In today’s data-driven landscape, organizations manage large volumes of sensitive data, including Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Protected Health Information (PHI), and financial records that must be protected from end-users who don’t have a business need for that information. Data Redaction was introduced in Oracle Database 12c to help limit exposure to sensitive data by dynamically redacting sensitive data in query results, without modifying the stored values or requiring application changes.
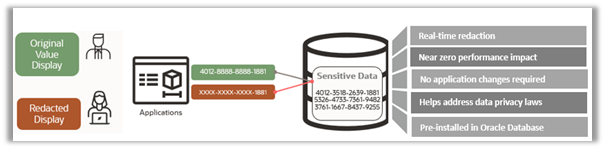
Since introducing Data Redaction more than a decade ago, thousands of Oracle customers have used it to ensure that users without a legitimate need to know the original sensitive data see only redacted information. For example, call center users would only be able to view redacted values for PII data. Because the redaction policy is implemented at the database level, no application changes are required. Additionally, as the performance impact is negligible, Data Redaction can be used on production databases. Our customers can easily specify the conditions under which data is redacted and how it is redacted. For instance, they can choose to redact all but the last four digits of a credit card number.
Oracle Database 23ai delivers major advancements to Data Redaction, making it more effective for today’s dynamic data environments. As real-world business applications depend on real-time analytics and complex SQL, redaction must be applied consistently while still allowing queries to run correctly and return expected results. This blog highlights such key enhancements, their business impact, and how they empower organizations to securely scale AI workloads.
What’s new?
Until now, Data Redaction primarily redacted sensitive columns in queries when those columns were not part of mathematical SQL constructs. With Oracle Database 23ai, Data Redaction now operates directly on the result set of SQL queries, preserving full query semantics while redacting sensitive column values. This ensures that users receive accurate and complete results, just as they would without a redaction policy, except that the sensitive column values are redacted. This enables Data Redaction to support a broader range of SQL constructs and workload types, making it well-suited for meeting data privacy requirements for modern applications.
- Support for mathematical and set functions
Data Redaction now supports aggregate functions (SUM, COUNT, MIN, MAX) and set operations (UNION, INTERSECT, MINUS). It also extends to advanced SQL constructs such as WITH and OUTER JOINs. This means queries run against the original underlying values in the database, but when the query results return, only the displayed output is redacted. For example, if a JOIN or UNION includes a redacted column, the operations proceed as if using the actual values, but the final result after JOIN or UNION is redacted. With this change, complex queries can run without exposing actual data or erroring out.
- Support for sorting and grouping on redacted columns
Operations like GROUP BY, ORDER BY, and DISTINCT can now use columns with redaction policies. This means the query still uses the actual values behind the scenes to group, sort, or remove duplicates, but when the results are shown, the sensitive column values are redacted in the output. For example, in a hospital, patient records may be grouped by insurance policy number. The grouping happens on the actual policy numbers, but the report displays them in redacted form (e.g., XXXXX123).
- Views with expressions
Redacted columns can now be used in SQL expressions on both regular and inline views. In addition, functions such as CONCAT, MIN, MAX, COALESCE, TRIM, etc., are supported when applied to redacted columns in views. This ensures consistent redaction across complex view definitions and improves usability of reports, etc., which are supported when applied to redacted columns in views. This helps to ensure consistent redaction across complex view definitions and improves usability in reporting scenarios.
- Support for redacting virtual columns in function-based indexes
In Oracle Database 23ai, virtual columns for function-based indexes are now automatically redacted when their underlying base columns are redacted. This ensures consistent redaction behavior, even when sensitive information is accessed through virtual columns.
Leveraging Data Redaction for critical business and AI workloads
Data Redaction offers a simple and effective way to help address data privacy wherever sensitive data is accessed or displayed. Data Redaction is increasingly valuable for AI developers and data science teams, especially in workflows where privacy, compliance, and responsible AI practices are critical.
- Secure BI & analytics
As business users and analysts access data through dashboards or ad hoc reporting tools, there is a risk of exposing sensitive fields such as customer names, emails, etc.
By implementing Data Redaction in the database, analysts can now use BI tools like Oracle Analytics, Power BI, or Tableau to generate trends or summaries on live data without exposing sensitive data.
- Redacted data for LLM workflows
Data Redaction enables the use of production datasets for LLM workflows without leaking sensitive data. Sensitive fields are dynamically redacted at query time, allowing real model input, ideal for RAG and other enterprise GenAI use cases.
For example, let’s say a financial firm is building a GenAI support chatbot using RAG. To develop and evaluate this functionality, they can safely query real customer records as sensitive fields such as names and account numbers are redacted at runtime. This approach provides safer yet realistic model input for development.
- AI-generated SQL
Agentic AI or LLMs can create arbitrary SQL queries that can leak sensitive information. Data Redaction ensures that even when such queries are executed, sensitive fields (e.g., names, identifiers) are dynamically redacted at runtime, preventing unintended data exposure. For example, an employee might generate SQL for customer insights. The query still runs on live production data, but Data Redaction masks sensitive values in the result set, helping preserve privacy.
Why Data Redaction enhancements matter
The latest enhancements mark a turning point as Data Redaction helps protect the privacy of sensitive data exposed through GenAI, RAG pipelines, real-time analytics, real-world applications with complex SQL, low-code/no-code app development, and live debugging. Whether you’re a first-time adopter or an existing customer of Data Redaction, it empowers teams to safely innovate with sensitive data without the need for workarounds or reengineering.
Try Oracle Data Redaction today!
To learn more about Data Redaction, visit the Advanced Security product page on the Oracle website.
For hands-on experience, try our free, interactive Oracle Data Redaction LiveLab.
For additional learning, explore the following resources:
