (ML) algorithms to create a normalized relational schema
- Eliminates duplication by identifying shared data across collections
- Uses functional dependency analysis to automatically identify primary keys for each entity and foreign keys between the identified entities
This sounds awesome; How do I use it?
The migrator exposes a set of easy-to-use PL/SQL functions and procedures (part of the dbms_json_duality package) to assist with schema inference, schema generation, schema validation, data import, and data validation.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| infer_schema | Infers the relational schema that represents all the input collections |
| generate_schema | Produces the code to create the required database objects for each duality view |
| infer_and_generate_schema | Performs both infer_schema and generate_schema |
| validate_schema_report | Validates the inferred schema against the input collections |
| import_all | Imports the existing document collections into the duality views (in fact into the underlying relational tables) |
| validate_import_report | Validates the imported data against the input collections |
High-Level Steps for Migration
We envision the migration process to involve the following steps.
- Import JSON collections from a document DB, such as MongoDB, into a set of tables with a single JSON column (either regular tables or JSON collection tables). This can be done using existing tools provided by Oracle and document databases, such as external JSON tables or DBMS_CLOUD.COPY_COLLECTION.
- Execute PL/SQL functions (infer_and_generate_schema, infer_schema, generate_schema) to find and create the relational schema for the input collections. a. You can use infer_and_generate_schema to do this in one-shot. b. You can also use infer_schema and generate_schema in combination to do this in two phases in case you want to fine tune the schema before generating the DDL script to create it.
- Validate the generated schema using the validate_schema_report API.
- Move data from JSON tables to duality views using the import_all API.
- Validate the imported data using the validate_import_report API.
- Fine-tune your applications to utilize the many features of duality views and Oracle’s converged database.
Let’s look at a conference scheduling example to understand how to use the Migrator. We run the JSON-to-Duality Migrator by invoking the infer_and_generate_schema function and import data by invoking the import_all procedure. You can find the complete script for this example here.
DECLARE
schema_sql clob;
BEGIN
-- Infer relational schema + duality views
schema_sql :=
dbms_json_duality.infer_and_generate_schema(
json('{"tableNames" : [ "ATTENDEE", "SPEAKER", "SESSIONS" ],
"useFlexFields" : true,
"updatability" : true,
"minFieldFrequency" : 0,
"minTypeFrequency" : 0,
"sourceSchema" : "ADMIN"}'));
-- Print DDL script
dbms_output.put_line('DDL Script: ');
dbms_output.put_line(schema_sql);
-- Create relational schema + duality views
execute immediate schema_sql;
-- Import data into duality views
DBMS_JSON_DUALITY.import_all(
JSON('{"tableNames" : [ "SESSIONS", "ATTENDEE", "SPEAKER" ],
"viewNames" : [ "SESSIONS_DUALITY", "ATTENDEE_DUALITY",
"SPEAKER_DUALITY" ]}'));
END;
/
Super simple, isn’t it? Download the Oracle Database 23ai Free version and try it today!
Key Takeaways
- The JSON-To-Duality Migrator automates the hardest steps in the migration process from document databases to Oracle duality views
- Namely, data validation, data normalization, and schema generation
- The Migrator is unsupervised, i.e., it requires no user input to operate
- Users are free to override the recommendations provided by the tool
- The Migrator significantly reduces the barrier for application developers to migrate to Oracle from document DBs like MongoDB
- Makes it as easy as migrating between document DBs

