In this blog post, we’ll look at using generative AI (Gen AI) to assist buyers and procurement executives in doing supplier risks assessment. This post highlights how generative AI can provide key information in this process, helping assess the risks and potential challenges across financial, operational, regulatory, and other critical areas for a comprehensive understanding of supplier risks and their potential impacts.
Data Gathering
We can pull in the audited financial information using third party services like Yahoo Finance and Alpha Vantage for publicly listed companies. These provide us with a company’s financials, with key finance parameters including total revenue, net income, EBIT, EPS, write-offs etc. We can also request that suppliers provide us with their last few years of audited financial statements, including balance sheet statement, income statement, and cash flow statement. These statements can be fed to Oracle 23.ai Vector Store using an OCI embeddings model.
Analysis using Gen AI
Once we capture the financial information and other relevant data, we make use of LLMs and the OCI Generative AI chat interface to seek detailed analysis on the collected information.
We define a prompt template as specified in the example below to do financial analysis on the collected financial information.
Given the {context} information please perform the below task and provide the response.
Please respond only in English.
Task
—–
Analyse the provided financial data.
Compare the financial between the quarters and years ,noting any significant movements or trends.
Analyse the debt to equity , debt to asset,EBITDA,Days of Payables Outstanding(DPO) and Day Sales Outstanding (DSO) with derived values.
Evaluate the implications of these movements for the company’s financial health and operation efficiency.
From the perspective of a company receiving services from this company highlight key risks for this purchaser
based on what you have gathered from the financials.
Please respond only in English.
“””
The financial information collected earlier is fed as context along with above prompt to provide us a preliminary analysis on the financial information.
Supplier Risk Assessment
Supplier risk refers to the potential adverse effects that may result from dependence on or association with suppliers or third-party providers of goods and services. These risks can impact a company’s operations, financial stability, reputation, and regulatory compliance. We can define the risk criteria for assessing both current and potential suppliers, common supplier risks can fall into below listed dimensions:
- Financial risks
- Operational risks
- Regulatory and compliance risks
- Geopolitical risks
- Ethical & environmental, social & governance risks
- Reputational risks
Once the preliminary analysis is performed on the collected financial data, we can use generative AI to do the assessment and seek insight on risks across the above parameters.
The common prompt template used to raise the queries to the designated LLM is:
The previous analysis response from the LLM is fed in as context to the above template, along with supplier name and the relevant question or query. For example, to see financial risks, the question below is set to the prompt template to provide us the response from the LLM:
Here’s a sample response based on the above analysis and query from the LLM:

Similarly, the LLM can discover insights and relevant information used to determine the risks around other parameters.
Here are a few additional questions for seeking information from LLM:
Please note that Gen AI analysis is only as good as its input and that users should consider many factors when making risk assessments.
Supplier Performance
Supplier performance management is critical in ensuring that suppliers are meeting the organization’s requirements and expectations. While assessing the operation risks, if we are dealing with existing suppliers, we can also consider past performance. The supplier’s delivery performance is measured for these KPIs:
- Delivery On Time in Full
- Delivery in Full
- Delivery on Time
- Quality Measure with Quantity Accepted Post Inspection
- Quality Measure with Quantity Rejected Post Inspection
Risks Scoring
Risk scores can vary in detail, but generally assess two main factors: the probability or likelihood of a risk occurring, and the severity of its potential impact.
While the risk likelihood can include labels such as “negligible”, “very high”, or “critical”, a straightforward and common approach is to rank risks simply as “low”, “medium”, or “high”.
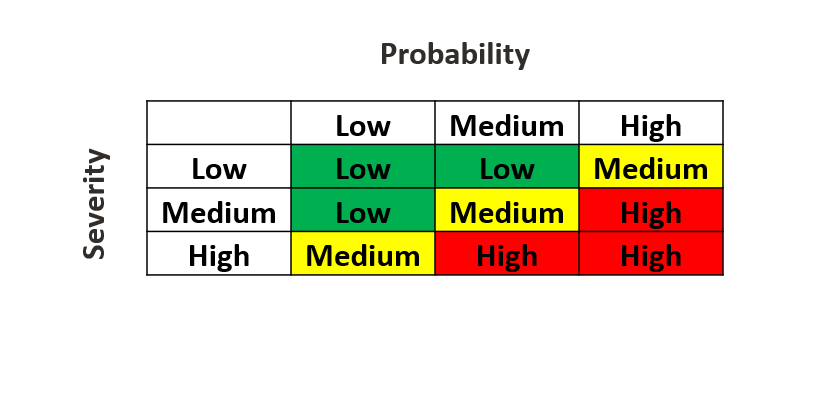
Based on the insights and relevant information across various aspects of procurement, the executive determines the probability and severity of the identified risks to arrive at a net risk score for the said supplier.
The integer values attributed for the risk level are as follows.
Low = 1
Medium = 2
High = 3
Low = 1
Medium = 2
High = 3
The final risk score is arrived at using the formula:
Risk Score = Risk Probability * Risk Severity
| S No |
Risk |
Probability |
Severity |
Score |
| 1 |
Financial Risks |
Medium |
High |
6 |
| 2 |
Operational Risks |
Low |
Medium |
2 |
| 3 |
Regulatory Risks |
Medium |
High |
6 |
| 4 |
Geopolitical Risks |
Low |
Medium |
2 |
| 5 |
Ethical Risks |
Low |
Medium |
2 |
| 6 |
Reputational Risks |
Low |
Medium |
2 |
The net risk score for XXX Inc is: 20.
Conclusion
Generative AI can transform supplier risk assessment by automating data analysis and risk scoring. By leveraging LLMs and AI-driven insights, procurement executives can make informed decisions with greater efficiency and accuracy. The ability to assess risks across financial, operational, regulatory, and other critical areas provides a comprehensive view of supplier stability. With a structured approach to risk scoring, organizations can proactively mitigate potential threats and create a more resilient supply chain. As AI continues to evolve, its role in procurement and risk management will only become more valuable, helping businesses to stay ahead in an increasingly complex global market.
