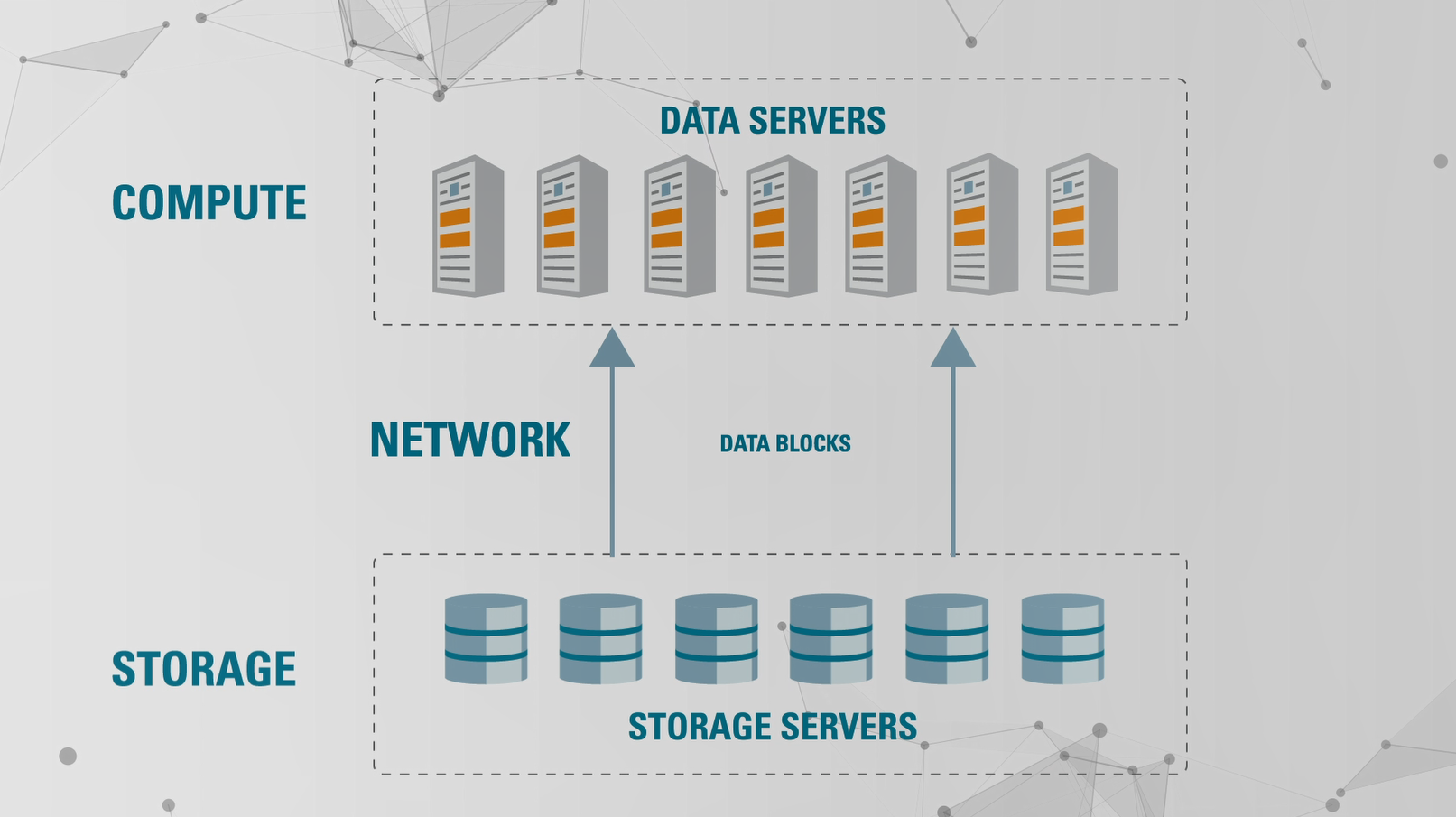
What is Exadata Smart Scan? To answer that, let’s first look at how a traditional data center operates. The database system consists of three components or layers: compute, storage, and network.
- Compute layer: It houses the servers that process data requests from users and returns results back to them. It makes up the back-end system of user-facing applications. Say you’re trying to purchase an airline ticket on an online booking app. The application sends a request to the database server, which processes the relevant data and returns the results to your application.
- Storage layer: This is where the data actually resides. Here, servers store, secure, and manage data in tables as a set of data blocks.
- Network layer: The network layer lies between compute and storage and passes data blocks from one to the other.
Click Video URL: What is Smart Scan?
The Data Center
The problem with this structure is that data centers must use specialized storage and compute appliances that can’t scale for critical workloads. What’s more, it can create bottlenecks at the network layer, because all the blocks from the data table are transferred across the storage network. This process consumes bandwidth, impacts response time, and creates an unnecessary burden on the compute layer.
To get around the scalability issue and reduce data transfer time, companies have combined compute, storage, and networking into a tightly integrated hyperconverged infrastructure. This solution was a compromise that provided basic configurations for generic workloads. It offered adequate storage and compute capabilities but was optimal for neither. Plus, it did nothing to reduce the bandwidth required to exchange broad swaths of data across the network.
Standard Hyperconverged Infrastructure
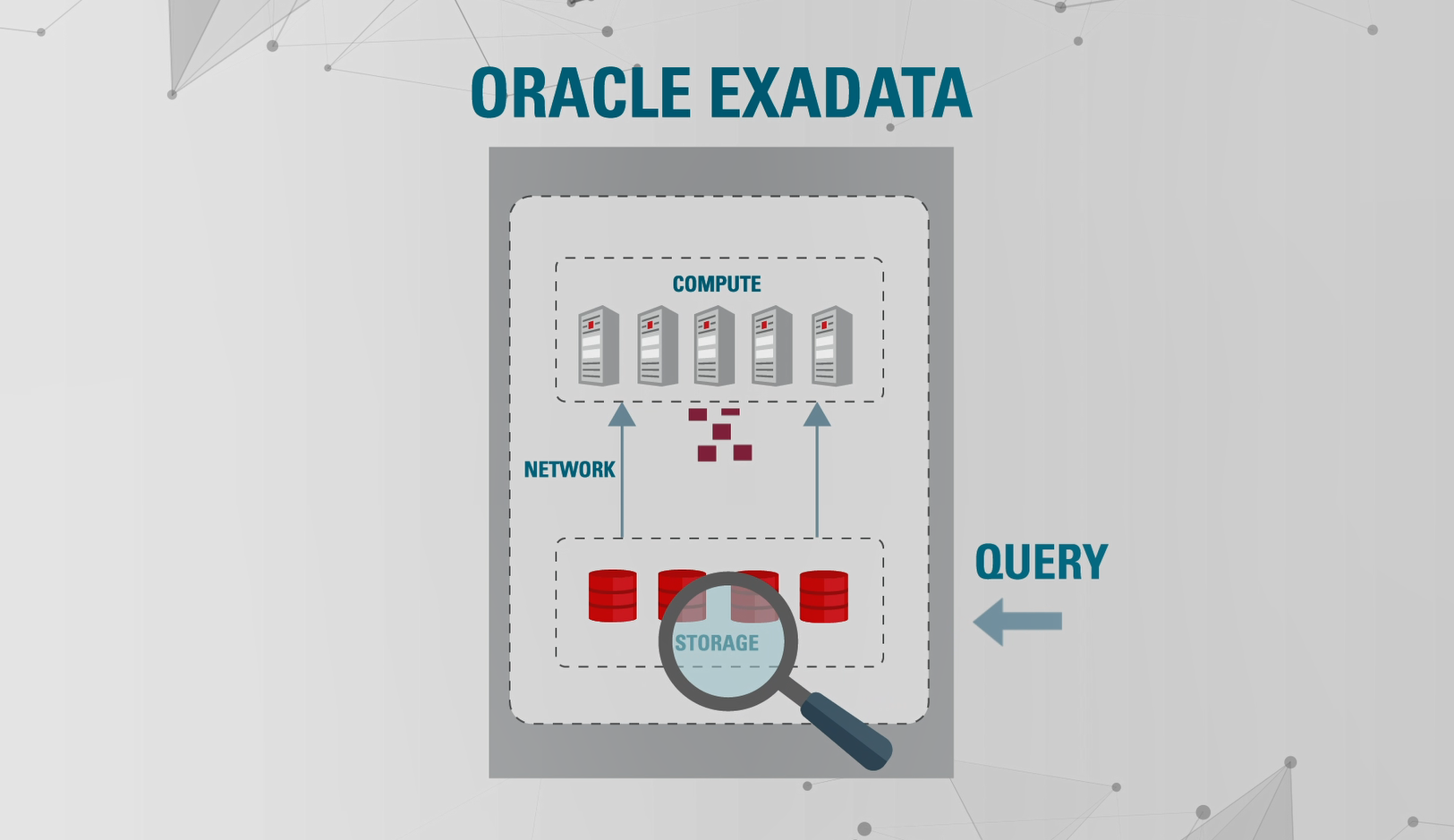
Oracle Exadata takes hyperconverged infrastructure and makes it smarter by integrating database-aware software and hardware innovations within and across compute, storage, and networking. These innovations create huge performance improvements leading to faster results.
How Does It Do This With Smart Scan?
Exadata turns the traditional model on its head. Instead of going to the compute layer, all queries are pushed directly to storage. There, data filtering based on the query occurs in parallel across all storage servers before it is sent to compute. This dramatically improves execution time and eliminates bottlenecks, because the network is transmitting a smaller set of relevant data blocks.
Oracle Exadata
Say, for example, you wanted to know which customers spent more than $500 on a plane ticket in April. You send a query to the Exadata system, which would forward it to the storage layer. There, Exadata employs Smart Scan to filter out flight bookings below $500 and not made in April. Once Exadata extracts the relevant customers from storage, only that data is sent up to the database servers. The database then consolidates the result and returns it to the client. Compare this to a database running on a conventional or hyperconverged system, which would send a huge portion of the table from storage to compute, easily leading to bottlenecks.
The result? Exadata Smart Scan drastically reduces CPU usage in the database servers, accelerates query execution, and eliminates network bottlenecks.
To learn more about Smart Scan, as well as Oracle Exadata’s other data-optimizing technology, contact an Oracle Exadata Sales Specialist.