Scope
Human Task instances and Workflow instances created at run time by APEX applications are subject to periodic purge routines which run in the background. A daily job checks for all human tasks that are either errored, expired, canceled or completed and purges them. For completed tasks, the Retention Period Days instance parameter is checked and only the tasks for which this period has elapsed, are purged. For errored, expired and canceled tasks, retention period does not apply. They are candidates for immediate purge. Another daily job checks for all workflow instances that are terminated or completed. The Workflow Retention Period Days instance parameter is checked and only the workflows for which this period has elapsed, are purged.
Users of the APEX Workflow and Approvals Component (Human Task) features often require that the information be retained beyond the retention period, for completed or canceled tasks and workflows , mostly for audit purposes. With APEX 24.1 , there are new views and APIs available that can be leveraged by APEX users to transfer the purgeable human tasks and workflows to their user schema prior to their deletion via the periodic purge job(s).
Existing Documentation
What does the APEX Documentation say about Workflow and Task purge?
As per the Application User’s Guide, the periodic purge of workflow and human task instances is performed according to the following rules.
For Workflow Instances the purge job ORACLE_APEX_WFS_PURGE runs nightly at 0300 hours UTC
- The instances that are in terminated or completed state, are purged after their retention period elapses.
- The retention period (Workflow Retention Period Days) is an Instance parameter with a default value of 30 days and a maximum value of 100 days.
- Workflow Instances that are Suspended, Faulted or Active – are not purged.
Further documentation is available here
For Human Task Instances, the purge job ORACLE_APEX_TASKS_PURGE runs nightly at 0200 hours UTC
- The instances that are in Errored, Expired or Canceled state are purged immediately
- Completed instances that are past their retention period, are purged.
- The retention period (Retention Period Days) is an Instance parameter with a default value of 7 days and a maximum value of 30 days.
- Human Task Instances that are in Assigned, Unassigned, or Information Requested state are not purged.
- The report of tasks that have been purged by the Task Purge job is located in Workspace Administration as a json file.
Further documentation is available here
Using the APEX_PURGEABLE_* views
APEX 24.1 introduces the following views
Tasks
| View Name | Description |
|---|---|
| APEX_PURGEABLE_TASKS | Contains all task instances scheduled to be purged as part of the next purge schedule |
| APEX_PURGEABLE_TASK_HISTORY | Contains the history of all task instances scheduled to be purged as part of the next purge schedule |
| APEX_PURGEABLE_TASK_COMMENTS | Contains the comments for all task instances scheduled to be purged as part of the next purge schedule |
| APEX_PURGEABLE_TASK_PARAMETERS | Contains the parameter values for all task instances scheduled to be purged as part of the next purge schedule |
Workflows
| View Name | Description |
| APEX_PURGEABLE_WORKFLOWS | Contains all workflow instances scheduled to be purged as part of the next purge schedule |
| APEX_PURGEABLE_WF_ACTIVITIES | Contains all workflow activity instances scheduled to be purged as part of the next purge schedule |
| APEX_PURGEABLE_WF_VARIABLES | Contains the variables, parameters and activity variable values of all workflow instances scheduled to be purged as part of the next purge schedule |
| APEX_PURGEABLE_WF_PARTICIPANT | Contains the participant (Workflow Administrator, Owner) values for all workflow instances scheduled to be purged as part of the next purge schedule |
| APEX_PURGEABLE_WF_AUDIT | Contains the historical audit information for all workflow instances scheduled to be purged as part of the next purge schedule |
and these APIs:
apex_human_task.get_next_purge_timestamp.:- Fetches the timestamp of the next scheduled purge for human task instances.
apex_workflow.get_next_purge_timestamp:- Fetches the the timestamp of the next scheduled purge for workflow instances.
Prerequisite
The steps in this blog assume that you already have a number of Completed, Errored or Canceled tasks and Completed or Terminated workflow instances from different applications in your workspace that are candidates for purge as part of the scheduled purge job. If you do not have such workflow or task instances , you can quickly create a few purgeable tasks and workflows by running the Sample Workflows, Tasks and Approvals sample application from the Application Builder Gallery and then canceling/ terminating them.
To check the number of purgeable tasks and workflows
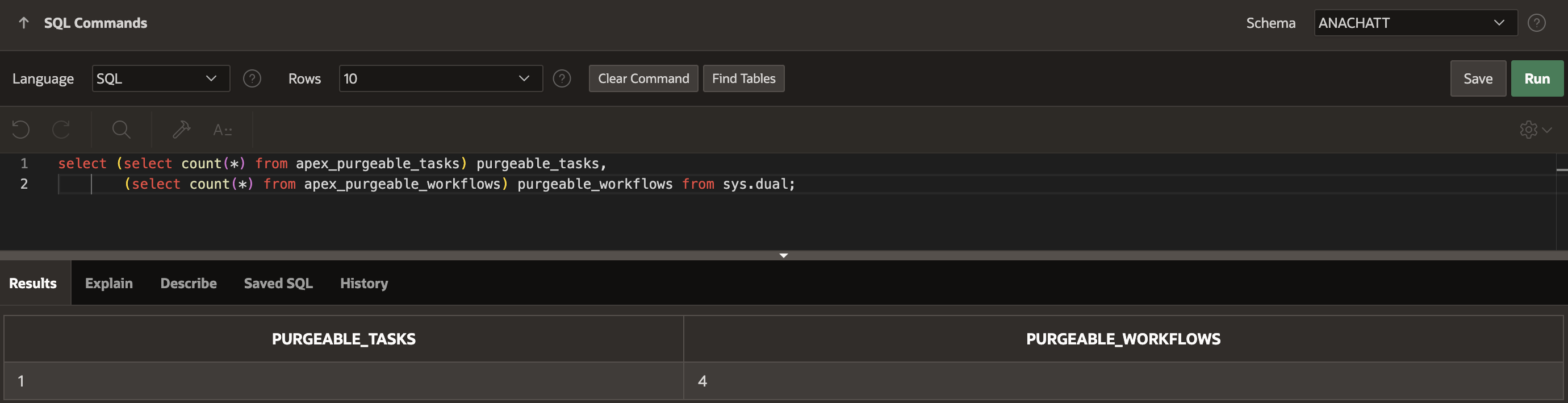
- Navigate to SQL Workshop and click SQL Commands
- Copy and Paste the commands given below into the Editor to check the count of purgeable tasks and workflows.
select (select count(*) from apex_purgeable_tasks) purgeable_tasks, (select count(*) from apex_purgeable_workflows) purgeable_workflows from sys.dual;
Creating the Archiver Application
- Navigate to App Builder
- Click Create
- Click New Application
For Name – enter Workflow Archiver Application
Install the Dataset
- Navigate to SQL Workshop and click SQL Scripts
- Click Create
- Copy and Paste the commands given below into the Script Editor to create a new user tables corresponding to the purgeable views described above.
- Save the Script as archiver_ddl
- Click Run
- Click Run Now.
create table archived_tasks as select * from apex_purgeable_tasks; create table archived_task_comments as select * from apex_purgeable_task_comments; create table archived_task_history as select * from apex_purgeable_task_history; create table archived_task_parameters as select * from apex_purgeable_task_parameters; create table archived_workflows as select * from apex_purgeable_workflows; create table archived_wf_activities as select * from apex_purgeable_wf_activities; create table archived_wf_participant as select * from apex_purgeable_wf_participant; create table archived_wf_variables as select * from apex_purgeable_wf_variables; create table archived_wf_audit as select * from apex_purgeable_wf_audit;
7. Navigate to Object Browser > Packages and right click on Create Package. Enter name as TASKS_ARCHIVER.
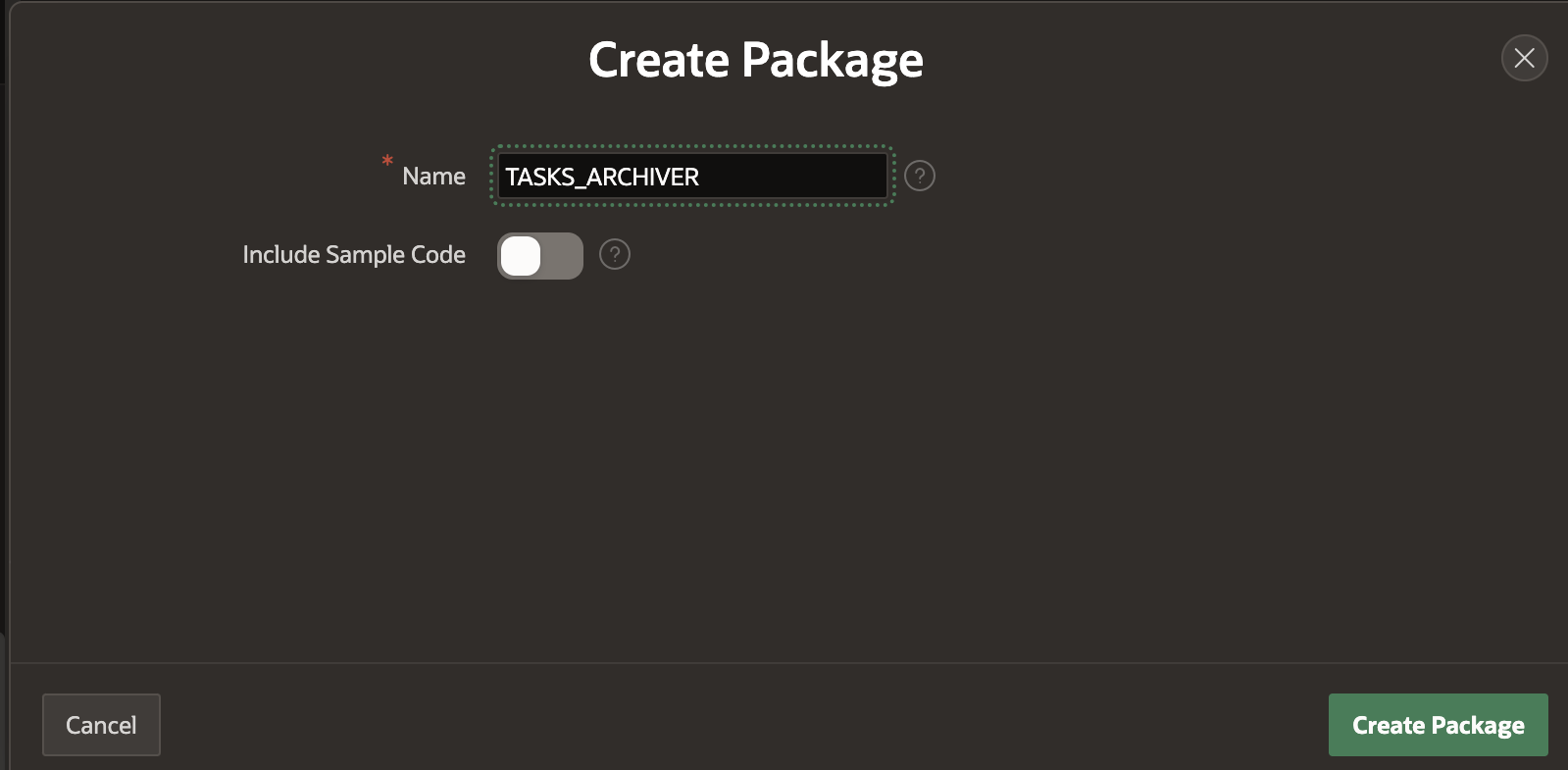
8. In the Specification editor, enter the following code:
create or replace package "TASKS_ARCHIVER" as procedure archive_tasks; procedure archive_comments; procedure archive_history; procedure archive_params; end "TASKS_ARCHIVER"; /
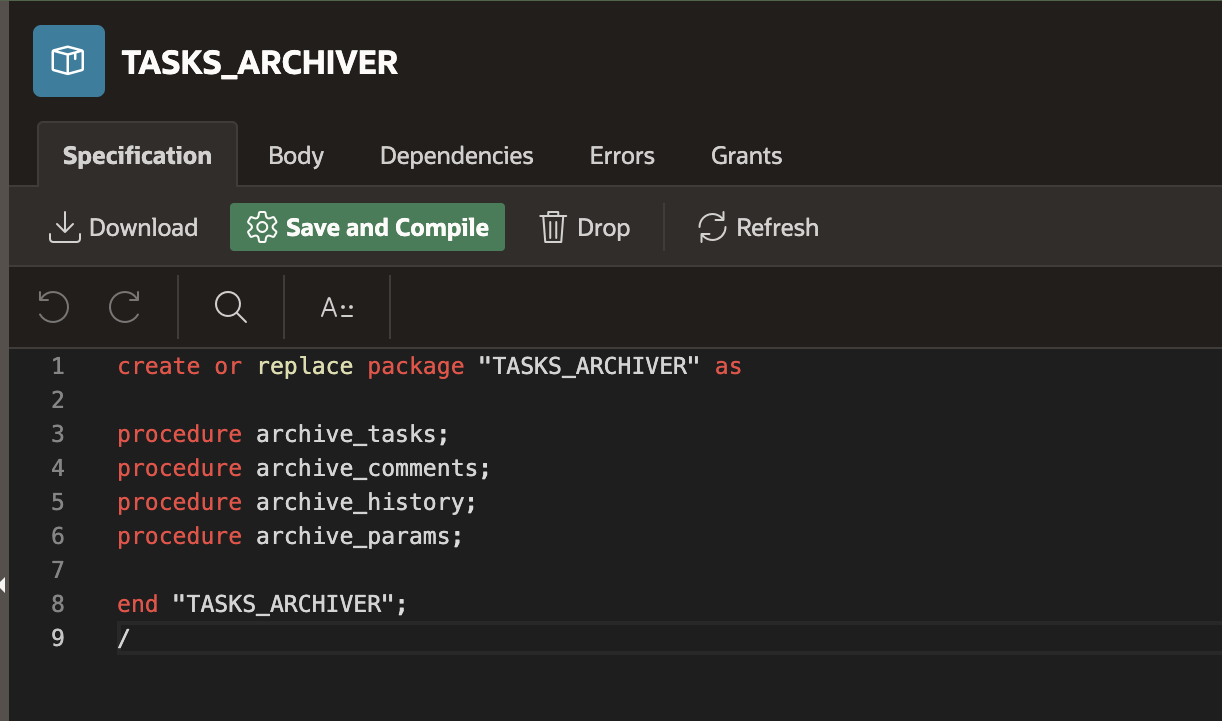
9. In the Body editor, enter the following code:
create or replace package body "TASKS_ARCHIVER" as procedure archive_tasks is begin merge into archived_tasks at using apex_purgeable_tasks t on (at.task_id = t.task_id) when not matched then insert (at.task_id, at.workspace_id, at.workspace, at.application_id, at.application_name, at.task_def_name, at.task_def_static_id, at.task_def_id, at.state, at.subject, at.task_type_code, at.state_code, at.initiator, at.detail_pk, at.outcome_code, at.due_on, at.priority, at.created_on) values ( t.task_id, t.workspace_id, t.workspace, t.application_id, t.application_name, t.task_def_name, t.task_def_static_id, t.task_def_id, t.state, t.subject, t.task_type_code, t.state_code, t.initiator, t.detail_pk, t.outcome_code, t.due_on, t.priority, t.created_on); end archive_tasks; procedure archive_comments is begin merge into archived_task_comments at using apex_purgeable_task_comments t on (at.task_id = t.task_id) when not matched then insert (at.task_id, at.workspace_display_name, at.workspace, at.application_id, at.application_name, at.text, at.created_by, at.created_on) values ( t.task_id, t.workspace_display_name, t.workspace, t.application_id, t.application_name, t.text, t.created_by, t.created_on); end archive_comments; procedure archive_history is begin merge into archived_task_history at using apex_purgeable_task_history t on (at.task_id = t.task_id) when not matched then insert (at.task_id, at.workspace_display_name, at.workspace, at.application_id, at.application_name, at.event_type_code, at.event_type, at.event_creator, at.event_timestamp, at.old_state_code, at.new_state_code, at.old_actual_owner, at.new_actual_owner, at.old_priority, at.new_priority, at.old_due_on, at.new_due_on, at.action_name, at.action_status, at.action_timestamp, at.success_msg, at.failure_msg, at.alternate_participants, at.participant_changed_reason, at.outcome, at.display_msg) values ( t.task_id, t.workspace_display_name, t.workspace, t.application_id, t.application_name, t.event_type_code, t.event_type, t.event_creator, t.event_timestamp, t.old_state_code, t.new_state_code, t.old_actual_owner, t.new_actual_owner, t.old_priority, t.new_priority, t.old_due_on, t.new_due_on, t.action_name, t.action_status, t.action_timestamp, t.success_msg, t.failure_msg, t.alternate_participants, t.participant_changed_reason, t.outcome, t.display_msg); end archive_history; procedure archive_params is begin merge into archived_task_parameters at using apex_purgeable_task_parameters t on (at.task_id = t.task_id) when not matched then insert (at.task_id, at.task_def_param_id, at.workspace_display_name, at.workspace, at.application_id, at.application_name, at.param_label, at.param_static_id, at.is_required, at.is_visible, at.is_updatable, at.param_value) values ( t.task_id, t.task_def_param_id, t.workspace_display_name, t.workspace, t.application_id, t.application_name, t.param_label, t.param_static_id, t.is_required, t.is_visible, t.is_updatable, t.param_value); end archive_params; end "TASKS_ARCHIVER"; /
10. Click on Save and Compile
11. Navigate to Object Browser > Packages and right click on Create Package. Enter name as WORKFLOWS_ARCHIVER.
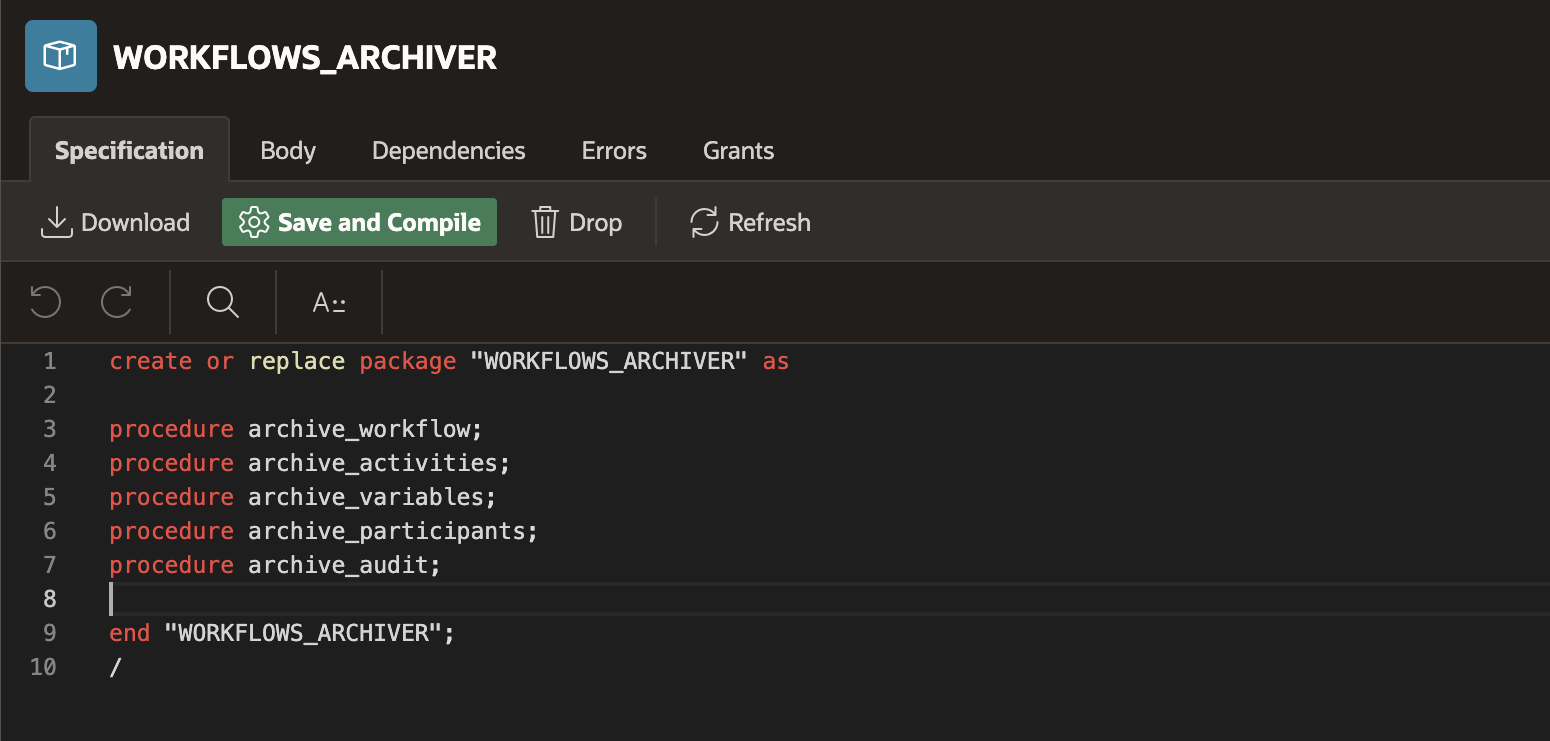
12. In the Specification Editor, enter the following code:
create or replace package "WORKFLOWS_ARCHIVER" as procedure archive_workflow; procedure archive_activities; procedure archive_variables; procedure archive_participants; procedure archive_audit; end "WORKFLOWS_ARCHIVER"; /
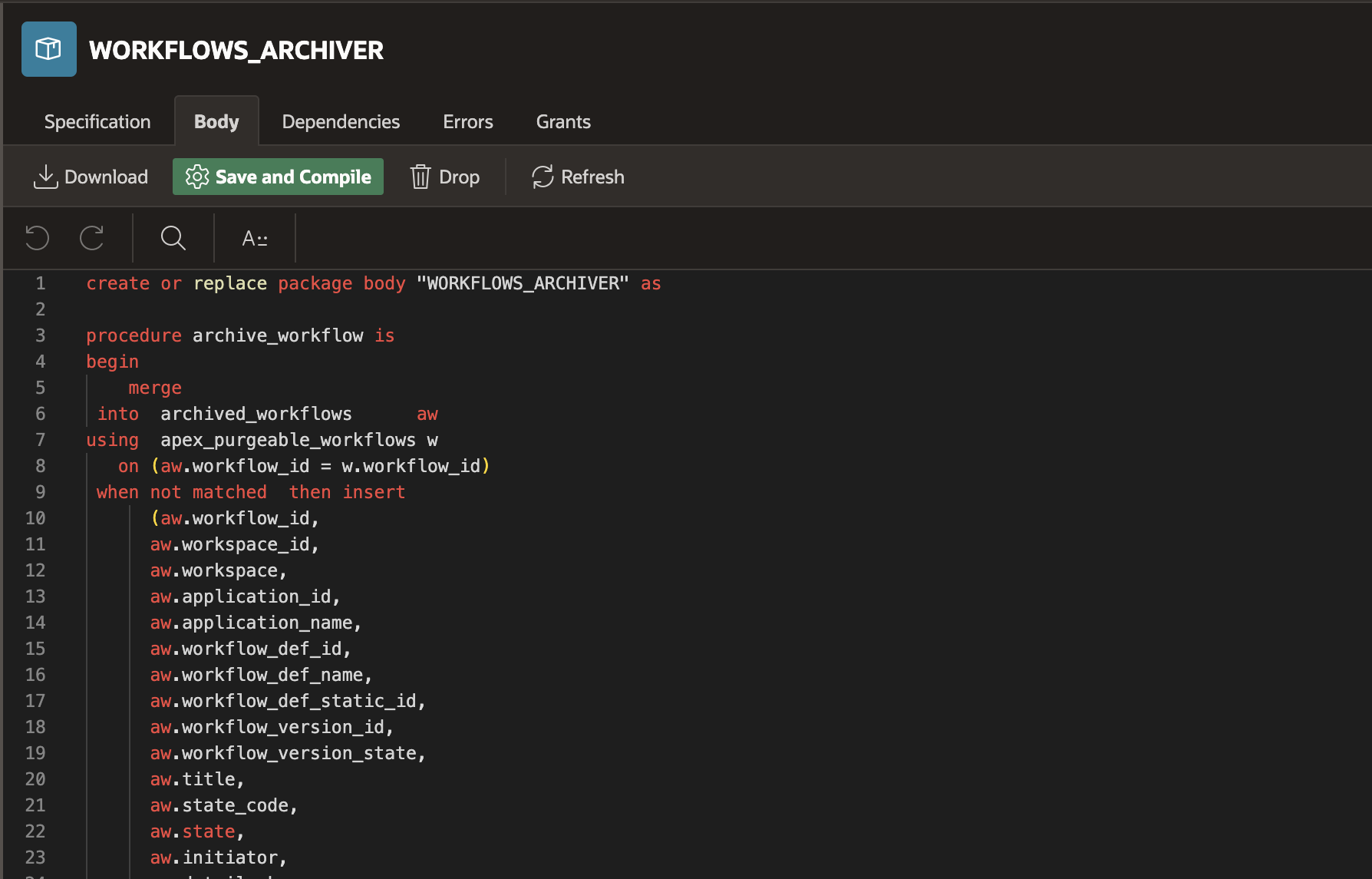
13. In the Body editor, enter the following code:
create or replace package body "WORKFLOWS_ARCHIVER" as procedure archive_workflow is begin merge into archived_workflows aw using apex_purgeable_workflows w on (aw.workflow_id = w.workflow_id) when not matched then insert (aw.workflow_id, aw.workspace_id, aw.workspace, aw.application_id, aw.application_name, aw.workflow_def_id, aw.workflow_def_name, aw.workflow_def_static_id, aw.workflow_version_id, aw.workflow_version, aw.workflow_version_state, aw.title, aw.state_code, aw.state, aw.initiator, aw.detail_pk, aw.is_dev_mode, aw.start_time, aw.end_time) values ( w.workflow_id, w.workspace_id, w.workspace, w.application_id, w.application_name, w.workflow_def_id, w.workflow_def_name, w.workflow_def_static_id, w.workflow_version_id , w.workflow_version, w.workflow_version_state, w.title, w.state_code, w.state, w.initiator, w.detail_pk, w.is_dev_mode, w.start_time, w.end_time); end archive_workflow; procedure archive_activities is begin merge into archived_wf_activities aw using apex_purgeable_wf_activities w on (aw.workflow_id = w.workflow_id) when not matched then insert (aw.workflow_id, aw.workspace_id, aw.workspace, aw.application_id, aw.application_name, aw.workflow_def_id, aw.workflow_def_name, aw.workflow_def_static_id, aw.workflow_version_id, aw.workflow_version, aw.workflow_version_state, aw.workflow_state, aw.name, aw.static_id, aw.label, aw.type_code, aw.activity_id, aw.state, aw.due_on, aw.error_message, aw.retry_count, aw.start_time, aw.end_time, aw.previous_id) values ( w.workflow_id, w.workspace_id, w.workspace, w.application_id, w.application_name, w.workflow_def_id, w.workflow_def_name, w.workflow_def_static_id, w.workflow_version_id , w.workflow_version, w.workflow_version_state, w.workflow_state, w.name, w.static_id, w.label, w.type_code, w.activity_id, w.state, w.due_on, w.error_message, w.retry_count, w.start_time, w.end_time, w.previous_id); end archive_activities; procedure archive_variables is begin merge into archived_wf_variables aw using apex_purgeable_wf_variables w on (aw.workflow_id = w.workflow_id) when not matched then insert (aw.workflow_id, aw.workspace_id, aw.workspace, aw.application_id, aw.application_name, aw.workflow_def_id, aw.workflow_def_name, aw.workflow_def_static_id, aw.workflow_version_id, aw.workflow_version, aw.workflow_version_state, aw.workflow_state, aw.static_id, aw.label, aw.data_type_code, aw.is_required, aw.variable_type, aw.variable_id, aw.direction, aw.activity_id, aw.display_value, aw.string_value, aw.number_value, aw.boolean_value, aw.timestamp_value, aw.timestamp_tz_value, aw.timestamp_ltz_value) values ( w.workflow_id, w.workspace_id, w.workspace, w.application_id, w.application_name, w.workflow_def_id, w.workflow_def_name, w.workflow_def_static_id, w.workflow_version_id , w.workflow_version, w.workflow_version_state, w.workflow_state, w.static_id, w.label, w.data_type_code, w.is_required, w.variable_type, w.variable_id, w.direction, w.activity_id, w.display_value, w.string_value, w.number_value, w.boolean_value, w.timestamp_value, w.timestamp_tz_value, w.timestamp_ltz_value); end archive_variables; procedure archive_participants is begin merge into archived_wf_participant aw using apex_purgeable_wf_participant w on (aw.workflow_id = w.workflow_id) when not matched then insert (aw.workflow_id, aw.workspace_id, aw.workspace, aw.application_id, aw.application_name, aw.workflow_version_id, aw.participant, aw.participant_type_code, aw.last_updated_by, aw.last_updated_on) values ( w.workflow_id, w.workspace_id, w.workspace, w.application_id, w.application_name, w.workflow_version_id, w.participant, w.participant_type_code, w.last_updated_by, w.last_updated_on); end archive_participants; procedure archive_audit is begin merge into archived_wf_audit aw using apex_purgeable_wf_audit w on (aw.workflow_id = w.workflow_id) when not matched then insert ( aw.audit_id, aw.workflow_id, aw.workspace_id, aw.workspace, aw.application_id, aw.application_name, aw.workflow_def_id, aw.workflow_def_name, aw.workflow_def_static_id, aw.workflow_version_id, aw.workflow_version, aw.workflow_version_state, aw.state_code, aw.state, aw.action_code, aw.action, aw.is_dev_mode, aw.initiator, aw.current_activity_id, aw.current_activity_state, aw.changed_variable_id, aw.old_variable_value, aw.new_variable_value, aw.display_msg, aw.created_on, aw.created_by) values ( w.audit_id, w.workflow_id, w.workspace_id, w.workspace, w.application_id, w.application_name, w.workflow_def_id, w.workflow_def_name, w.workflow_def_static_id, w.workflow_version_id , w.workflow_version, w.workflow_version_state, w.state_code, w.state, w.action_code, w.action, w.is_dev_mode, w.initiator, w.current_activity_id, w.current_activity_state, w.changed_variable_id, w.old_variable_value, w.new_variable_value, w.display_msg, w.created_on, w.created_by); end archive_audit; end "WORKFLOWS_ARCHIVER"; /
14. Click on Save and Compile to compile the package.
Create Automations in your Application
Navigate to App Builder > Workflow Archiver App > Shared Components > Workflows and Automations
Create the Tasks Archiver Automation
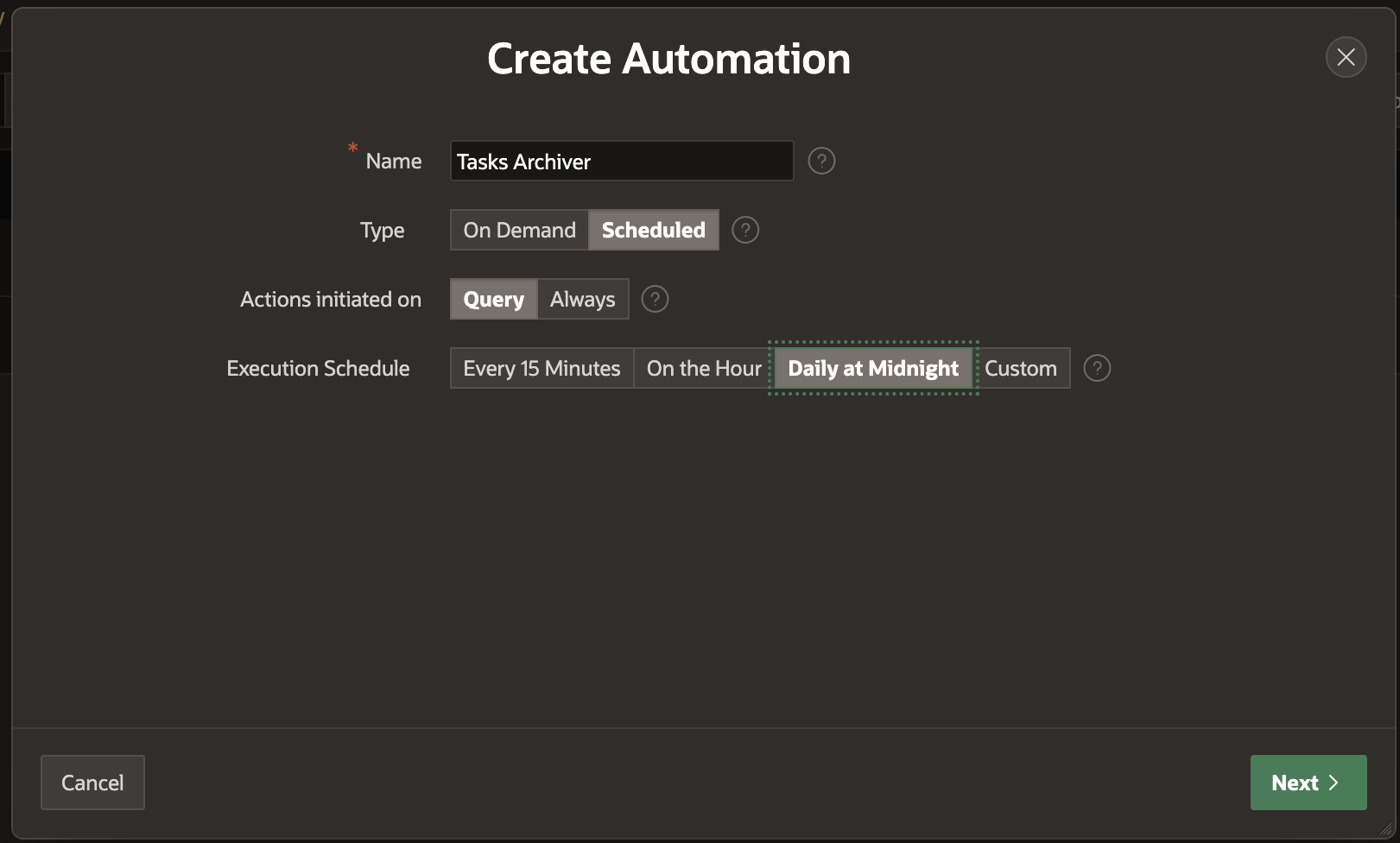
Click on Create to launch the Create Automation Wizard and enter the details as shown below
- Name: Tasks Archiver
- Type: Scheduled
- Actions Initiated On: Query
- Execution Schedule: Daily at Midnight
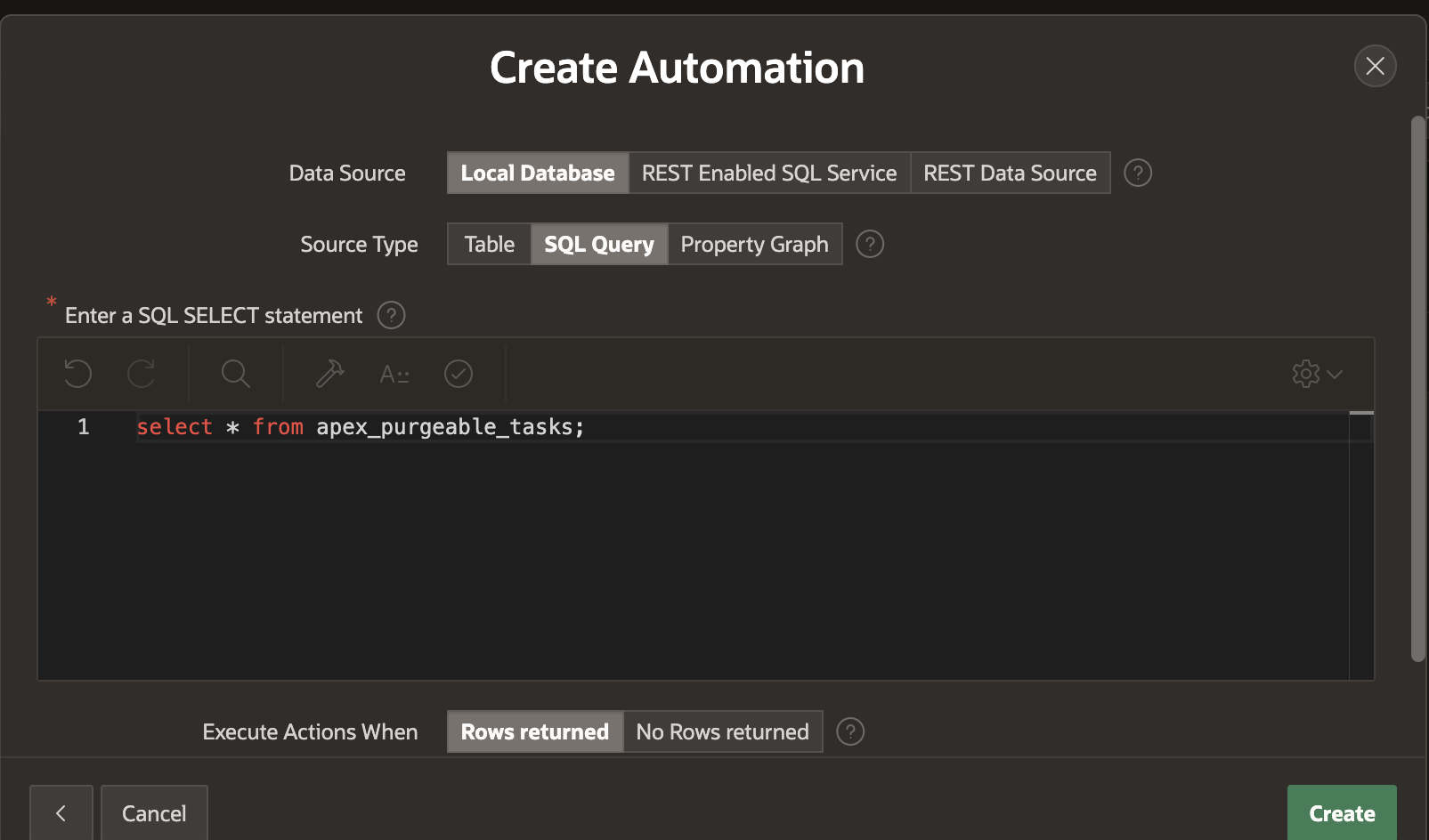
Click on Next and enter the details in the next screen as shown below
- Data Source: Local Database
- Source Type: SQL Query
- In the code editor enter:
select * from apex_purgeable_tasks;
4. Click on Create
In the Automation Edit Page, click on the Actions tab and edit the New Action as shown below
- Name: Archive Tasks
- Type: Execute Code
- Code:
begin tasks_archiver.archive_tasks; tasks_archiver.archive_params; tasks_archiver.archive_comments; tasks_archiver.archive_history; end;
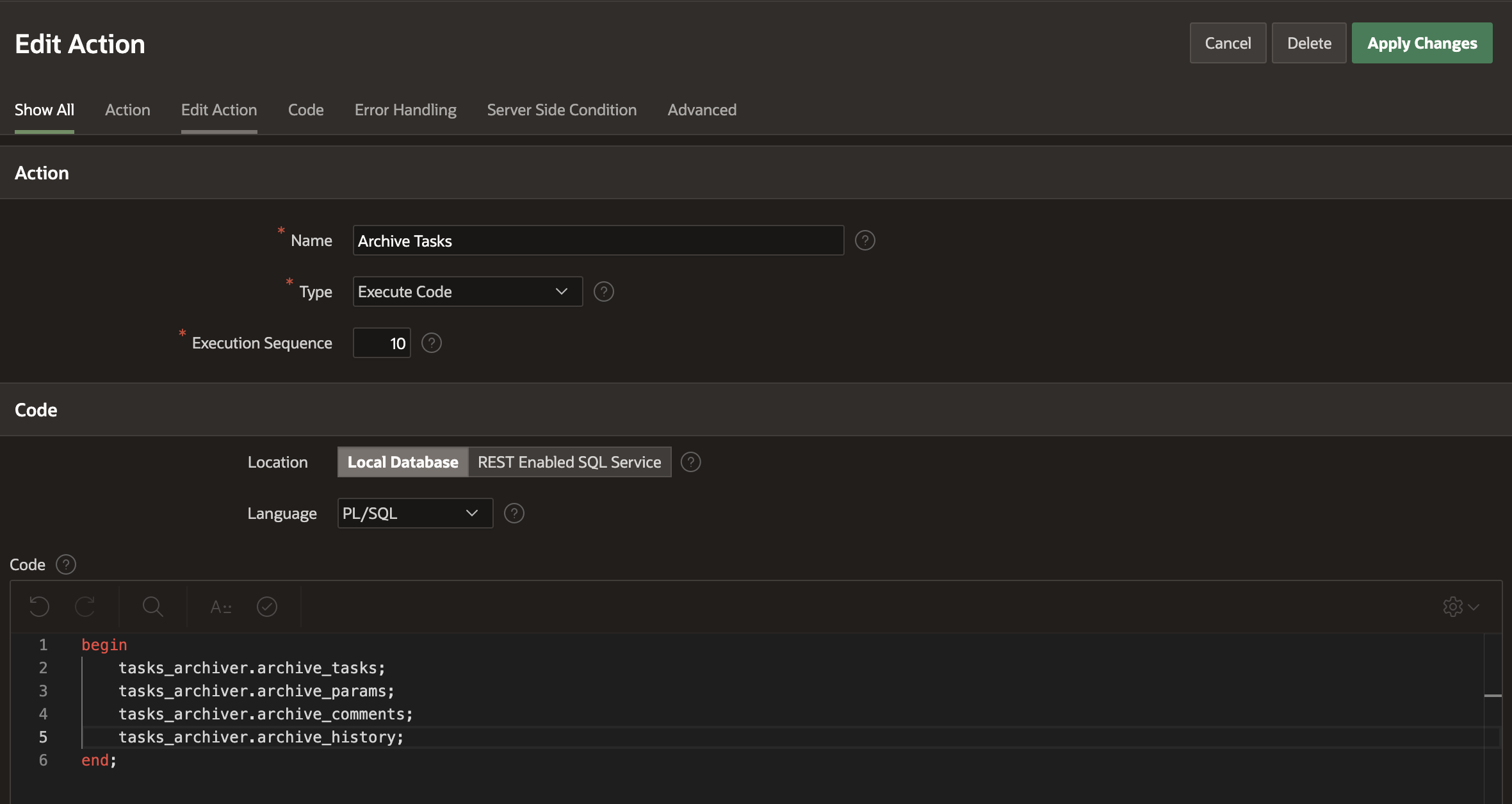
4. Click on Apply Changes.
5. In the Edit Automation Page, change the Scheduled Status in the Settings Section to Active from Disabled.
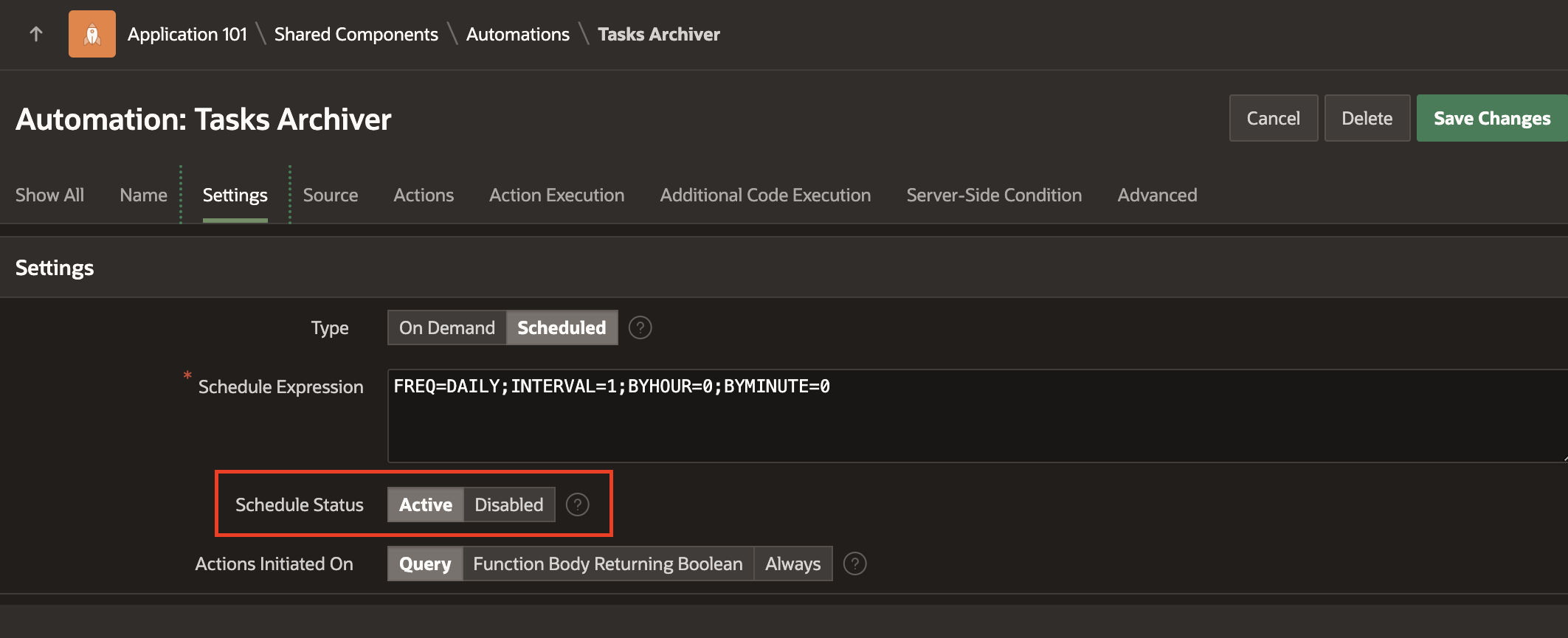
6. Click on Save Changes
Create the Workflow Archiver Automation
Repeat the steps above to create another Automation for archiving the purgeable workflows. Name the automation Workflow Archiver.
For the Automation Source use the following code:
select * from apex_purgeable_workflows;
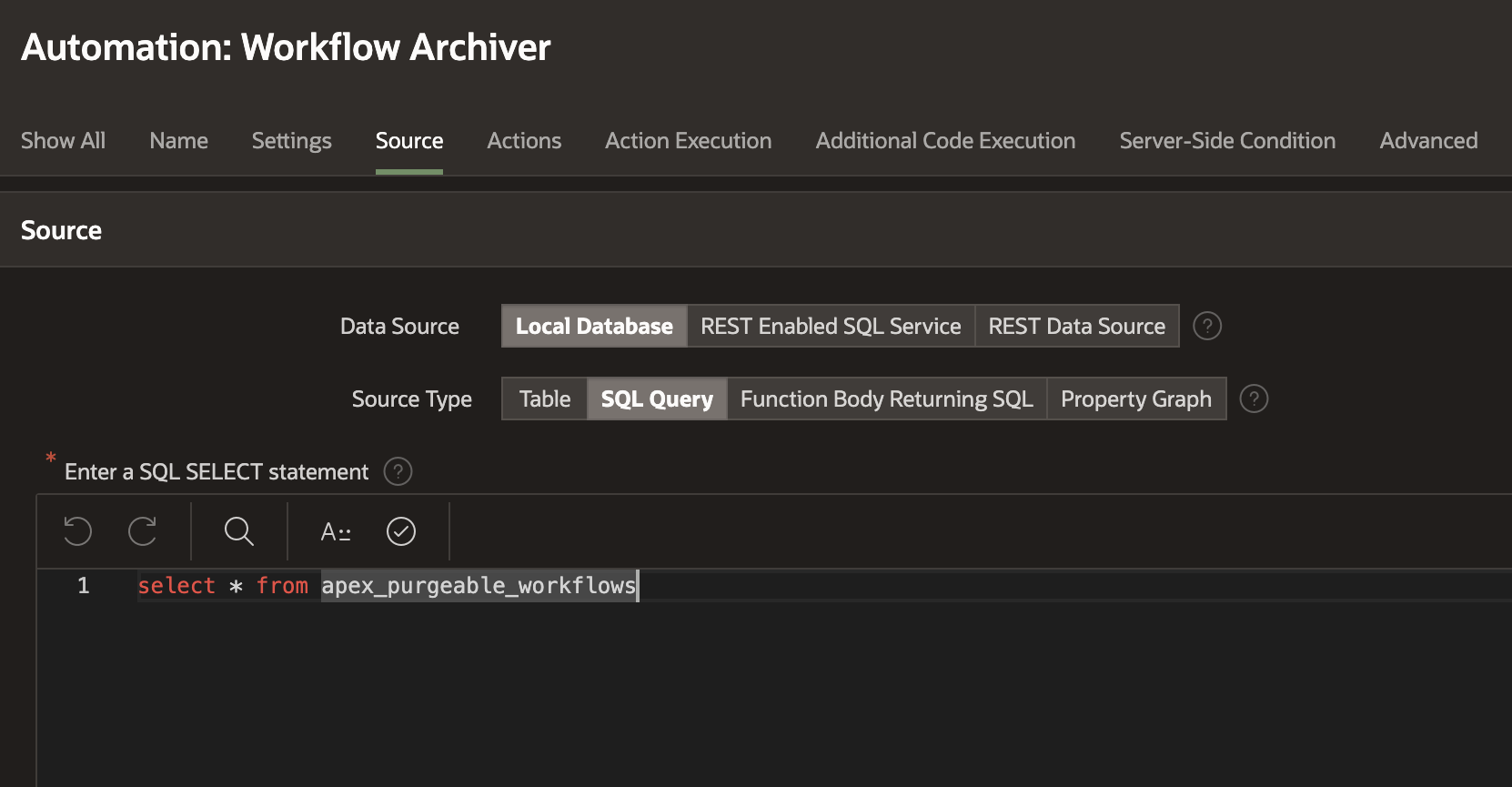
For the Automation Action, enter the following code
begin workflows_archiver.archive_workflow; workflows_archiver.archive_activities; workflows_archiver.archive_variables; workflows_archiver.archive_participants; workflows_archiver.archive_audit; end;
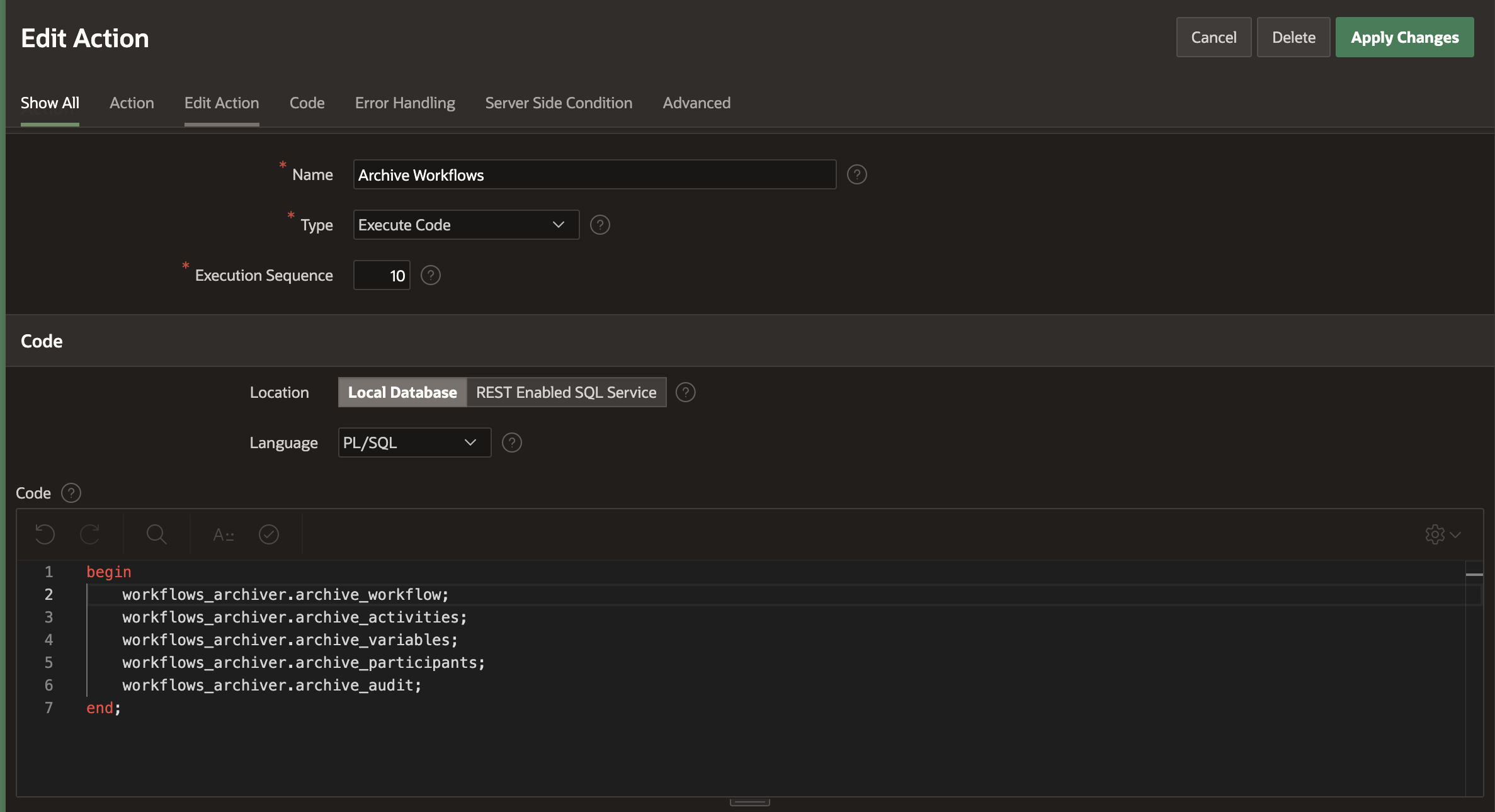
Save your changes. The Automations Page should show both the automations in Active state.
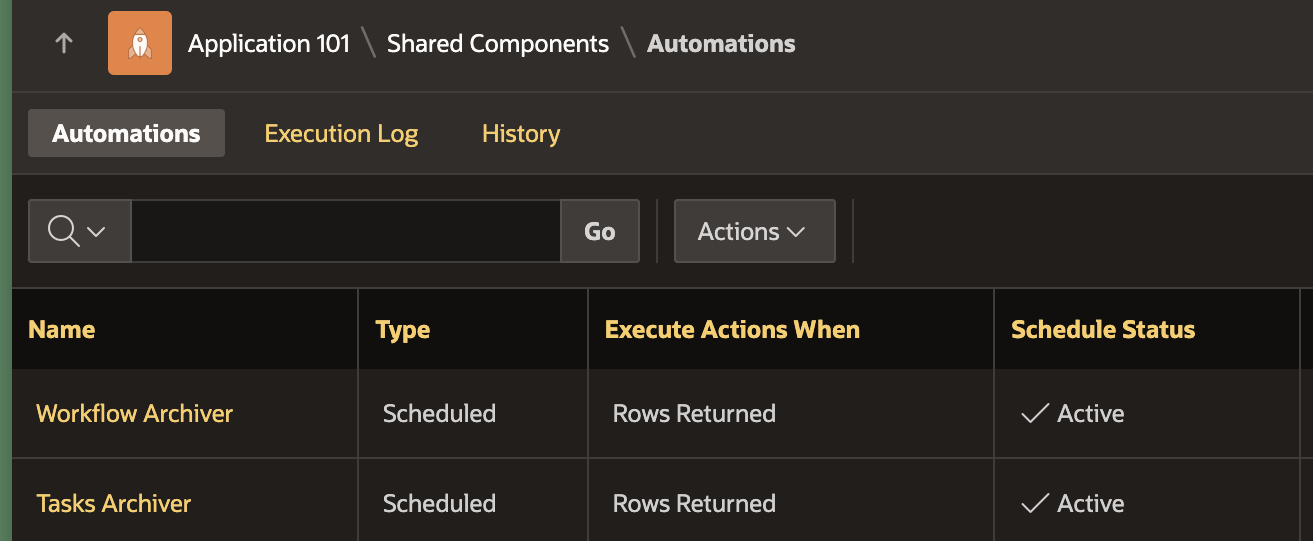
Run the Automations
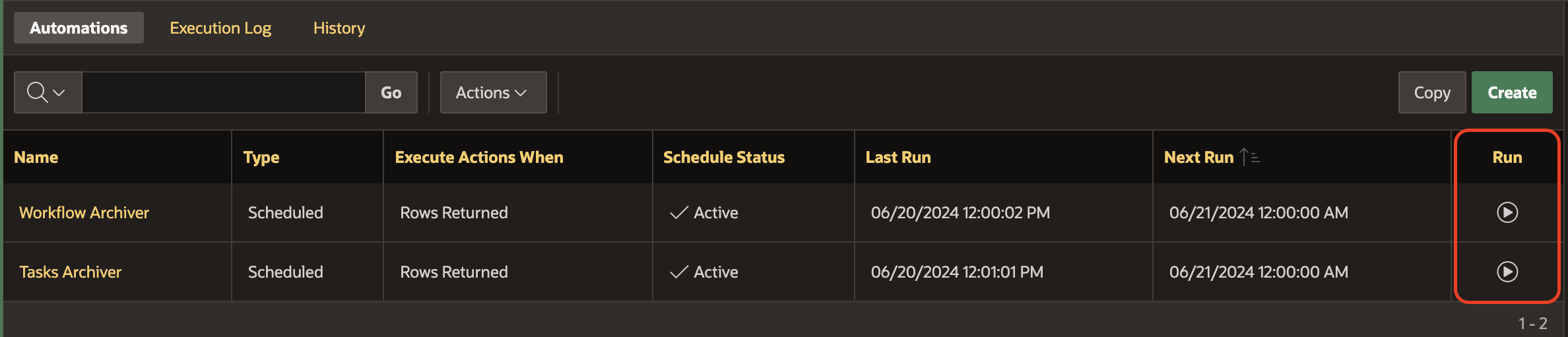
- Although the automations are now scheduled, you might want to test them to see if they run successfully.
- Click on the ► button to Run both automations one after the other.
Check the Execution Log to see the result of the execution.
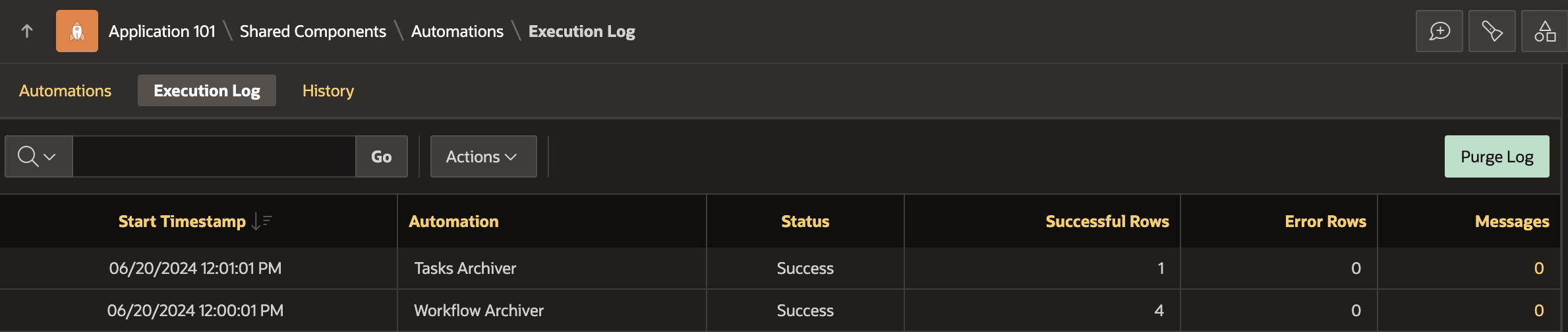
The status is Success for both automation executions which means that when these automations are executed at the scheduled hour, they will ensure that the workflows and task instances are successfully copied to the user schema (the tables created earlier) before they get purged by the auto purge jobs running.
Viewing the archived instance data
You can create Interactive Reports / Classic Reports or any other viewing option of your choice on top of the ARCHIVE_* tables created earlier. The automation executions will ensure that these tables have the workflow and human task instance data before they get purged from APEX.
The image below shows an interactive report created on top of the ARCHIVED_TASKS and ARCHIVED_TASK_HISTORY tables.
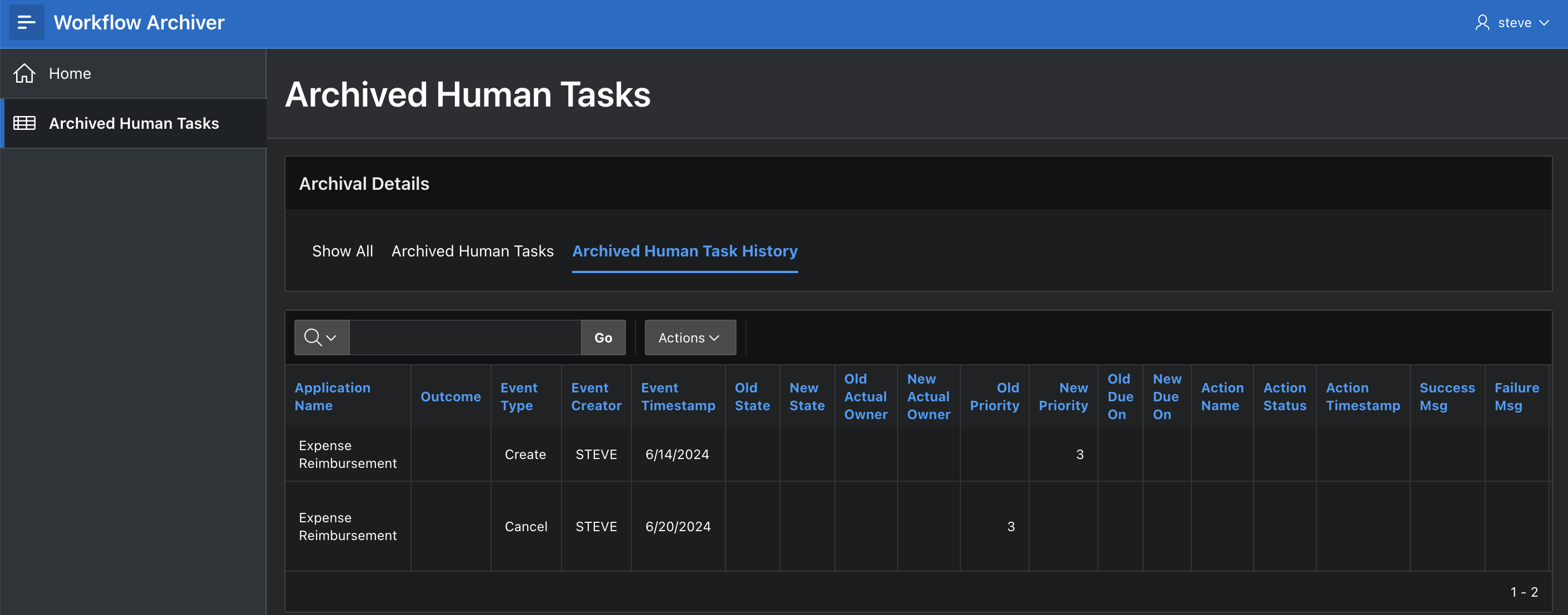
Create similar reports on the other ARCHIVED_TASKS_* and ARCHIVED_WORKFLOWS tables to view the archived instance data.
Key Takeaways
- With this blog, we now know how to automate the transfer of purgeable workflow and task instances to the user schema.
- The above steps were just one way of wrting the automations. You can also choose to create a single automation that takes care of both human task and workflow instances.
That’s all for now. Stay tuned for more interesting blogs on all the cool features in APEX 24.1
