Ransomware attacks are still very prevalent and some have very visible and costly results like the attack on MGM Resorts in Las Vegas. The SEC has also introduced a rule that requires incident disclosure for public companies, so incidents will gain even higher public exposure in the future. This makes recovery from these incidents even more critical, especially for mission-critical data in the Oracle Database.
To help customers ensure backups are safe against deletion or alteration attempts by ransomware and malicious users, the Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service has introduced a new feature that allows the retention period for backups to be locked. Once locked, the backup retention time can’t be reduced by any user or administrator in the customer tenancy.
This functionality is exposed in the configuration for a user-defined protection policy. The “26 Days – Prod” protection policy in Figure 1 below has the retention lock enabled with a scheduled lock time starting Nov 30 at 00:00 UTC. Scheduling the retention lock in the future gives the database administrators time to understand the space utilization for database backups before the lock becomes active.
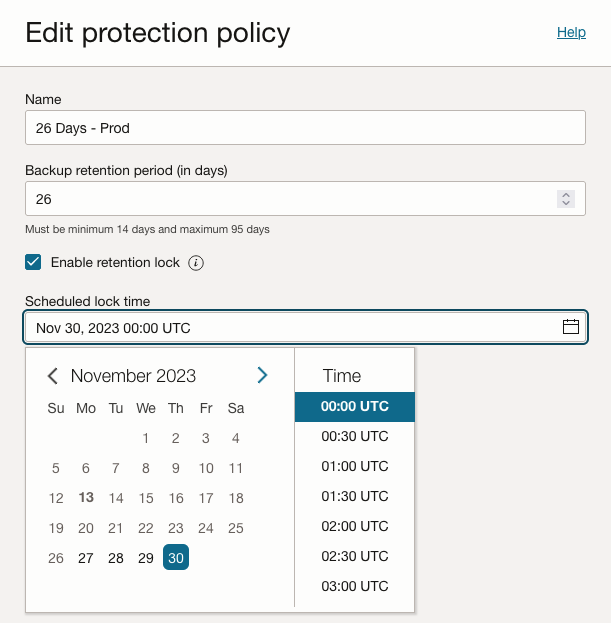
Figure 1- Retention lock option for the protection
Once the retention lock becomes active, the following restrictions are enabled:
- Prevent the backup retention period from being reduced by ANY user or administrator in the tenancy. This helps ensure that all backups from the retention period are available for recovery operations. Note that the retention period can be increased and will take effect immediately.
- Prevent databases from being moved to another policy. Moving the database to a protection policy with lower retention would bypass the retention lock so the move operation is blocked.
- Prevent database termination (deletion) from simultaneously deleting backups. The retention in the policy will always control the backup deletion when the retention lock is active and override the 72-hour backup deletion option for the database. The backups are also maintained in the context of the terminated database and are easy to locate in the database management UI.
- Prevent the SYSDBA from manually deleting backups with RMAN. Blocking the delete operation directly from RMAN ensures the backup can’t be deleted even if the OCI backup automation is bypassed.
Any database added to the protection policy after the retention lock becomes active can still be removed from the policy within the first 14 days. This allows time for the administrator to adjust in case of a mistake since the retention period will impact the total storage cost for the database backup and cannot be changed once locked. After the 14-day grace period has passed, the restrictions mentioned above will take effect.
With the backup retention locked in the protection policy, you can also take protection to the ultimate level with real-time protection of the database. Your database will then have backups that cover the latest sub-second of database transactions and are locked from deletion until the specified retention has expired. Think about how powerful that can be if malicious activity took place right now. There is no panic in trying to discover when the last database backup occurred. Enabling real-time protection is a click away (Figure 2) in “Configure automatic backups” and perfectly complements the retention lock capability.
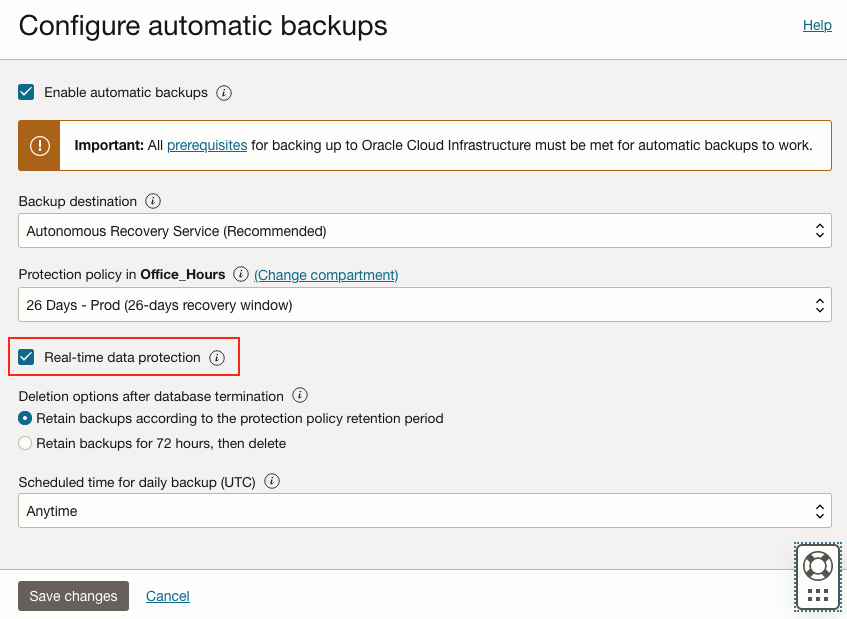
Figure 2 – Real-time protection option in automatic backups configuration
By ensuring that your backups are retention locked, the backups can’t be deleted by any user in your tenancy, and by protecting databases in real-time, the latest subsecond of transactions are protected, you are elevating your company readiness to a higher level for both internal and external threats. This unique combination of real-time protection and retention lock for backups is only available when using the Autonomous Recovery Service.
For more information
The documentation links below provide additional instructions for enabling automatic backups, real-time protection and retention lock.
Back Up and Recovery in Base Database Service
https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/paas/base-database/backup-recover/index.html
Manage Database Backup and Recovery on Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure – Using the Console to Manage Backups
https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/exadatacloud/exacs/ecs-managing-db-backup-and-recovery.html#GUID-789EF0AD-A176-4862-947E-3E725CDF359D
Recovery Service – Retention Lock
https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/paas/recovery-service/dbrsu/protection-policy-locking.html#GUID-B47C5BDD-7F0C-4B17-8BAE-018239C83859
Recovery Service – Real-time Data Protection
https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/paas/recovery-service/dbrsu/about-real-time.html#GUID-CFBF7CA4-627F-42BB-B24F-8242F5FEAB1D
