Introduction
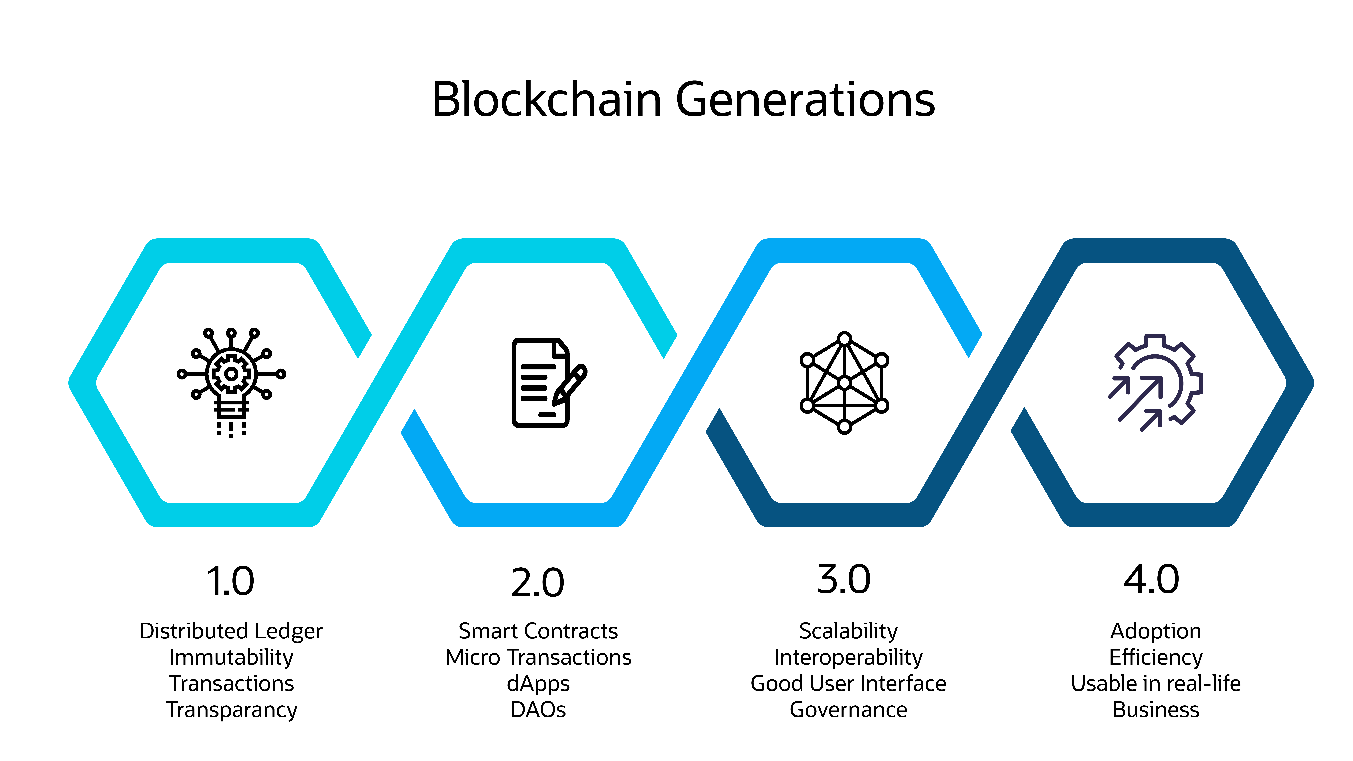
This blog post will discuss the step from blockchain generation 3.0 to 4.0 and how DA (Data Analytics) and ML (Machine Learning) can augment blockchain-built solutions. The first generation of Blockchain was mainly around the use of basic capabilities and cryptocurrencies or Fintech use, whilst in the second generation, application logic was added in the form of code-based smart contracts to widen its applicability. The third generation was much more about scalability, interoperability and creating good user interfaces to level up with existing business applications. Today, we are looking at generation 4.0, focusing on cross-industry adoption and making enterprise blockchain more usable in real-life business[1].
This raises the question of how more value can be added to these blockchain applications to meet business user expectations. With the growing adoption, the volume of transactions is growing rapidly and a whole new data lake of information is created. Leveraging this lake of timestamped data offers great potential for technologies like DA and ML. As part of an internship at Oracle, the possibilities of the confluence of these technologies have been explored.
Blockchain augmented with data analytics and machine learning
Blockchain has become a technology enabler and gradually serves as the backbone of more and more business processes. As the result, enterprise blockchain applications use DA and ML to create more business value, although each domain may have a slightly different focus. DA can augment blockchain by visualizing the timestamped data in the form of real-time timelines, inventory heat maps, product content charts, supply chain relationships, and other graphs and statistics. These visualizations make it easier to interpret the data on the blockchain ledger and make it more comprehensive.
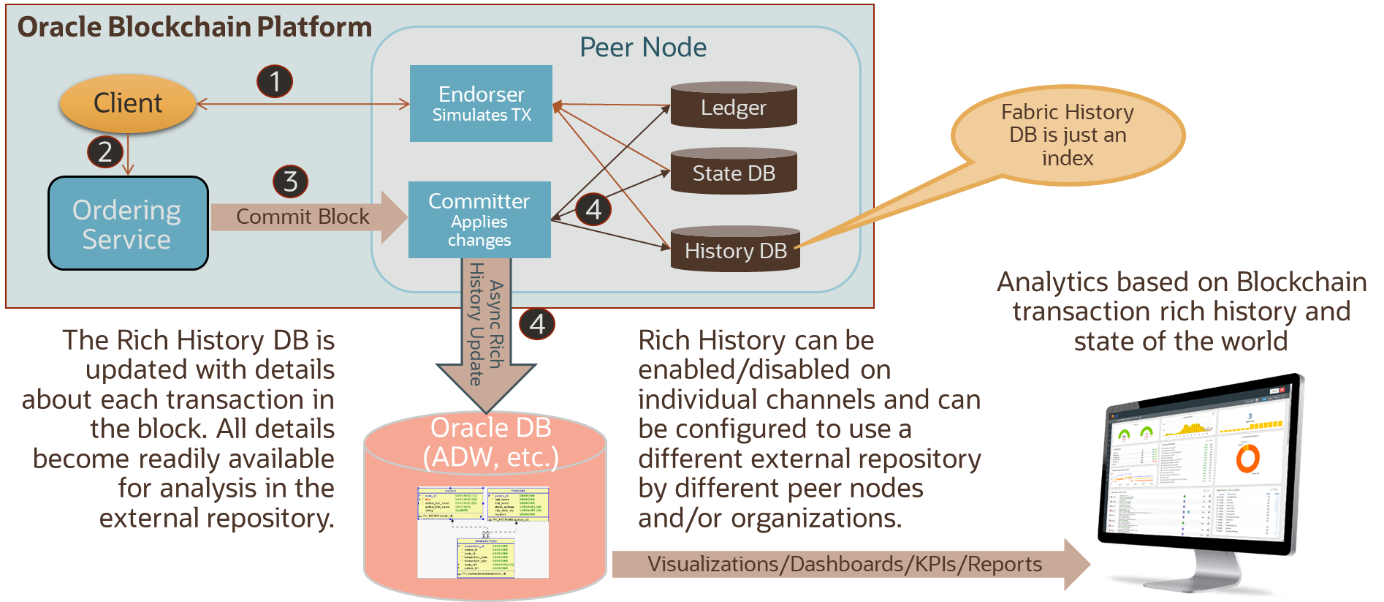
ML on the other hand can be used in a later stage when enough data has been gathered both for training ML models and for its predictions. It can help find interesting patterns, make predictions, look for anomalies and help cluster data. In the future ML might even help to improve the code generation of smart contracts and apply best practices. Although these technologies could supplement each other well, it is still in the early stages. To automate DA, Oracle has already added a specific function to its blockchain offering: ledger data and blockchain operations history is streamed to the Rich History Database in Oracle Blockchain Platform. From the Rich History Database, which is a data schema in Oracle Database synchronized with the ledger’s transactions, transaction payloads and transaction history can be clustered, analyzed and visualized.
Promising industries and use cases
Real time examples of promising industries and use cases where Blockchain applications can be augmented with ML/AI and DA are:
- Health Care: A Blockchain network can help enable secure and patient-authorized data exchange between care provider (e.g, a hospital lab and an external specialist, who needs to access patient’s test results.) Patients can provide consent for access to their medical files, while doctors can share the medical results securely through a permissioned Blockchain. The core capabilities blockchain offers here are control, full traceability, identity, and security. DA is used to visualize the data and show the grouping of patients and doctors per hospital/clinic. Statistics, outliers, and reference lines enhance the visualization of the data. ML could provide predictions about e.g. the occupancy rate of the hospitals/clinics, which would have been an interesting proposition during the COVID-19 pandemic.
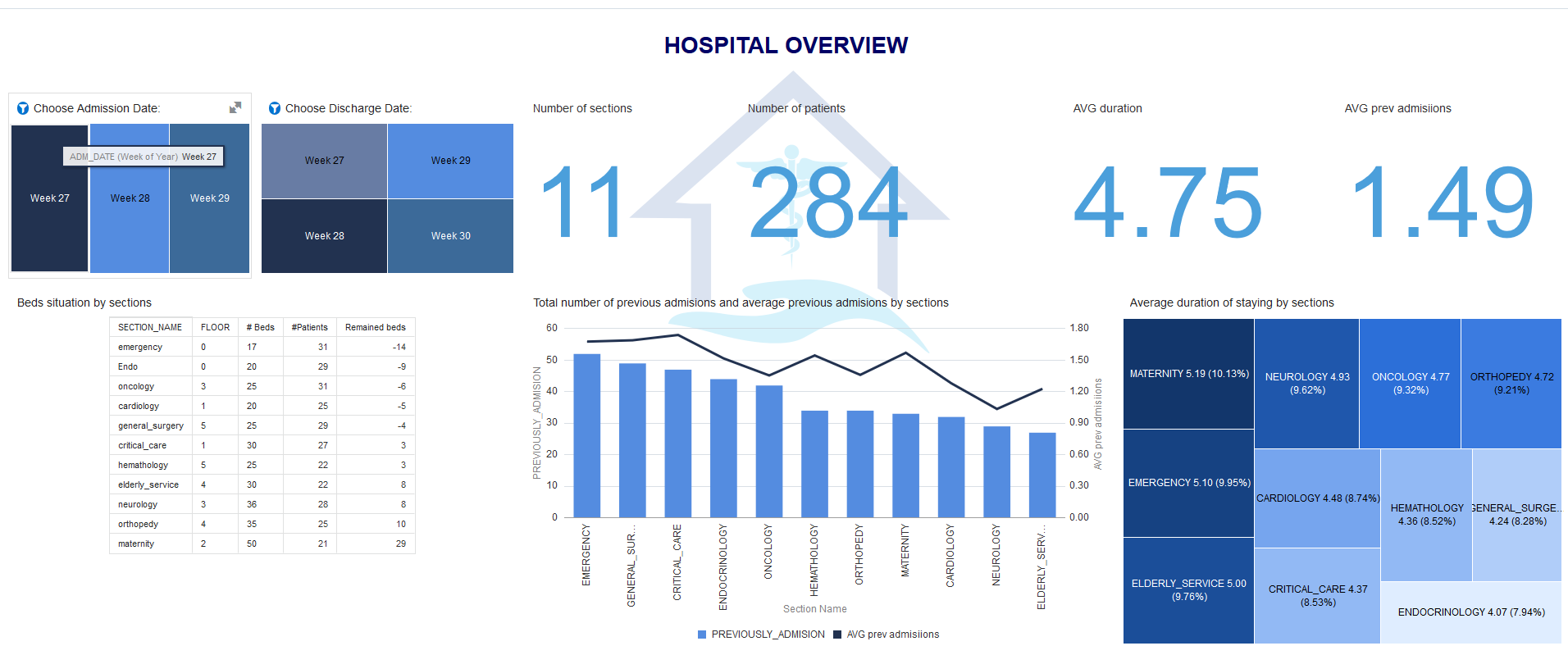
Figure 3. Data Analytics and Forecasting Using EHR Tracking Blockchain Transaction History Using Oracle Blockchain Platform. - Corporate Finance: Blockchain provides a secure way to handle and reconcile invoices between different entities and business units. Blockchain offers a holistic view and full traceability of these invoices. ML can analyze the timestamped data to detect anomalies in real-time and address why invoices were rejected or have taken a much longer route to get paid. DA can be used to visualize the data in real-time with heat maps and Sankey diagrams to show the flows. When using Oracle Analytics it can also generate natural language explanations of the data using AI/ML. This can smoothen the process, generate insights into why certain invoices get rejected more often than others, and eliminate inefficiencies.
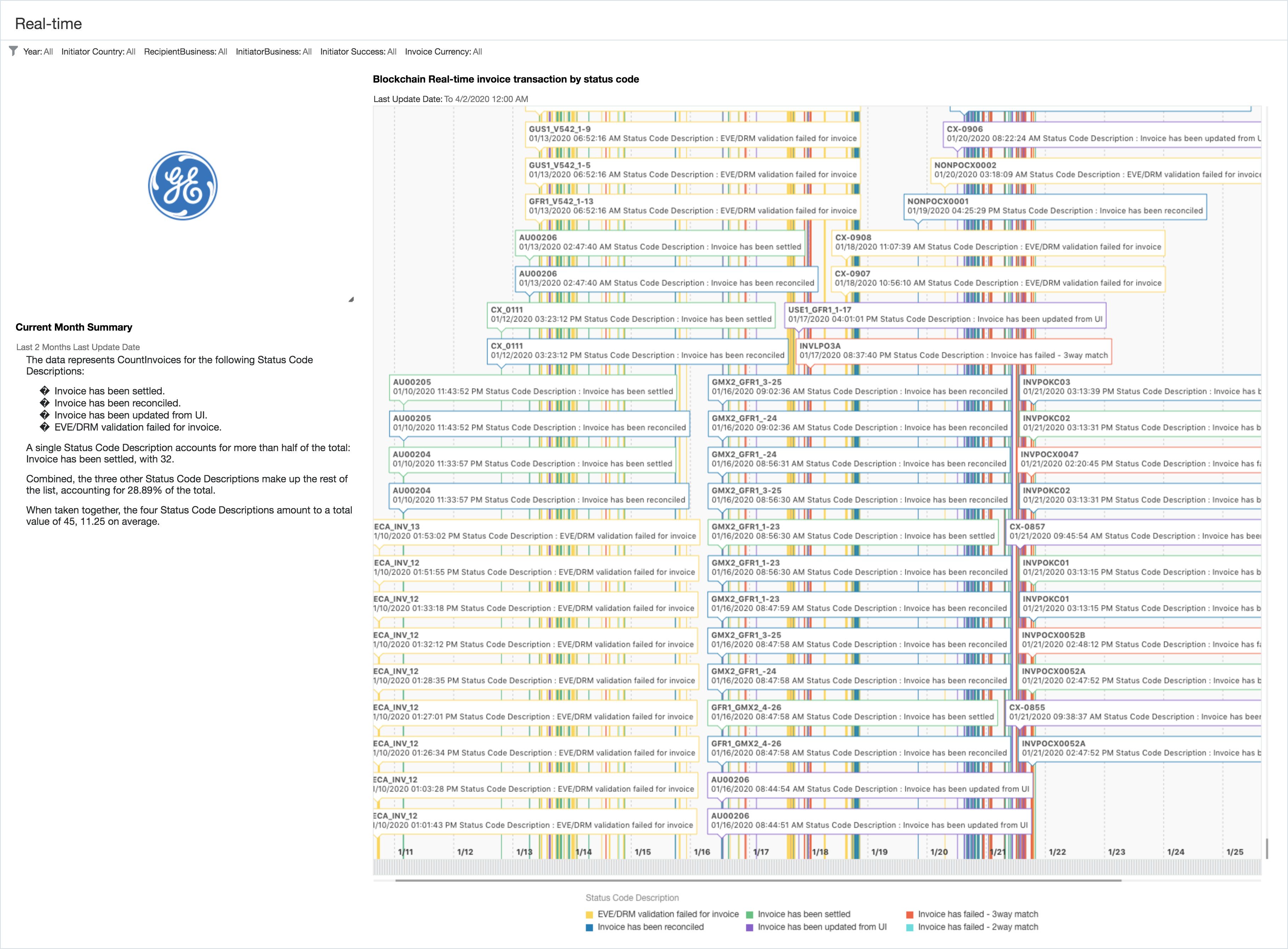
Figure 4. Timeline View and Natural Language Narrative Generated by Oracle Analytics from Intercompany Financials Reconciliation Using Oracle Blockchain Platform. 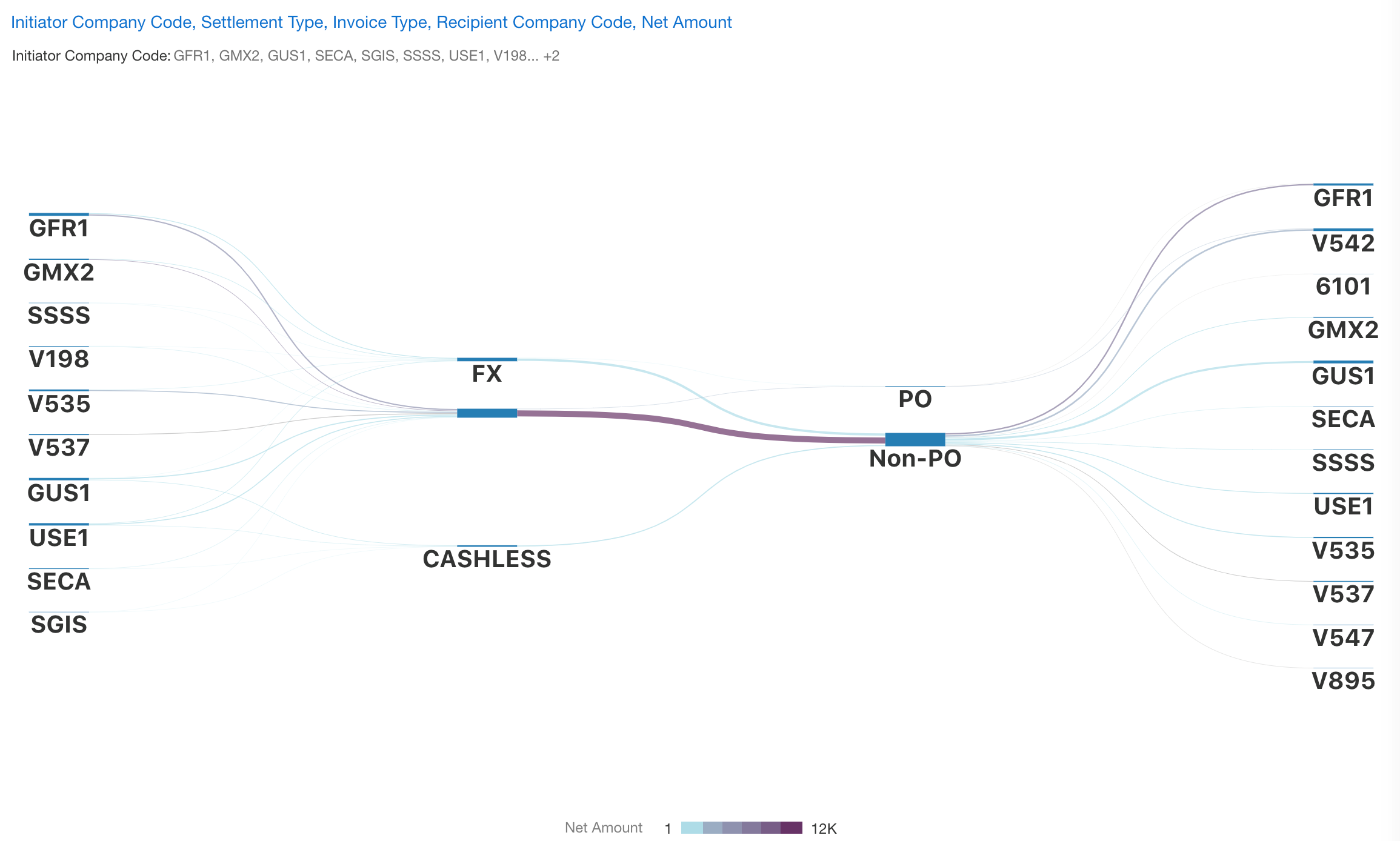
Figure 5. Cross-Entity Invocing Sankey Diagram Generated by Oracle Analytics from Intercompany Financials Reconciliation Using Oracle Blockchain Platform. - Supply Chain: Blockchain can help create a trusted supply chain with authenticated provenance. This creates guaranteed product authenticity for businesses and consumers. Blockchain makes the process faster, offers full traceability based on immutable records, and provides a holistic view across a multi-level supply chain. DA can help visualize the timestamped data in an immutable supply chain timeline and this can even be accessed on the end-product using a QR code that customers could scan. Customers could see product composition and the end-to-end sourcing across multiple suppliers, verify sustainability claims, drill down into source of recycled content, and much more. This is not only helpful for sustainability management, as customers and businesses are ensured that a product is truly sustainable, but helps to increase retailer’s business as case studies indicate that when customers can access such data they are more likely to buy from these retailers[2]. ML can also help optimize supply chain routes and predict where potential bottlenecks or disruptions could arise.
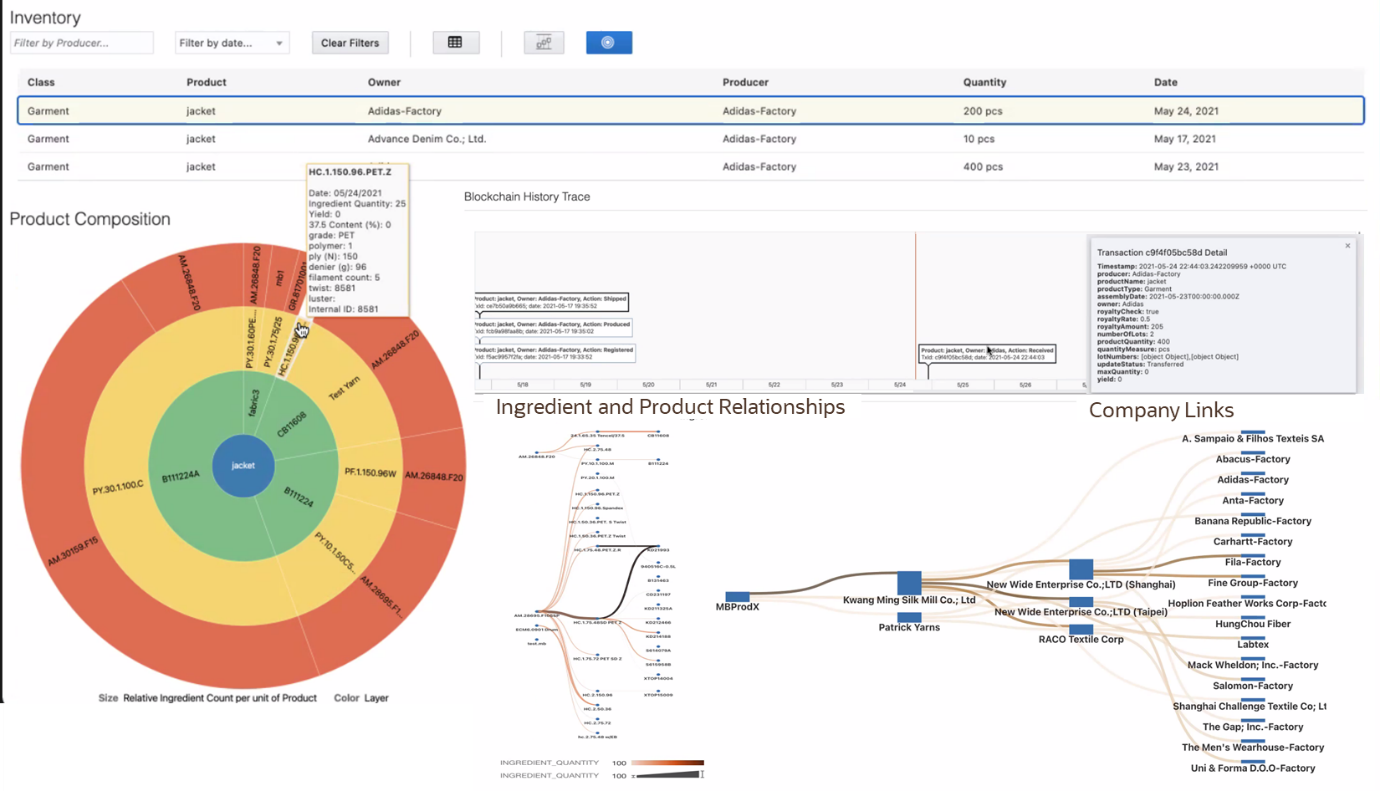
Figure 6. Example of Product Composition Drill Down and Products/Companies Relationships Generated by Oracle Analytics from Oracle Blockchain Platform Transaction History in Textile/Clothing Manufacturing.
Conclusion
| We believe there is more value to Blockchain applications when it is augmented with ML and DA, especially with the transition to Blockchain 4.0. Due to the disruptive nature of blockchain in terms of business processes, it is recommended to ensure organizations get the Blockchain concept first, before blockchain applications are enhanced with these technologies. |
The Rich History Database offers the tools to support the confluence of these technologies, starting with the visualization of the ledger’s data. When enough data has been gathered ML models and tools built-in within Oracle Database can be used to further augment the application discovering patterns, trends or anomalies. Consider the right order, but early adaptors will accelerate the value delivered from their Blockchain solutions as DA and ML complement Blockchain 4.0 capabilities. |
[1] www.researchgate.net/publication/351263701_Blockchain_10_to_Blockchain_40-The_Evolutionary_Transformation_of_Blockchain_Technology
[2] https://www.retraced.com/en/news/client-success-story-boyish-x-retraced-case-study

