Quarterly maintenance on the Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure is an Oracle-managed, automated process. The quarterly process applies software updates to the database server hosts, storage servers, and fabric switches. It is important to apply the maintenance updates to ensure the stability, security, and performance of your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) by fixing security vulnerabilities and bugs, introducing new features and enhancements, and meeting industry and regulatory standards.
The OCI control plane provides the ability to schedule when and how the maintenance is performed. The Exadata software updates are applied in a rolling manner, node by node, and for the database servers, this includes a graceful shutdown and restart of each VM. Continuous availability for applications using databases hosted on the VMs can be achieved by following the MAA best practices for RAC rolling updates.
In this blog, we will explore and provide a comprehensive understanding of the enhanced infrastructure maintenance controls for Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure that provide greater visibility of maintenance actions, timings, and the ability to perform additional actions before the updates on the nodes.
Enhanced Features
- Non-rolling maintenance: Reduce the maintenance window by performing the updates when all database resources are shutdown. With the non-rolling method, all of the storage servers and database servers are updated at the same time.
- Custom action: Perform additional tasks, such as run a script to place the application in a specific state or verify database instances or listeners are up and running before maintenance begins on the next database server. You can specify up to 2 hours for a custom action which adds additional time to the maintenance window but provides the flexibility to execute a specific task for your application or database.
- View maintenance plan: The console provides for greater visibility of the maintenance plan by displaying total estimated maintenance time, database and storage server estimated maintenance time, and the order in which resources are updated.
OCI Console Experience
Let’s look at how you can view and update your maintenance preferences from the OCI Console and manage a running maintenance task.
1. Edit Maintenance Preferences
From the Exadata Cloud Infrastructure details page, click the Edit Maintenance Preferences button.
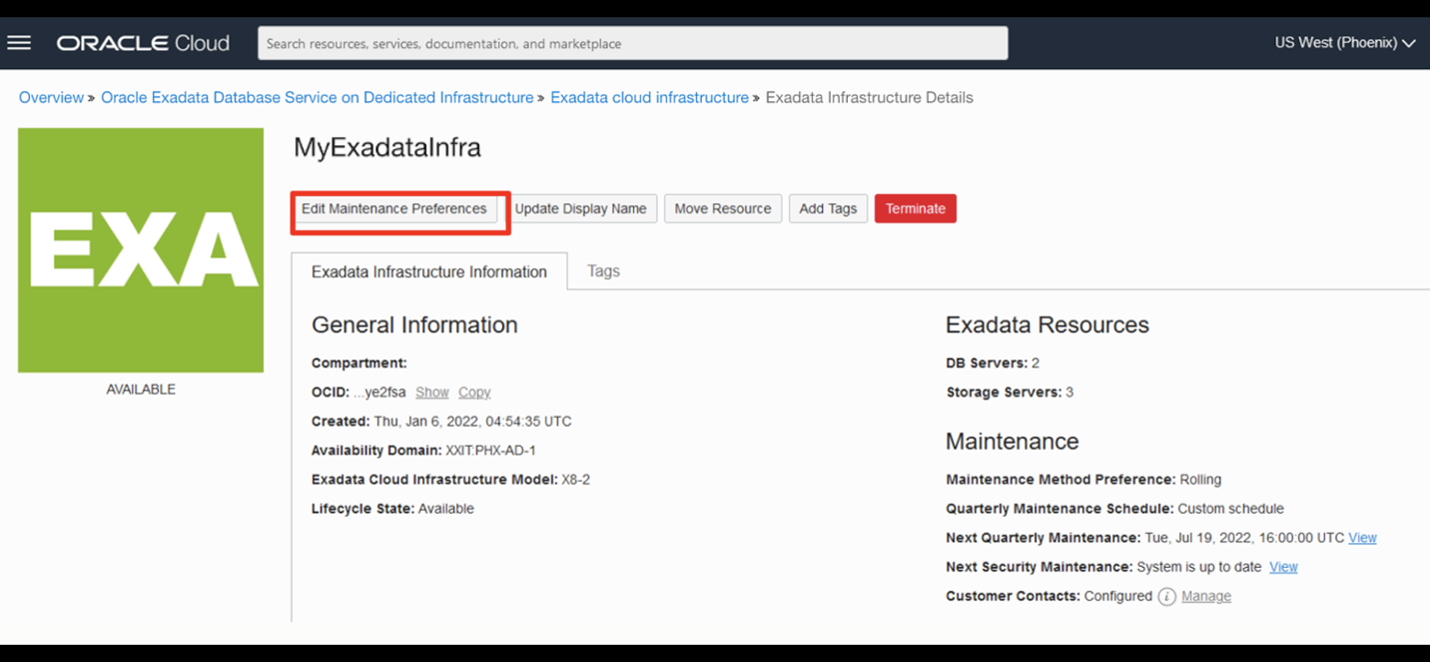
This will display the Edit Maintenance Preferences panel.
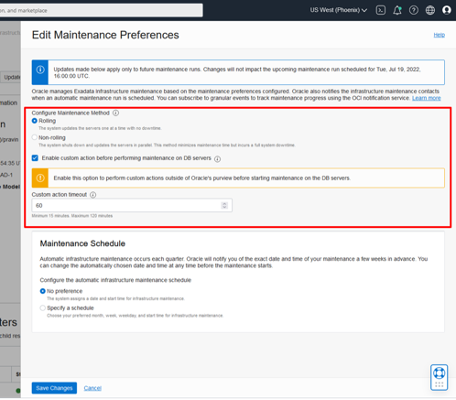
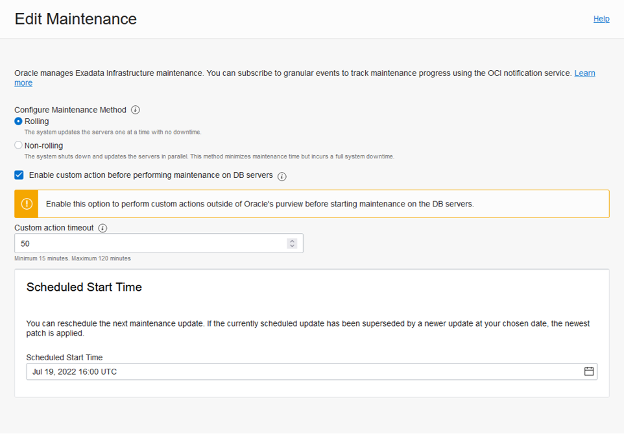
You can choose the maintenance method to be Rolling or Non-rolling. Rolling maintenance updates the servers one by one while continuing to maintain the availability of the underlying RAC databases. Non-rolling maintenance shuts down and updates the servers in parallel. This method minimizes maintenance time but incurs full system and database downtime.
Optionally you can enable a custom action time to allow you to run custom scripts or actions before performing maintenance on the database servers. After clicking the checkbox, enter the time in minutes for the custom action time. The custom action option will wait for that amount of time before starting maintenance on each database server. For maintenance configured with the non-rolling method, the maintenance run will wait up to the configured custom action time before starting maintenance across all database servers.
The Edit Maintenance Preferences panel also provides the ability to configure the preferred maintenance schedule.
2. Edit a scheduled maintenance plan
Once a quarterly infrastructure maintenance plan is scheduled, the date and time will appear next to Next Quarterly Maintenance under the Maintenance heading on the Infrastructure Details page. Click on the View link, next to the date, to view and edit the maintenance.
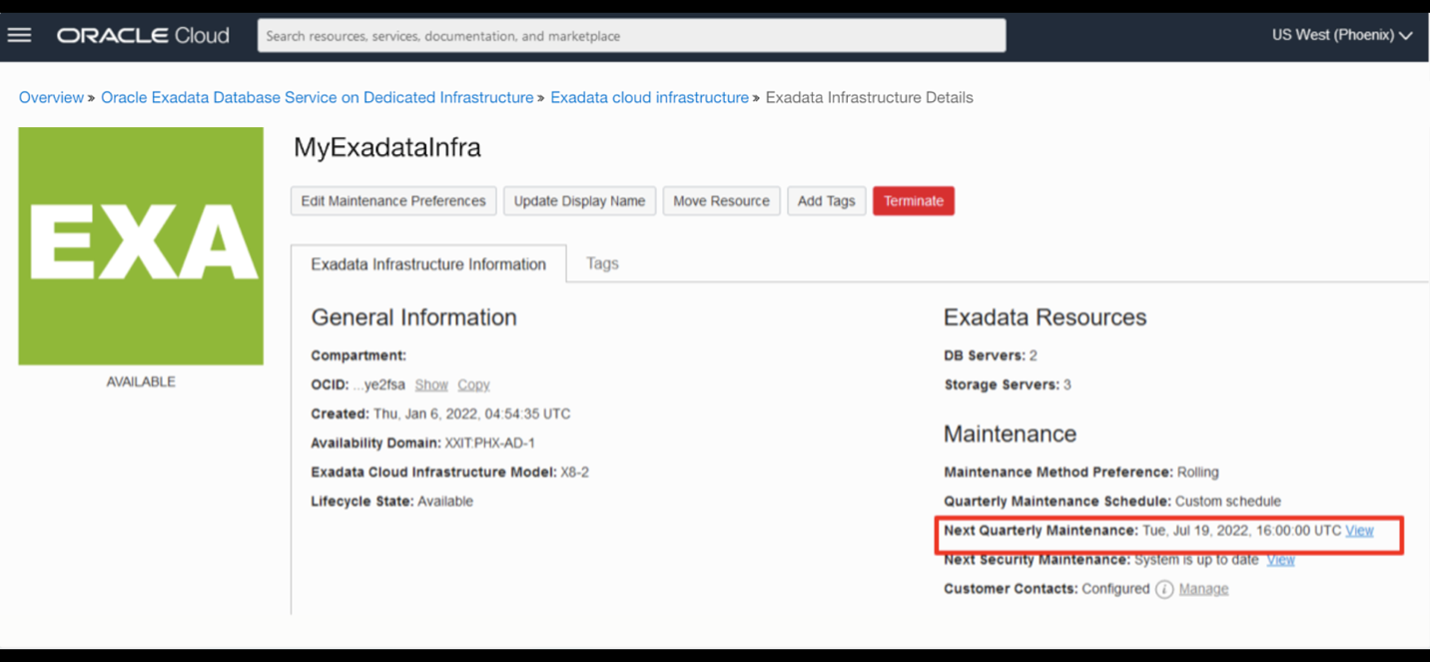
The Maintenance Details page displays the configured maintenance method, custom action time, total estimated maintenance time, and the target database server and storage server versions, which will be applied by the scheduled maintenance.
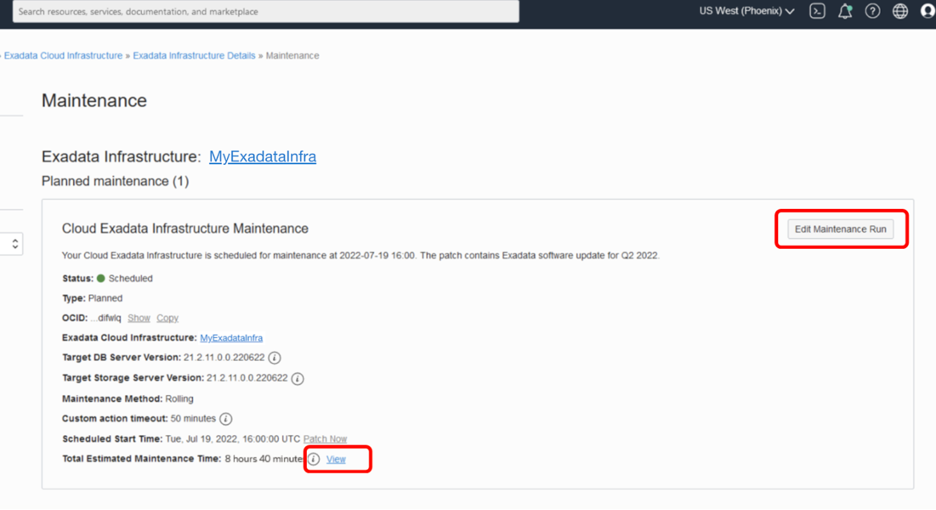
If the configured maintenance method is rolling, click the View link next to the Total Estimated Maintenance Time. The Estimated Maintenance Time Details panel shows the order and total estimated maintenance time broken down at a component level of the database and storage servers, and the network switches. Click on Show Details under Number of VMs Impacted to open a panel listing each VM on the database server.
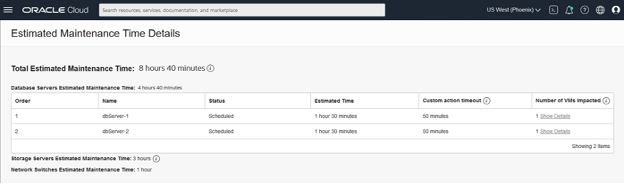
If you need to update the maintenance method, change the custom action time, or reschedule the start time of the maintenance, click the Edit Maintenance Run button.
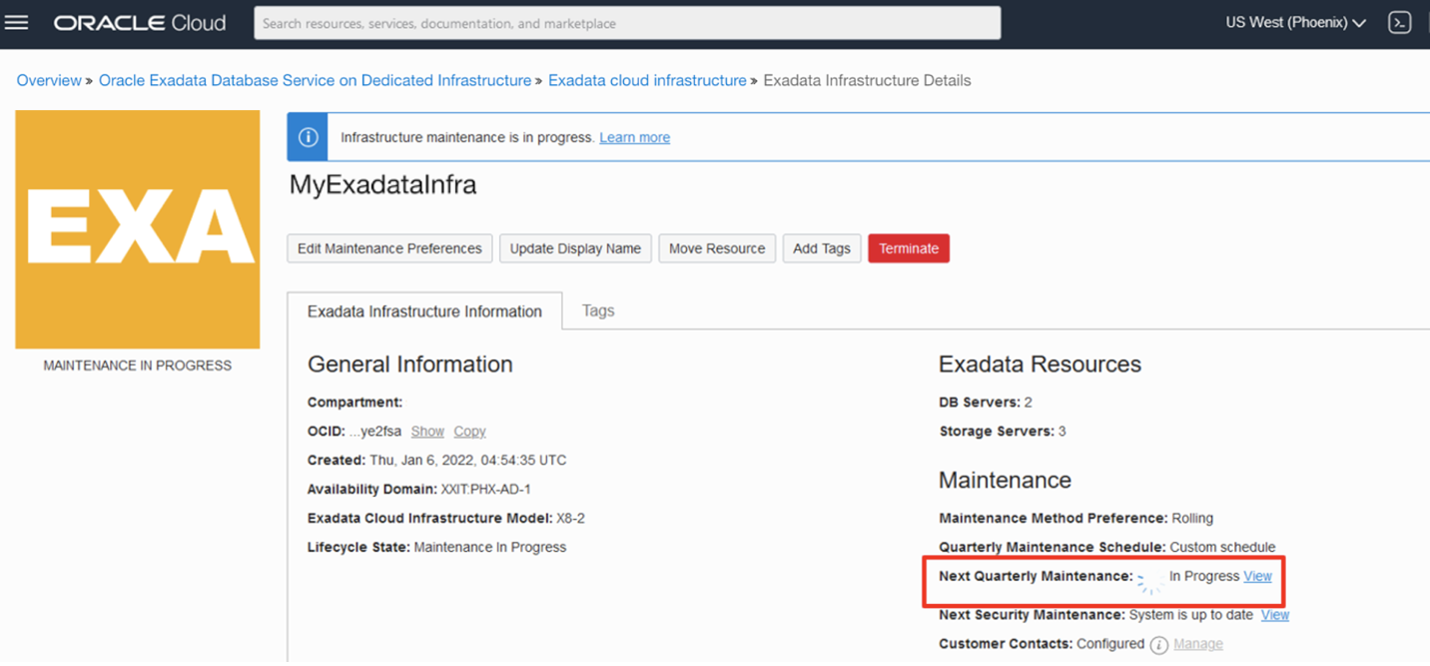
3. Edit an in-progress maintenance operation
When a quarterly infrastructure maintenance run has started, the Exadata Infrastructure resource and the Next Maintenance will show as “Maintenance in Progress” on the infrastructure details page. Click on the View link next to the Next Quarterly Maintenance field to view and edit the in-progress maintenance.
The Maintenance Details page will display the resource that is currently being updated and the status.
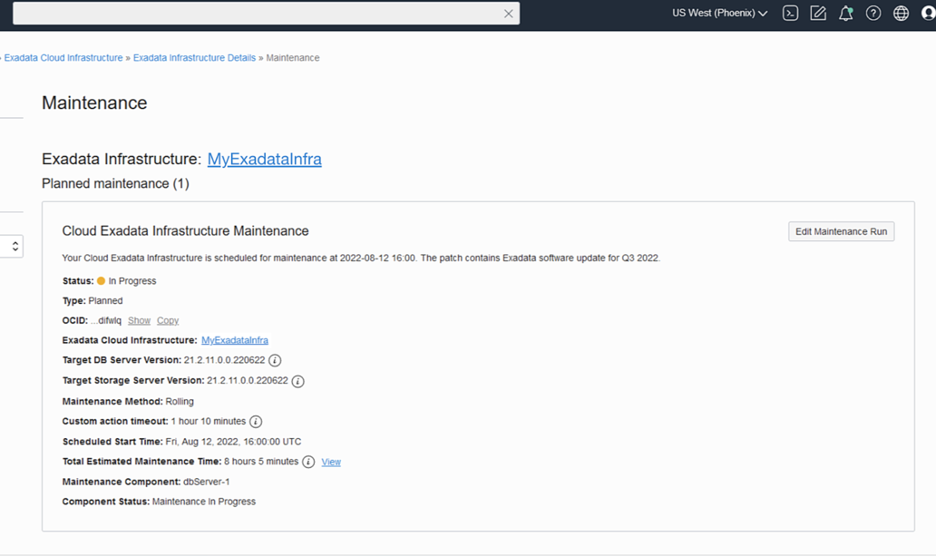
During the database server maintenance, click on the Edit Maintenance Run button to modify the custom action configuration. Any changes will be effective prior to database servers that have not yet been updated.
If the maintenance update is waiting for a custom action time to complete, an Info Block appears providing a button to Resume Maintenance Now, which immediately starts the maintenance on the next database server. If you need to extend the custom action time, click on Extend Custom Action Timeout, which allows extending the current custom action time in 30-minute blocks up to the maximum of 120 minutes.
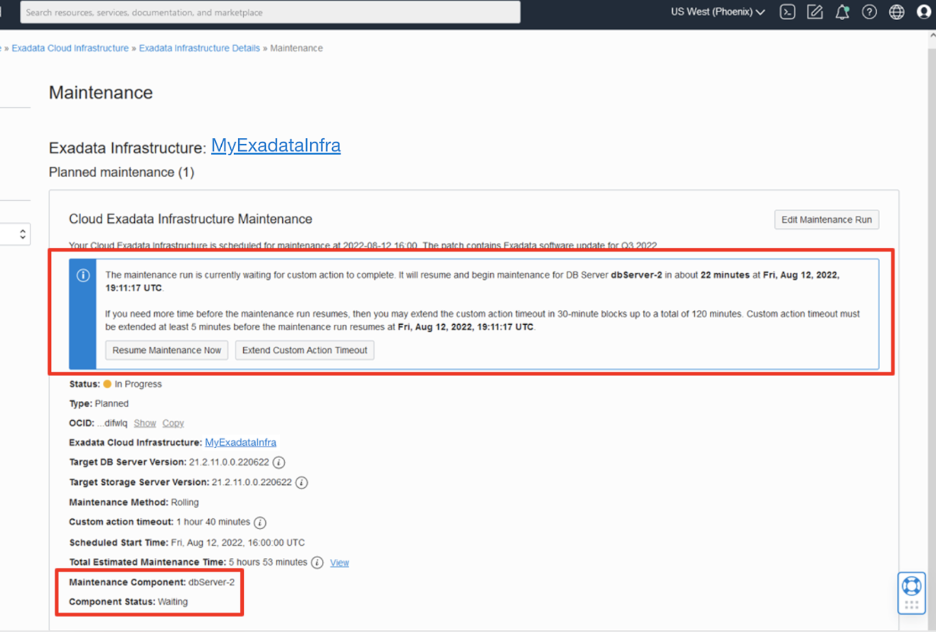
If the configured maintenance method is rolling, click the View link next to the Total Estimated Maintenance Time. This will display the progress of the maintenance at a component level to reflect the updated estimated maintenance time and the database server status of Scheduled, Maintenance in Progress, or Complete.

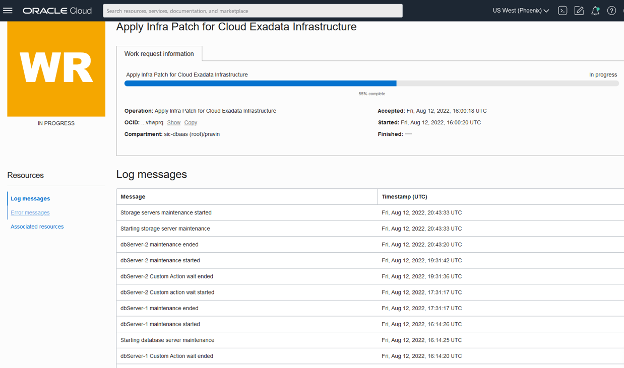
You can view the Log Messages to track the progression of the maintenance run. The OCI events service is also available to track the maintenance progress at an individual component level to provide messages for the start and end of each custom action time, each database server, and other components.
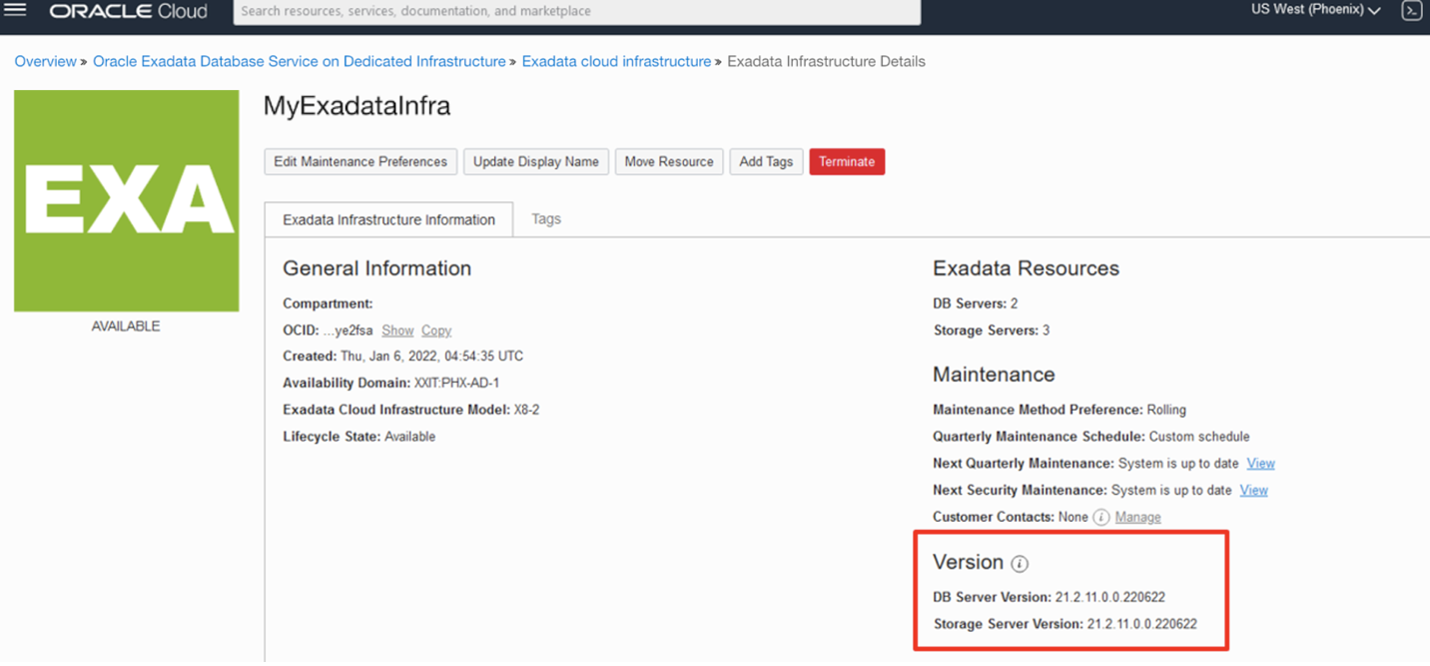
Once the maintenance completes, the Exadata Infrastructure returns to an Active state, the version is updated on the Infrastructure Details page, and a record of the maintenance is displayed on the Maintenance History page, accessible from Maintenance details.
Summary
By allowing greater control and visibility to monitor cloud maintenance including a choice of rolling and non-rolling maintenance methods, ability to perform custom actions before maintenance, and granular tracking of the maintenance progress at a component level will help you to ensure that your cloud infrastructure remains secure and up to date. As organizations move more of their operations to the cloud, it’s important to have a thorough and well-planned maintenance process in place.
Oracle continues to enhance maintenance updates to further automate and simplify the management of OCI database services. Cloud infrastructure maintenance is a critical component of ensuring the security, stability, and performance of a cloud environment.


