This is part – 2 of our blog: “Generative AI and its use cases for enterprise applications”. In our previous blog, we talked about Generative AI in general and listed various use cases where Generative AI can be applied. We also discussed what tools are available on OCI around Generative AI and why OCI is best positioned to help you develop your next Generative AI solutions. In this blog we will pick one Generative AI use case and discuss solution architecture by leveraging the tools and services available on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
Use case: AI Knowledge Assistant
Background & Description:
Almost every organization has dozens of documentations related to their business processes such as purchase agreements or internal processes such as policies, how-to-guides, FAQs, etc. Whether you need one question answered or 10 questions, you still need to go through the full document to get your answer. An AI assistant which knows all this data can answer questions much faster and effectively thereby significantly reducing the amount of time spent by an employee and reducing human mistakes.
Solution:
This is where AI assistant can help as it can abstract the complexity and reduce the overall effort and time needed from the user. In this solution, we will store the knowledge documents in a repository. This repository can be either an object store or a document db. Next, we will ingest all the documents, create chunks and store these chunks into a vector db. This process is called embedding. The Vector DB can be Oracle Database 23ai or a managed open-source database like OCI Search with OpenSearch. Once this process is done, OCI Generative AI Agents service is ready to answer queries from users. These queries can be made via OCI console, REST APIs, SDKs or CLIs. You can also integrate OCI Generative AI Agents Service with Oracle Digital Assistant (ODA) and provide a chatbot interface as a front end. ODA provide the NL2SQL capabilities using which users can interact with the Generative AI Model using Natural Language. Alternatively, you can create a front-end using Application Development Platforms like Oracle APEX, Oracle Visual Builder Cloud Service or even your homegrown application and call the corresponding REST APIs to interact with the OCI Generative AI Agents service. The OCI Generative Agents Service will also leverage OCI Cache which uses Redis/Valkey behind the scenes to cache user interactions that will allow the model to maintain chat history and retain the context for better responses.
When the user submits a query to the generative ai agent, users request is chunked and embedded, and a similarity search is done within the vector database to retrieve the most closely matching vectors from the database. These vectors are then used to enhance the users query with relevant information. The augmented or enhanced query that is called as the prompt. This prompt is then passed on to the LLM for generating a response which is then displayed to the user [illustrated in Fig 2].
See couple of examples in our AI Solution Hub
- Transform Customer Engagement and Business Processes with Oracle AI Solutions
- Create a Knowledge Assistant with AI Vector Search in Oracle Database 23ai
- Deploy an Oracle Digital Assistant Chatbot Powered by OCI Generative AI Agents
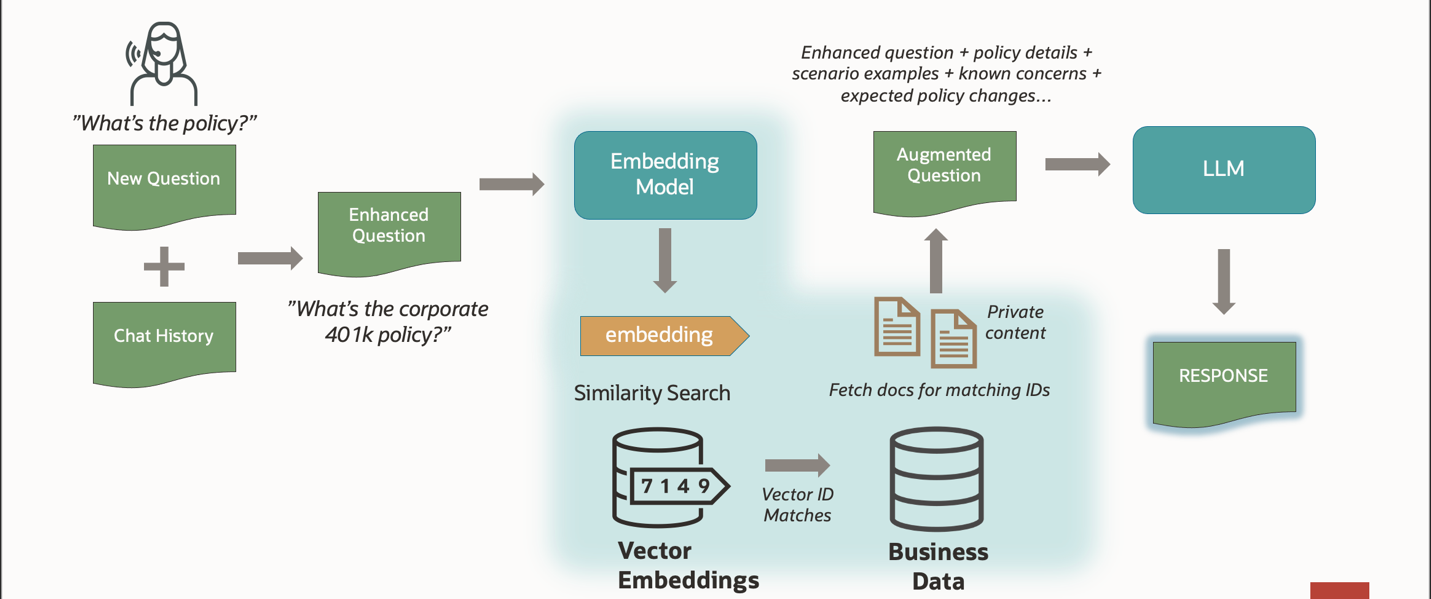
Figure 1: How does vector search work?
Components:
- OCI Object Store
- OCI Generative AI Service
- OCI Database 23ai
- Oracle Apex on 23ai
Solution Architecture:
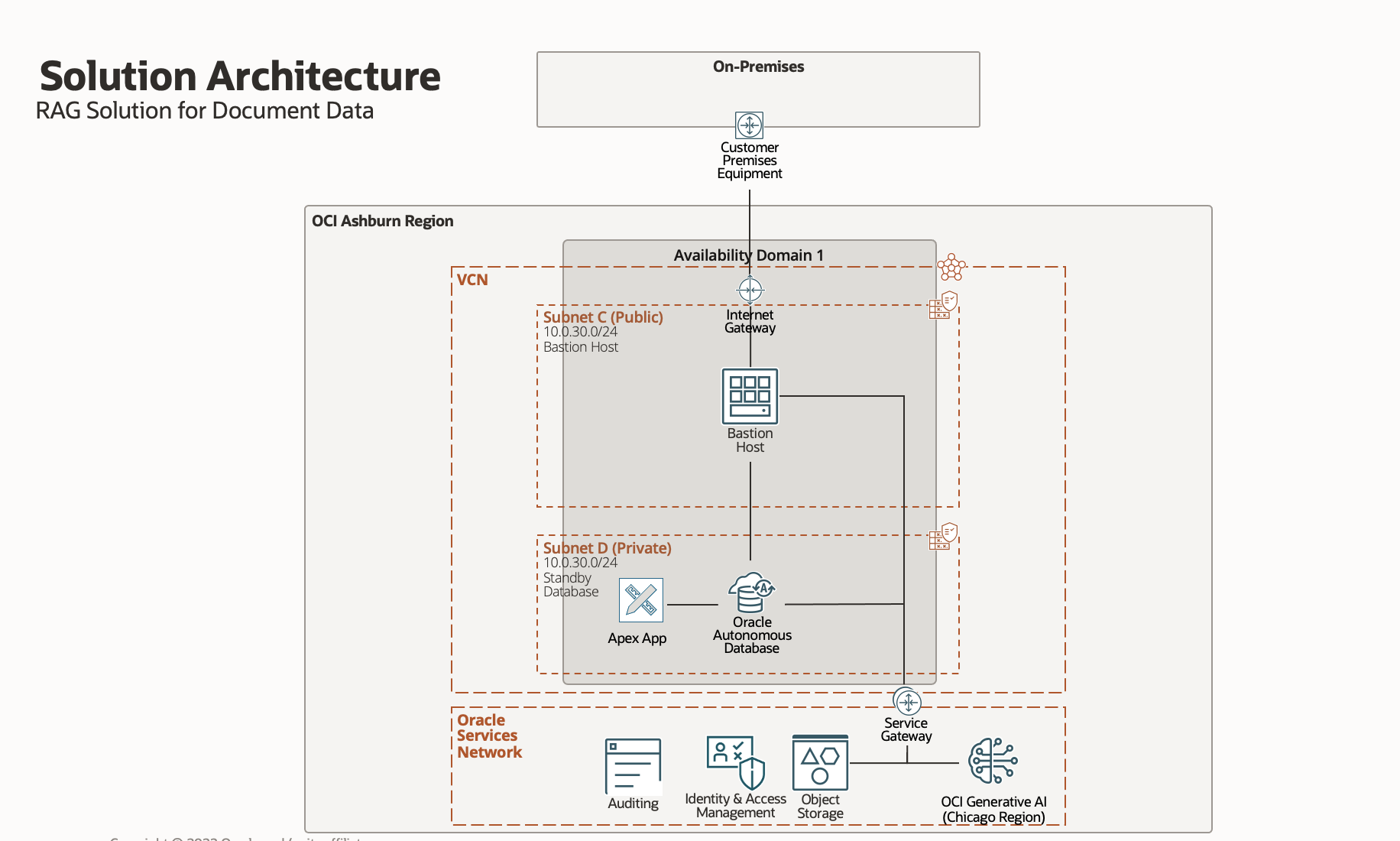
Figure 2: Solution architecture for implementing vector search with Oracle Database 23ai
Implementation Steps:
- Setting up IAM Policies
- Provisioning Resources
- Subscribing to Generative AI Services
- Creating an Object Storage Bucket
- Creating Networking Resources to create Compute and Database Instances
- Create Service Gateway to access Gen AI endpoint
- Create Security Rules and attach them to the subnet
- Creating an Autonomous Database Instance
- Creating a Bastion Instance (For accessing private resources)
- Upload documents to Object Storage
- Building a Vector Search Application using SQL
- Build Frontend using APEX (Low Code – No Code App Dev Platform)
- Executing Vector Search Queries against our documents.
Please note that detailed steps for creating or provisioning resources is not covered in this blog. Please refer to the Hands-on lab link mentioned in the References section if you need them.
Step 1 : Setting up IAM Policies
The below policies are umbrella policies. However, you can go more granular based on your requirement. For Eg, you can restrict the policy to a specific compartment, region, etc.
|
Allow group NetworkAdmins to manage virtual-network-family in tenancy Allow group InstanceLaunchers to manage instance-family in compartment ABC Allow group InstanceLaunchers to read app-catalog-listing in tenancy Allow group InstanceLaunchers to use volume-family in compartment ABC Allow group InstanceLaunchers to use virtual-network-family in compartment XYZ Allow group ObjectAdmins to manage buckets in tenancy Allow group ObjectAdmins to manage objects in tenancy Allow group DatabaseAdmins to manage autonomous-database-family in tenancy
|
Step 2 : Provisioning Resources
Please refer to the documentation links provided below or the Hands-on lab in the references section for detailed steps to create the necessary resources for this solution.
Step 3 : Subscribe to OCI Generative AI Service
Please follow the documentation to subscribe to OCI Gen AI Service.
Step 4 : Provision Object Storage bucket
Provision Object Storage bucket for storing Knowledge Documents (Documentation). By default, the bucket is created with a private access only.
Step 5 : Creating Networking Resources to create Compute and Database Instances.
Provision OCI VCN, Subnets and networking resources (security lists and gateways) (documentation). We will need 2 subnets 1 private to create the database and one public to create the bastion host. If you have a IPSec VPN or a Fastconnect between your on-premise datacenter and OCI. You can directly access the database from any on-premise server and can skip this step.
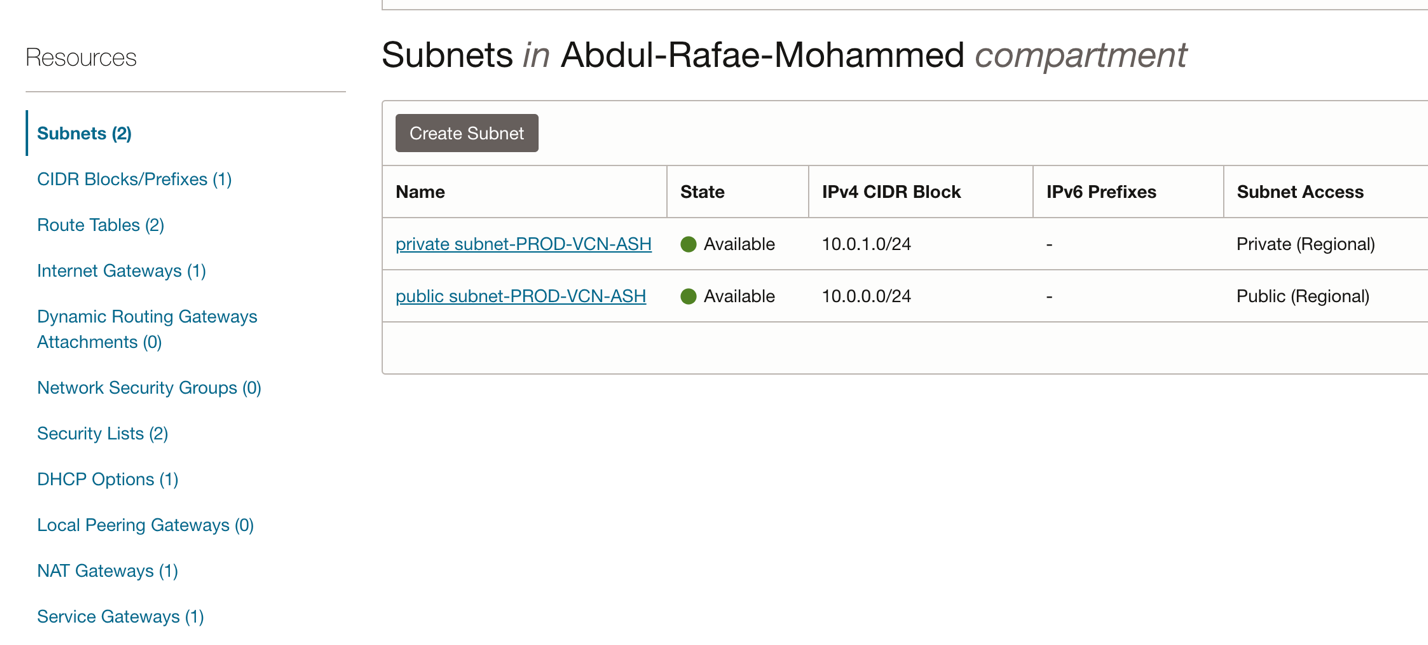
Fig 3: Subnets
Step 6 : Create Service Gateway to access Gen AI endpoint
Please note that you need to setup service gateway to access OCI Generative AI and Object Storage services from Autonomous Database via the Oracle Backbone Network instead of the public internet.
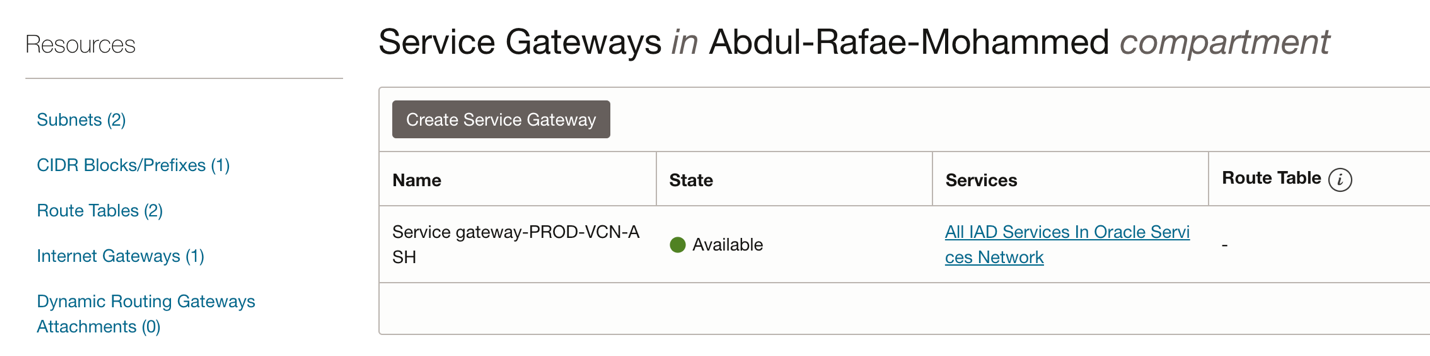
Fig 4: Service Gateway
Step 7 : Create Security Rules and attach them to the subnet
Configure Security Rules to control network traffic going in and out of the public and private subnet.
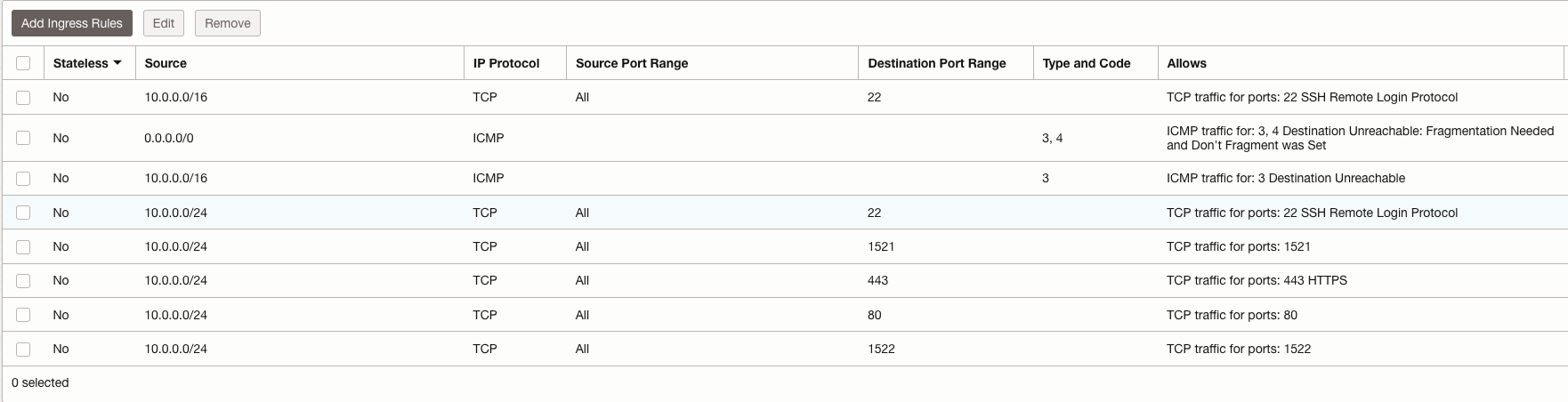
Fig 5: Security Rules for Private Subnet

Fig 6: Security Rules for Public Subnet
Step 8 : Creating an Autonomous Database Instance
Provision Autonomous Database 23ai (documentation). We will ingest data into this database, chunk it and then create vectors mapping to the chunks which we will later use to execute similarity search queries.
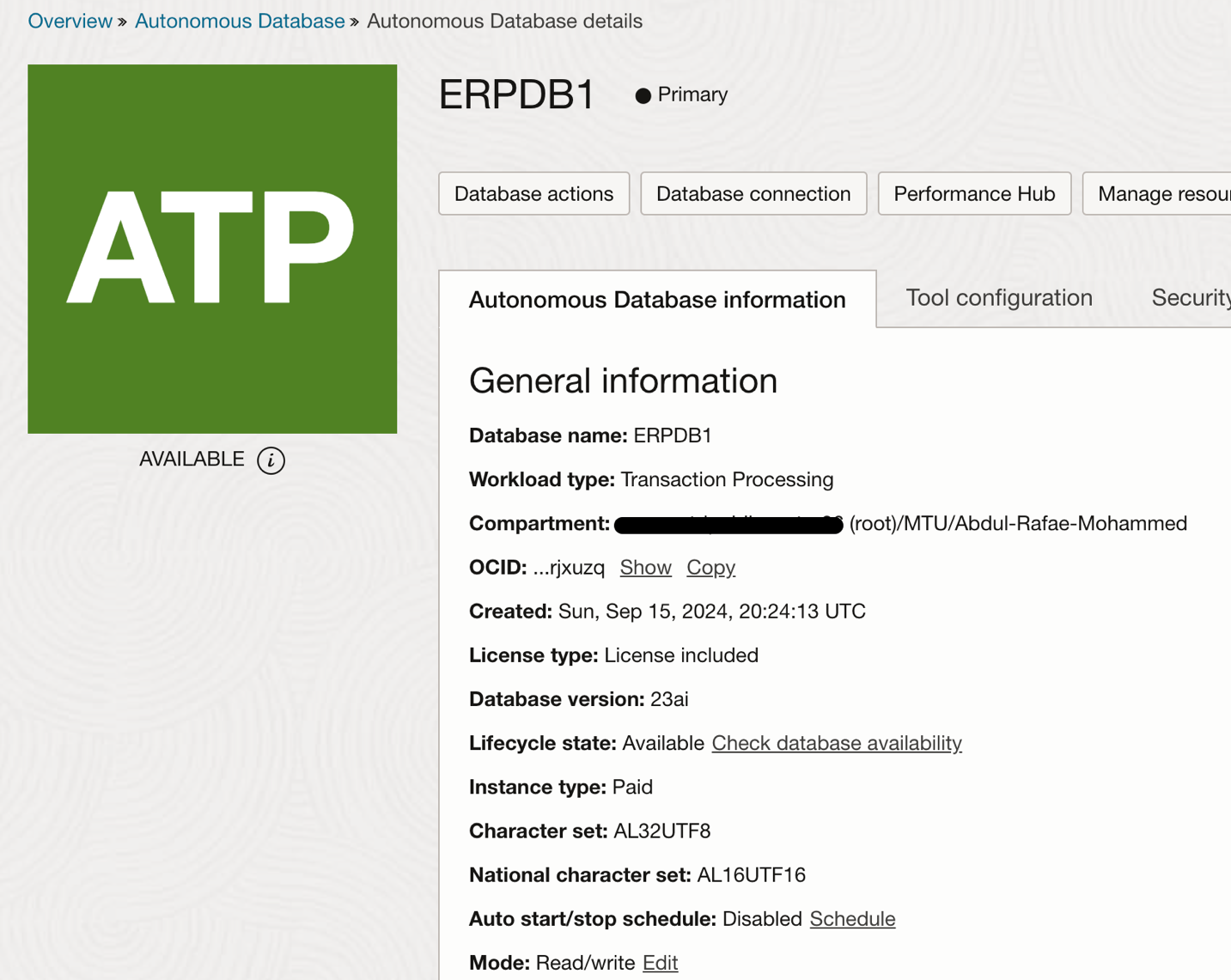
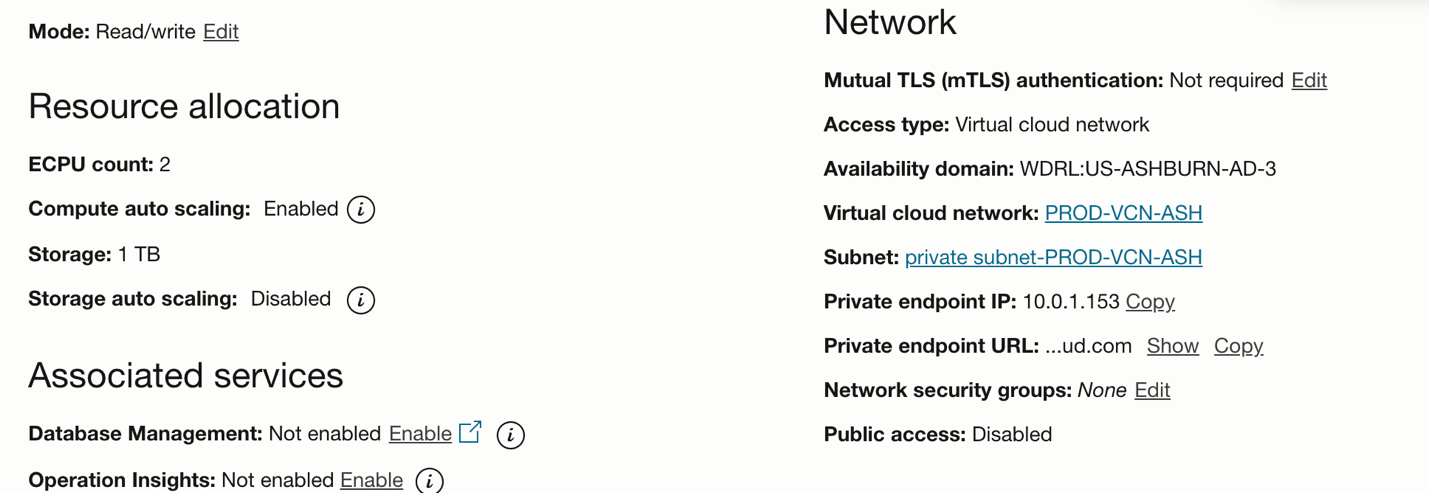
Fig 7: Oracle Database 23ai details
Step 9 : Creating a Bastion Instance
Provision a compute instance which will act as a bastion host (Documentation).
Now, we have completed provisioning of all the components we need. In the next part, we will continue with the rest of the steps.
References:
- Oracle Database 23ai – Vector Search Documentation
- Oracle Database 23ai – hands-on-lab by Steve Nichols


