A must-have release for Ransomware Protection and Cyber-Resilient Architectures
We are excited to announce the general availability of Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance (RA) 23.1 Software Release! In this 2-part blog series, we will discuss exciting new features focused on enhanced and unique data security that boosts protection from ransomware threats, and further simplifies administrative operations. Let’s start with the topic of cyber protection and a new capability to compress and encrypt database backups while maintaining an efficient, incremental forever strategy.
Defending against Cyber Attacks
Given the increasing number of cyber attacks aimed at exfiltrating data for ransomware purposes, implementing Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) in Oracle databases is a common requirement and a best practice recommendation in the Oracle Maximum Security Architecture. In addition, it is a requirement for all databases deployed in Oracle Cloud.
However, customers using TDE face an unexpected setback: general-purpose backup appliances fail to effectively deduplicate TDE encrypted database data. They also fail to achieve significant compression savings, sometimes resulting in unpredictable 3X or more increase in backup storage consumption. Though Recovery Manager (RMAN) supports processing of TDE-encrypted databases through decrypting, compressing, and re-encrypting data during backup operations, the resulting backup data format renders deduplication and compression very challenging, if not impossible. This greatly diminishes the value of generic backup appliance investments for Oracle databases, increasing their costs and reducing their ROI, thus presenting difficult decisions for customers in backup storage capacity planning…Until now.
Introducing Space-Efficient Encrypted Backups
With the new Space-Efficient Encrypted Backups capability in RA 23.1, TDE database backups remain compressed and encrypted end-to-end under an incremental forever strategy. The Recovery Appliance Backup Module for RMAN, installed on the protected database server, decrypts, compresses, re-encrypts the backup blocks, and formats the data for RA-native virtual full backups, as shown below. This process results in 3X or more storage savings compared to TDE backups on general purpose backup appliances.
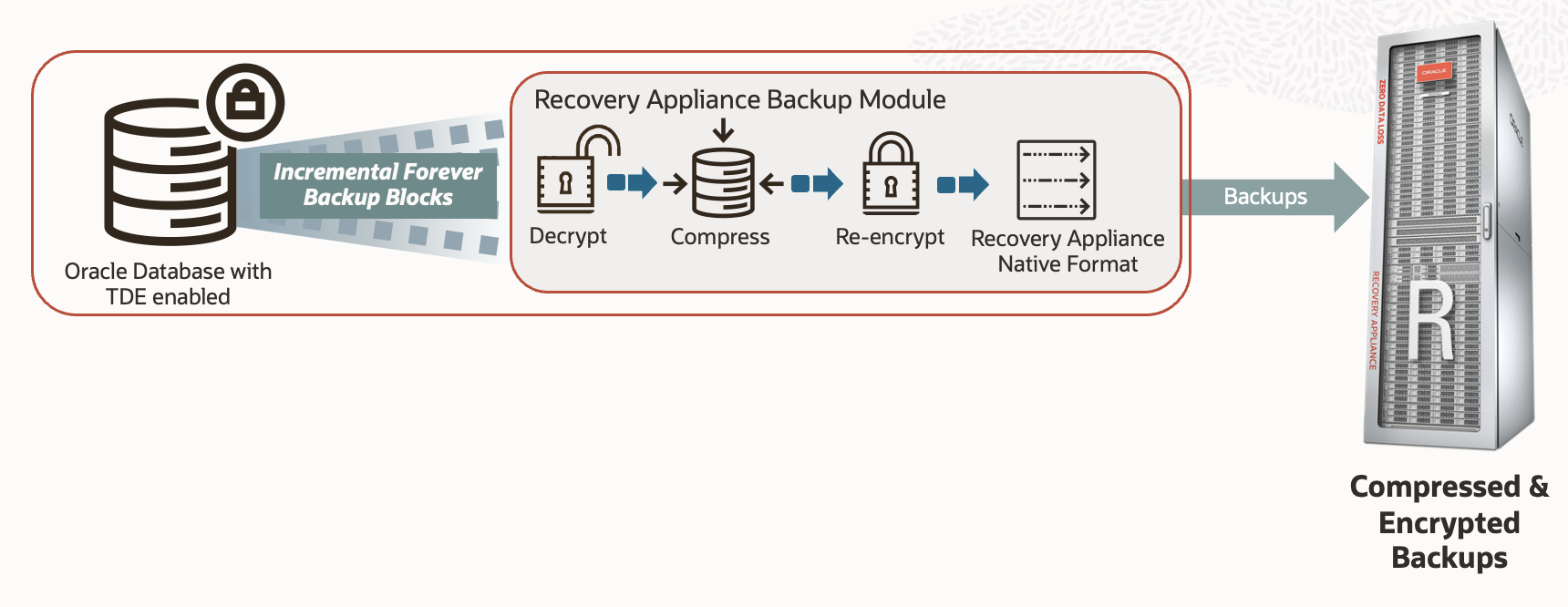
To ensure end-to-end data security, encrypted data is never decrypted at rest by the Recovery Appliance and remains encrypted when copied to, or restored from, cloud or tape. Encryption keys are stored and managed only on the protected database, preserving separation of duty between database and storage administrators.
By compressing backup data on the protected database, this feature not only reduces storage consumption but also significantly improves backup and restore performance. Our tests with a 30 TB database encrypted with TDE, running space-efficient encrypted backups from an Exadata X10M-EF (Extreme Flash) 4 DB Node and 10 Storage Cell rack to an RA23 appliance with 14 Storage Servers was able to reduce backup size by over 3X to 6 TB, compared to 22 TB without compression, while attaining 60 TB/hour throughput.
For non-TDE databases, the Recovery Appliance Backup Module can compress and encrypt the data during backup operations, again done in conjunction with the efficient incremental forever strategy.
Auto-tuned Reserved Space for Immutable Backups
RA 23.1 release also includes new capabilities to simplify management activities. For this blog, we will review the Auto-tuned Reserved Space feature, and discuss other automation features in Part 2 of this blog series.
On the Recovery Appliance, each protected database is associated with a Reserved Space value to specify the minimum space allocation that its backups can consume. If there is free space in the appliance, new backups can be accepted even if that Reserved Space is exceeded, to meet specified retention goals. In case of space pressure, the appliance automatically purges backups of databases that exceed their Reserved Space. During this process, backups that are needed to meet retention goals may be purged and thus necessitate expansion of storage or reduction of retention settings.
However, for backups that have been set immutable, they can never be purged under their retention period. Therefore, the Reserved Space must be set large enough to support that period. As shown in the diagram below, this can result in new backups being rejected if Reserved Space is set too low, even if there is free space in the storage location. The administrator must increase the Reserved Space, reduce retention, or expand storage capacity in such situations, so that backups can continue. This could pose an administrative challenge, especially for environments with large number of protected databases.
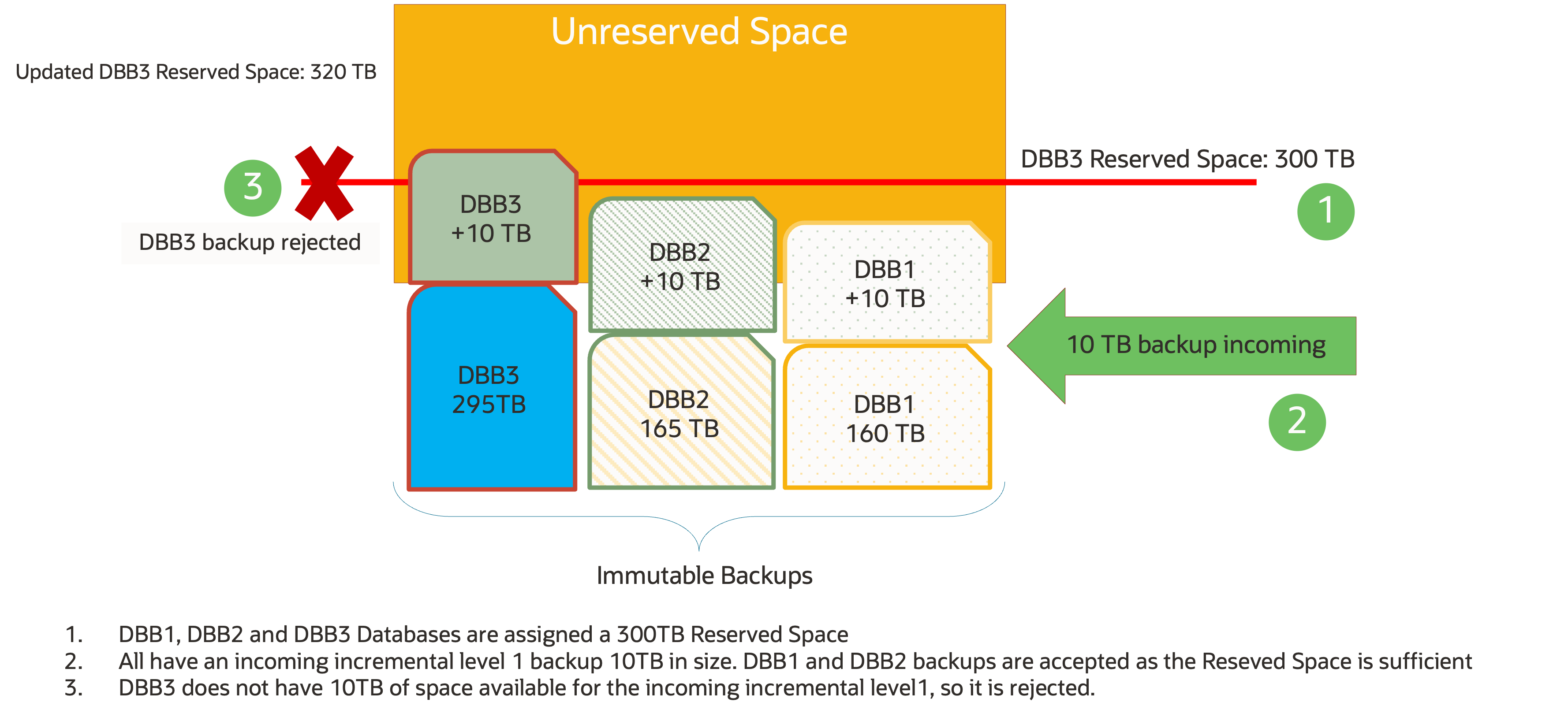
The Auto-tuned Reserved Space feature, introduced in the RA 21.1 software release, was designed to relieve this administrative effort by allowing the appliance to automatically adjust Reserved Space based on each database’s retention goals using total available space on the system. In RA 23.1, this feature now supports immutable backups. If capacity is available in Recovery Appliance, reserved space is automatically increased as needed to accommodate increased backup volume and conversely is decreased when space needs are lower to maintain immutable backup retention periods per-database.
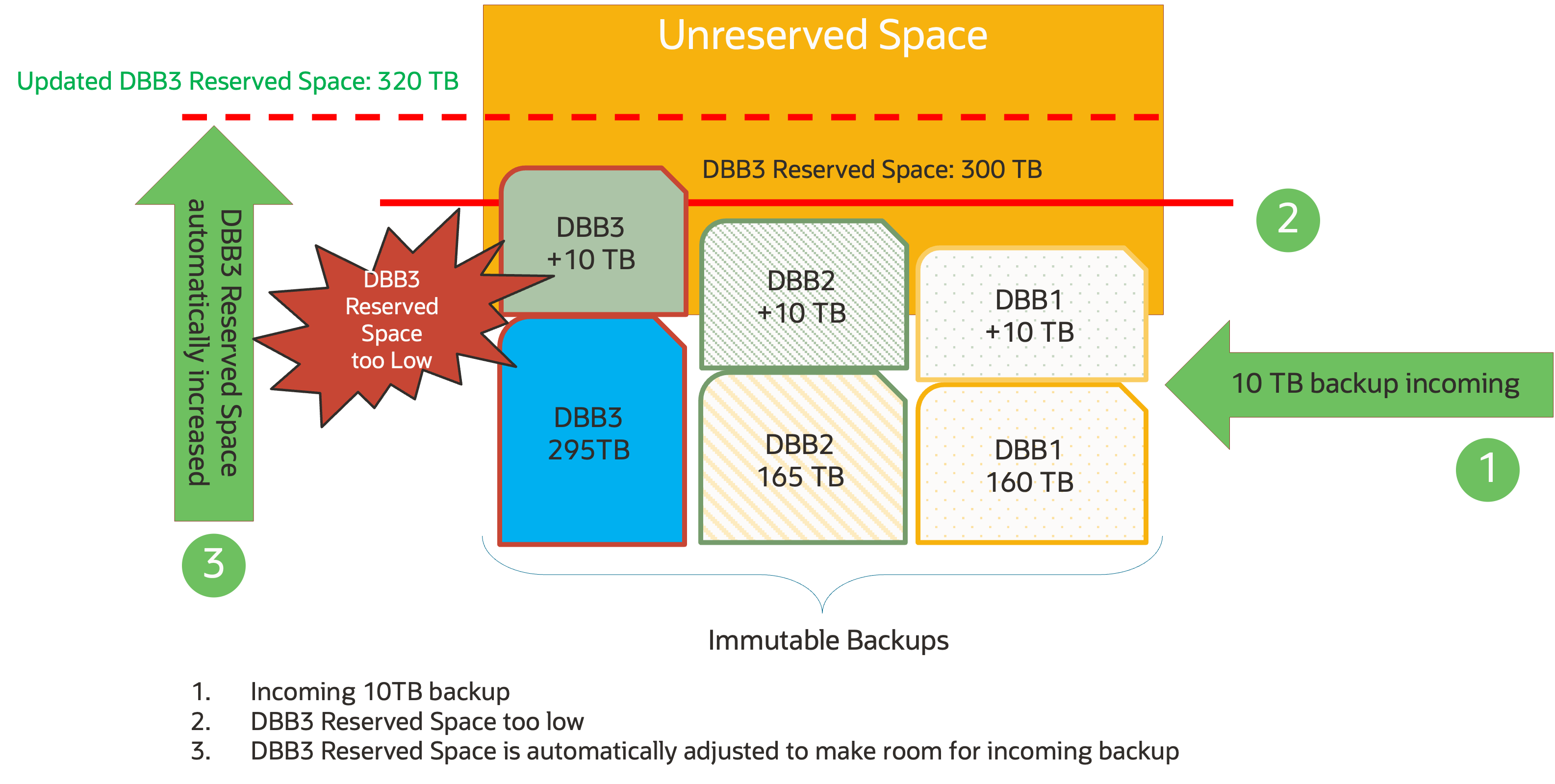
With Auto-Tuned Reserved Space, administrator effort to monitor and adjust reserved space is reduced, especially when there is sudden increase in backup activity across one or more databases that require immediate space adjustments. Auto-tune immediately checks for available free space that can be used and frees space used by obsolete backups so that backups continue being received and stored to meet required retention settings. If there is no more available space on the appliance that can be reserved for new immutable backups to maintain the specified retention period, the backup is finally rejected and an alert is generated with the following errors:
- ORA-45102: unable to allocate
%sbytes of storage. - ORA-45117: There is not enough space for this task.
Refer to the Error Message Reference chapter in the Recovery Appliance Administrator’s Guide for more information.
Stay Tuned for RA 23.1 New Features Part 2!
In this blog, we presented new Space-Efficient Encrypted Backups to achieve encrypted and compressed incremental forever backups, dramatically reducing storage consumption compared to general purpose backup appliances. We also presented new Auto-tuned Reserved Space support for immutable backups, relieving administrators from monitoring and adjusting reserved space settings as backup activities fluctuate, allowing more efficient overall space usage based on each database’s retention needs. Both of these features are crucial to supporting a sound Cyber Resilient Architecture against ransomware. Encrypted and compressed backups are useless for exfiltration purposes, and Auto-tuned Reserved Space makes immutable backups much easier to manage.
For more information on these new features, see the Recovery Appliance Administrator’s Guide and stay tuned for Part 2 of this blog series, where we will continue with the other exciting new capabilities in the RA 23.1 release.
