Why this matters now
Hospitals and care teams are under pressure to do more with less: expand virtual care, improve chronic disease outcomes, reduce readmissions, and meet strict security requirements. At the same time, clinical data is exploding from ECG patches and continuous glucose monitors to DICOM imaging and EHR events. The question isn’t “do we have data?” It’s “can we turn it into safe, actionable insight at the point of care?”
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) gives health systems a practical path to do exactly that. OCI provides predictable performance, end-to-end SLAs, secure networking and first-party analytics/AI services that fit healthcare reality: hybrid by design, standards based and cost efficient. In this post, I outline a reference IoMT (Internet of Medical Things) workflow on OCI from sensor to signal to insight and the outcomes it unlocks.
What counts as a “wearable” in clinical workflows?
Wearable health devices are patient-worn sensors that continuously monitor physiological signals and transmit them for analysis such as:
- ECG patches (arrhythmia detection)
- Continuous glucose monitors (CGM)
- Smart rings and watches (SpO₂, temperature, HRV, sleep)
- Home blood-pressure cuffs and weight scales
- Connected hearing aids and respiratory monitors
In a clinical context, the value isn’t the gadget, it’s the signal quality, reliability and workflow integration: FHIR/HL7 interoperability, audit trails, role-based access and the ability to blend telemetry with imaging, labs and notes for a 360° view.
Typical IoMT System Architecture
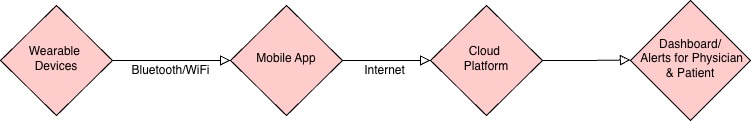
- Wearable sensors detect health signals (e.g., ECG, glucose, temperature).
- Microcontroller or Bluetooth module processes and transmits data.
- Smartphone/gateway device aggregates, formats, and uploads data to the cloud.
- Cloud servers provide analysis, long-term storage, and machine learning-based insights.
- Healthcare professionals and patients receive processed data, alerts, and actionable insights in real time.
OCI IoMT Workflow steps
Here are the OCI recommended steps and products that can be leveraged in building IoMT workflow:
- Data Capture at the Edge: Wearable IoMT devices (e.g. ECG patches, smart glucometers) continuously collect patient vital signs (heart rhythm, blood pressure, glucose levels, etc.) at the point of care in real time.
- Secure Cloud Data Ingestion: Device readings are securely transmitted from the patient’s environment to OCI, often via a smartphone app or IoT gateway. Oracle’s IoT services and API Gateway ensure encrypted, reliable streaming data ingestion into the cloud.
- Scalable Storage and Processing: Once in OCI, the data lands in scalable storage (e.g. Object Storage or Autonomous Data Warehouse) and is processed through both streaming and batch pipelines. OCI can ingest massive volumes of structured or unstructured health data and use stream processing (like Oracle Stream Analytics) for real-time event analysis, while also persisting data in data lakes or databases for historical analytics and integration with electronic health records (EHR).
- AI/ML Analysis: OCI’s integrated AI/ML services (Data Science, Oracle Machine Learning, etc.) analyze the health data to detect anomalies and predict events. Machine learning models running on high-performance compute (GPUs/CPUs) can identify patterns (for example, flagging an impending heart failure episode or irregular heart rhythm before clinical symptoms appear). Trained models are deployed as APIs or built into analytics dashboards, enabling proactive care through early warnings.
- Real-Time Alerts and Dashboards: Insights are delivered via live dashboards and alerting systems. OCI’s analytics tools (e.g. Oracle Analytics Cloud with Stream Analytics) power real-time clinical dashboards showing current patient metrics, trends, and AI predictions. Clinicians receive instant alerts if a vital sign crosses a critical threshold or if a model predicts a high-risk event.
- Integration with Healthcare Systems: OCI enables interoperability by integrating IoMT data with existing healthcare systems. Data from wearables and remote monitors is unified with EHR records, lab results, and other clinical data, eliminating silos. This allows IoMT-generated insights to be viewed in context with a patient’s medical history and seamlessly incorporated into clinical workflows, which is critical for provider adoption.
- Security and Compliance: End-to-end security is built into every stage. Data is encrypted in transit to OCI and at rest in storage, and access is tightly controlled via identity management and network isolation (VPCs, VPNs, etc.). Oracle’s cloud infrastructure is HIPAA-audited (with the necessary BAA in place) and compliant with healthcare regulations, so Protected Health Information (PHI) can be processed safely. Tools like Oracle Data Safe and audit logs further ensure that sensitive data is accessed only by authorized parties, providing a robust, healthcare-grade cloud environment for IoMT workloads.
Key Benefits of OCI Enabled IoMT
- Proactive Chronic Care: Continuous monitoring via wearables allows early intervention for chronic conditions, reducing hospitalizations.
- Faster, Preventive Diagnosis: AI-powered analysis of real-time data helps detect issues before symptoms appear.
- Secure & Compliant: OCI ensures HIPAA-compliant data protection with built-in encryption and access controls.
- Cost-Efficient Care: Remote monitoring and automation lower healthcare costs and optimize clinical workflows.
- Patient Engagement: Real-time insights empower patients to take control of their health and improve outcomes.
High-Level OCI Healthcare Workflow Summary
From patient interactions to digital imaging and clinical history, all data is centralized.

- Medical images and patient records move securely from on-premises PACS (picture archiving & communication system) to OCI.
- Diverse healthcare data is ingested and stored in scalable OCI services.
- Data undergoes preparation via ETL pipelines for analytics readiness.
- Data scientists train AI/ML models using notebooks, then deploy models as APIs.
- AI models assist clinicians by analyzing data for diagnoses or alerting care teams.
- Data is accessed by clinicians and staff through secure dashboards, facilitating rapid care decisions.
- Comprehensive enterprise-grade security ensures HIPAA compliance and protects sensitive data.
IoMT Integration Architecture for Healthcare in OCI
The diagram below illustrates a robust framework for integrating Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) device data into your healthcare analytics platform on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).

Conclusion
Wearable health devices and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) are ushering in a new era of data-driven, patient-centered healthcare. These technologies are already making a tangible difference in patients’ lives, giving people better control over their health and improving communication with providers and they enable clinicians to make better diagnoses in less time, often without an in-person visit. The combination of continuous sensing, connectivity, and intelligent cloud analytics is transforming how we manage health and disease.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure plays a pivotal role in this transformation by providing the robust cloud services needed to fully leverage wearables and IoMT at scale. OCI’s strengths in secure data ingestion, scalable storage, AI/ML processing, and real-time analytics allow healthcare organizations to turn an avalanche of device data into meaningful clinical action. With OCI, hospitals and health systems can implement integrated workflows that support chronic care management, enable early diagnosis and intervention, ensure compliance with health regulations, reduce the cost of care delivery, and empower patients – all within a unified, cloud-based ecosystem.
Sign up for the Free Tier of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and experience what works best for your organization.
For more information, see the following resources:
