Introduction
Distributed databases are becoming increasingly popular and significant due to their ability to handle large and complex data sets, their scalability and flexibility, and their fit for contemporary application designs and architectures. As organizations continue to adopt cloud-based solutions and microservices-based architectures, the demand for distributed databases is expected to rise. Businesses are continuously searching for new and innovative database solutions that enable horizontal scalability and ensure data durability and high availability while adopting more flexible strategies.
Scaling databases is necessary to handle transactional volume and ensure efficient performance. Moreover, as the business world becomes increasingly global, it’s important to consider geographic scaling, so services can be tailored to customers located in different parts of the world.
Resilience is also a vital factor to consider when scaling databases, as businesses need to ensure they can survive the failure of an entire AZ/AD (Availability zone/Availability Domain) or cloud provider.
The growing demand for distributed databases, as well as the need for horizontal and geographic scaling, is driving businesses to adopt next-generation methodologies like Oracle Sharding to ensure efficient performance and resilience while meeting modern consumer expectations.
Oracle Sharding is a data distribution system that provides advanced ways to partition the data across multiple servers, or shards, to deliver exceptional performance, availability, and scalability.
The purpose of this blog is to discuss the concepts of Oracle Sharding, its development by Oracle to provide the greatest advantages to its users, and the different ways in which Oracle Sharding can be applied.
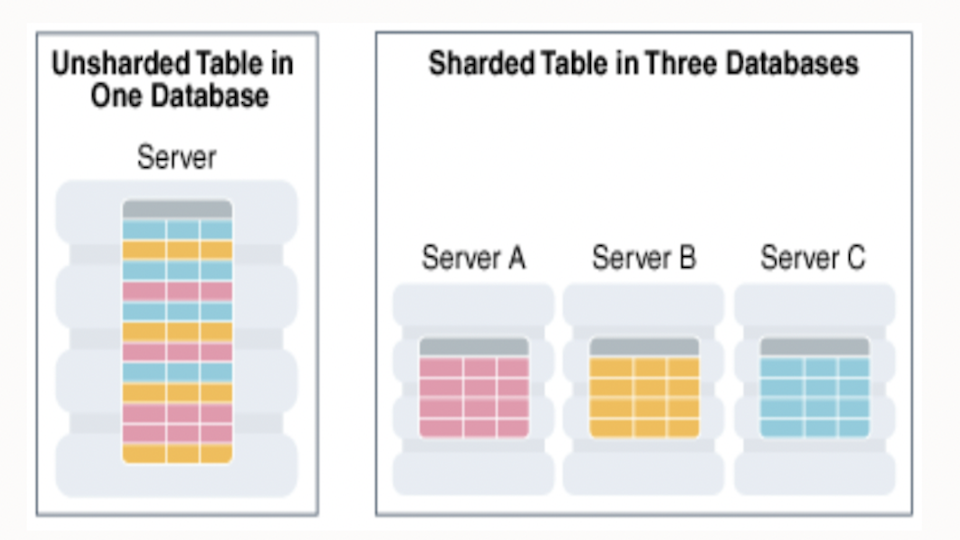
The Emergence of Oracle Sharding
The exponential growth of data has made it difficult for enterprises to manage and process it using traditional database systems, which led to the emergence of distributed database solutions.
Sharding is a key technique in distributed databases that allows data to be horizontally partitioned across multiple servers or shards. But, manual sharding can be a daunting task for any organization looking to scale their database. From deciding how to break up the data, to reworking application logic, to handling operational tasks, manually sharding a database can be a time-consuming and complex process that diverts precious engineering resources away from other important projects like developing new features.
Managing and operating a manually sharded database also adds complexity to management and operations tasks, such as schema modifications, backups, analytical operations and software updates. Furthermore, as companies continue to scale up, they will have to redo much of the work already done to rebalance the database, adding even more engineering hours to the already substantial cost.
This is where Oracle Sharding comes in. Oracle Sharding is a powerful and automated solution that allows organizations to horizontally scale their databases without the added complexity of manual sharding.
Oracle Sharding is an Oracle Database data distribution feature that was created to address the problems caused by the complexity and volume of data that are becoming more and more prevalent in the modern IT landscape. With Oracle Sharding, data is automatically distributed across multiple nodes, while still allowing the application to treat the database as a single instance.
Oracle Sharding builds on the generic sharding concept and extends it to offer an enterprise-grade distributed database solution that can handle massive amounts of data with ease. With Oracle Sharding, businesses can achieve higher performance and availability by distributing the data across multiple shards or servers that can be located in different regions. It ensures that data replication is automatically configured and deployed when the sharded database is created to provide high availability and disaster recovery.
Oracle Sharding provides a transparent view of the sharded database to applications, making it easy to use and deploy, while also offering robust management capabilities to database administrators. Oracle Sharding has made it possible for organizations to handle and process data on a scale that was previously impossible, while also ensuring high levels of availability and performance.
Oracle Sharding – Overview
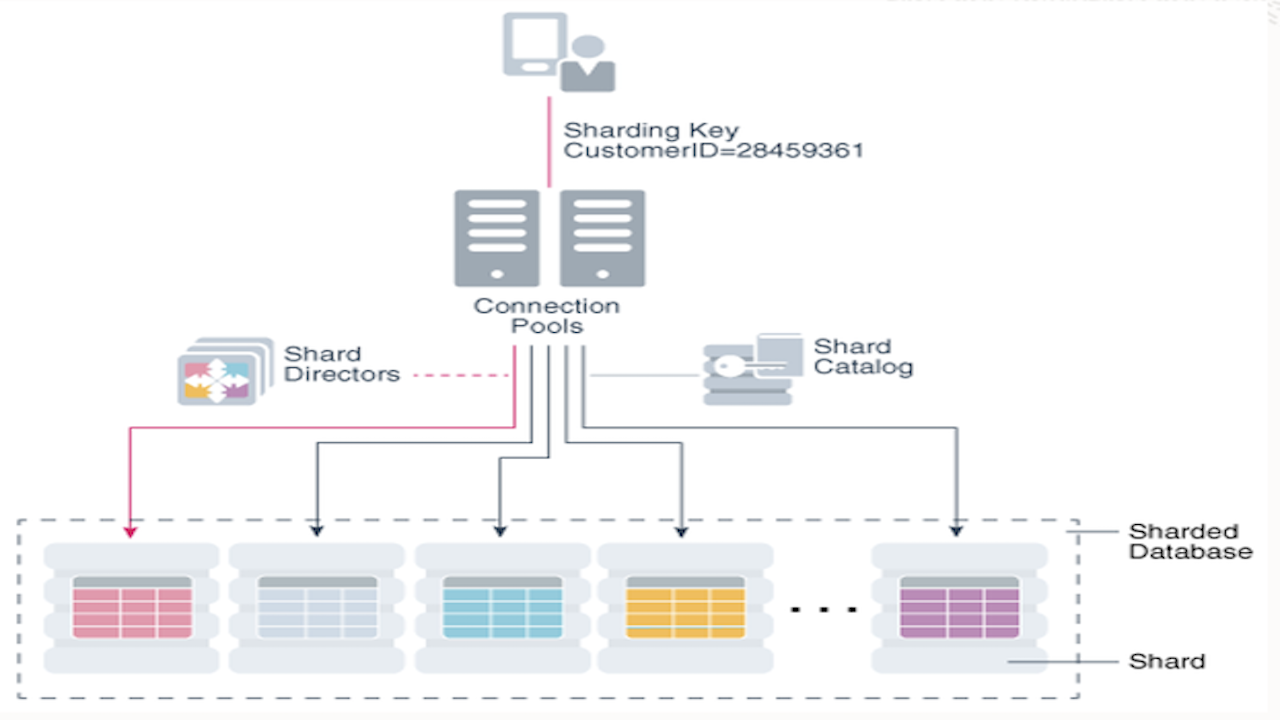
Key Features:
- Oracle Sharding automates the distribution and placement of data on specific shards, eliminating the need for manual data preparation and saving time.
- Oracle Sharding allows the addition or removal of shards and data rebalancing without incurring any downtime or data loss.
- Oracle Sharding allows centralized management and monitoring of sharded databases as a single logical database, with the shard catalog playing a vital role. This feature supports automated shard deployment and multi-shard queries as well, enabling users to perform critical tasks like configuring shards, ensuring high availability, improving security, applying patches, and monitoring the system without needing to handle complex application code changes.
- Oracle Sharding is natively supported by Oracle Database client drivers (JDBC, OCI, UCP, ODP.NET) and allows automatic request routing to shards, automated routing of multi-shard queries to the query co-ordinator, automated failover to standbys, and automatic sharding key identification (Oracle Database 21C JDBC).
- A sharded database protects against unplanned outages and provides mechanisms for online planned operations, allowing applications to meet stringent availability SLA.
- Oracle Database 21c allows data and redo to be stored in local persistent memory, enabling faster SQL execution by bypassing traditional disk storage.
Stated below are some of the benefits of Oracle Sharding:
Linear Scalability
Oracle Sharding removes performance bottlenecks and allows for linear scaling of performance and capacity by adding shards.
Extreme Availability and Fault Isolation
Oracle Sharding is a shared-nothing infrastructure that eliminates single points of failure and provides strong fault isolation. The failure or slowness of one shard has no effect on the performance or availability of other shards.
Geographical Distribution of Data
Oracle Sharding allows specific data to be stored close to its consumers while also meeting regulatory requirements when data must be located in a specific jurisdiction.
Rolling Upgrades
Applying configuration changes to one shard at a time does not affect the other shards and allows administrators to test changes on a small subset of data before making broader updates.
Oracle Sharding offers benefits that apply to a diverse range of use cases and scenarios:
- Real-time OLTP applications :Review sharding features for OLTP
- Hyperscale Applications :Read How Oracle BlueKai Data Management Platform scales to 1 Million transactions per second with Oracle Database Sharding deployed in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Global Applications/Data Sovereignty :Read How customers are achieving Data Sovereignty with Oracle Sharding
- Internet of Things and Data Streaming Applications :Read High-throughput data ingest (Loading data into an Oracle Sharded Database)
- Machine Learning :Read about Applications
- Big Data Analytics : Review massively parallel processing architecture
- Multi-Cloud Deployment : Read Deploying linearly scalable Oracle sharded databases across multi-cloud (Oracle Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services)
Conclusion
Say Goodbye to Database Scaling Woes and Unlock the Power of Enterprise-Grade Distributed Database with Oracle Sharding
- No more laborious planning needed for splitting data across shards
- No application code is required to route data to the correct shard
- No need to refactor code to work with Oracle Sharding
- No additional effort to handle reads and writes that span multiple shards
- No need to worry about updating the schema without downtime, as the database will handle this seamlessly
- No need to repeat any of these tasks when scaling the system up or down
To summarize, Oracle Sharding is a distributed database solution that provides the best of both worlds – the extreme scalability and availability of NoSQL databases and the reliability of traditional RDBMS. Oracle Sharding distributes segments of a data set across many databases (shards) on different computers, on-premises, or in the cloud, allowing for horizontal scaling, improved performance, and fault tolerance. It enables globally distributed, linearly scalable, multi-model databases. With Oracle Sharding, customers can enjoy the benefits of a distributed database while maintaining ACID compliance, strict data consistency, zero data loss, two-phase commit (2PC), and complex joins, triggers, and stored procedures that are characteristics of relational databases.
What sets Oracle Sharding apart is the enterprise features that it brings to the table – InMemory, Columnar, Partitioning and Sub Partitioning, Advanced Compression, Secondary Indices, Advanced Security, RMAN, ASM, Oracle Data Guard, Oracle GoldenGate, Parallel Query, high-performance storage engine, SMP scalability, Oracle RAC, Exadata Database Machine and more. Customers can be confident that they have access to all of the features they need to manage large and complex data sets. Furthermore, Oracle Sharding provides a simple and cost-effective solution that requires no code changes to existing applications. All in all, Oracle Sharding is a compelling option for businesses looking to take advantage of a distributed database, while also leveraging the power of enterprise features to meet their specific needs.
