I am excited to announce the launch of Multiple VM Autonomous Database on Exadata Cloud@Customer. One of our customers’ most frequently requested features has been the ability to create Autonomous Database VM clusters and Exadata Database VM clusters on a single Exadata Cloud@Customer infrastructure. With the launch of Multiple VM Autonomous Database, customers can now create multiple Autonomous Exadata VM Clusters and Exadata Database VM Clusters on all their existing Exadata Cloud@Customer platforms from X7 Gen 2 to the newest generation.
Oracle’s Exadata Cloud@Customer is the world’s simplest path for customers to realize cloud benefits for database: self-service API agility, pay-per-use financial model, high availability, security, and standardization that reduces business risk. It brings these cloud benefits to the customer, behind their firewall, inside their data centers, and fully managed by Oracle using cloud native APIs. Exadata Cloud@Customer allows organizations to modernize their database estate and take advantage of cloud benefits without changing anything at the application layer in their enterprise architecture while meeting security, governance, and regulatory requirements.
Oracle Autonomous Database is the most operationally complete and simple to use database service for developers and administrators of database applications. The service provides machine-learning driven touchless mission critical capabilities with automatic and dynamic scaling, performance, and security. The service is especially well suited for modern application architectures that utilize multiple data types, workloads, and analytic functions in a single solution.
Autonomous Database on Exadata Cloud@Customer (ADB-C@C) were announced together in July 2020, providing an operationally complete and simple to use database service with all the benefits of the cloud in customers’ data centers.
To take advantage of ADB-C@C, customers have to create four primary resources:
- Exadata Cloud@Customer infrastructure
- Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster
- Autonomous Container Database
- Autonomous Database
However, as shown in Figure 1, the original deployment architecture required customers to dedicate the entire platform to either an Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster or Exadata Database VM Clusters.
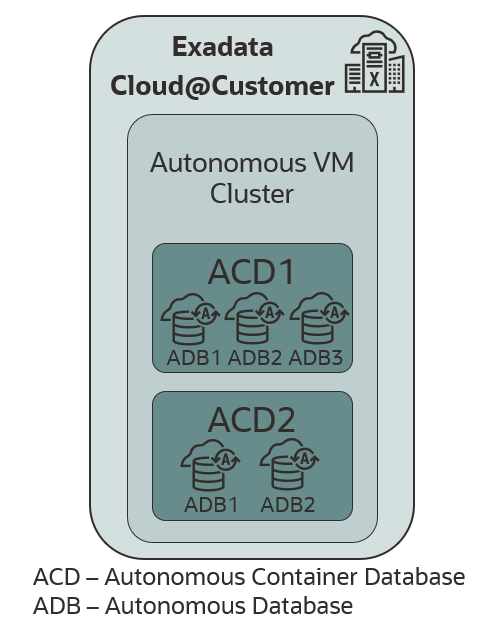
Figure 1: Autonomous Database on Exadata Cloud@Customer in 2020
With the announcement and general availability of Multiple VM Autonomous Database, customers can now create multiple Autonomous Exadata VM Clusters and Exadata Database VM Clusters on a single Exadata Cloud@Customer – as shown in Figure 2.
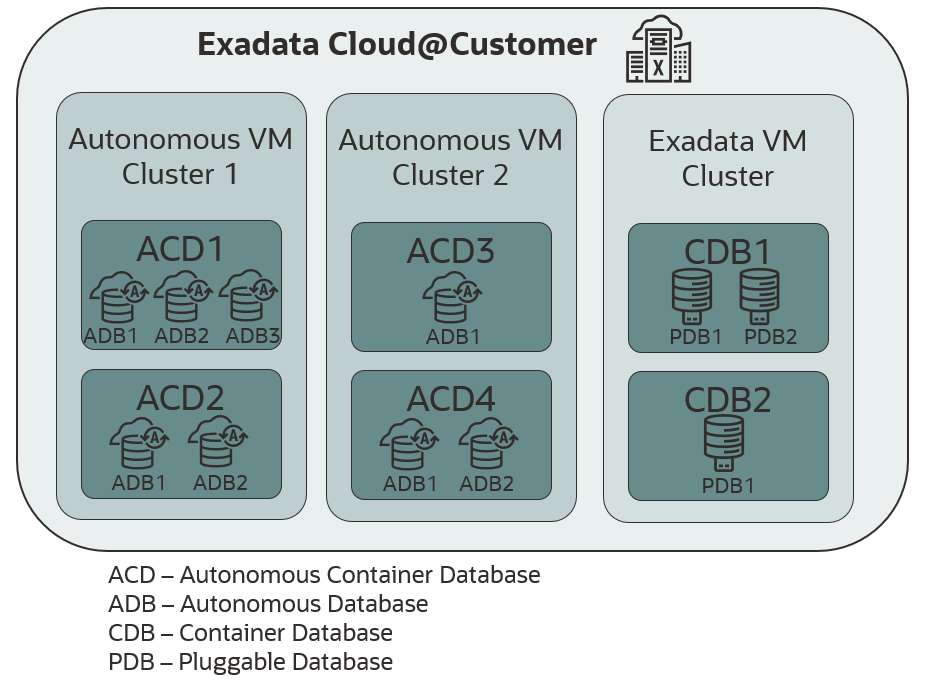
Figure 2: Multiple VM Autonomous Database on Exadata Cloud@Customer
Multiple VM Autonomous Database runs on a group of symmetric Virtual Machines that isolate highly available Autonomous Database Service instances and can be deployed alongside Exadata Database VM Clusters, running on a single Exadata Cloud@Customer infrastructure.
Each Autonomous VM Cluster supports separate network configuration, maintenance scheduling, license type selection (BYOL and License Included), and customizable memory, storage, and compute allocations on an Exadata Cloud@Customer to create and run Autonomous Databases.
Multiple VM Autonomous Database allows customers to provision isolated operational environments such as dev-test, staging, and production with their own access rules, quotas, and performance SLOs. This, in turn, enables organizations to not only migrate and modernize existing databases to gain cloud benefits, but also to create a self-service database application development platform that meets corporate governance standards. This allows internal developers to build new applications using autonomous databases that auto-tune, auto-scale and auto-manage.
By employing multiple VM clusters on existing and new Exadata Cloud@Customer deployments customers gain multiple benefits:
- Single Infrastructure with both Exadata Database Service and Autonomous Database Service
- Gain Autonomous Database experience using capacity on your existing infrastructure
- Efficiently allocate resources for different workloads on the same physical resources
- Incrementally upgrade all databases and conveniently migrate to Autonomous Database on the same Exadata Cloud@Customer
- Lowest Cost to Adopt Autonomous Database
- Set up Autonomous VM Clusters at no cost, enabling the creation of a cost-effective private Database as-a-Service (DBaaS) environment
- Pay only for running Autonomous Database workloads
- Leverage fractional CPU cores, auto-scale consumption as needed, and start/stop individual databases to reduce cost
- Simplify new and existing workloads
- Fully automate and optimize existing workloads
- Provide developer self-service databases for creating new applications
- Flexible License types
- Use both BYOL and License Included Autonomous Databases on the same Exadata Cloud@Customer infrastructure
- Defer production costs for critical deployments
- Create and test Autonomous Data Guard between Autonomous Exadata VM Clusters on the same Cloud@Customer infrastructure
- Enable dev/test use cases that require Autonomous Data Guard at a low cost
- Enable specialized workloads
- Customize compute, storage, and memory of each Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster configuration to optimally support different workloads
- Secure environment separation
- Network isolated Autonomous Exadata VM Clusters to provide enhanced security and predictable performance for specific workloads (dev-test, staging, and production)
OCI Console Experience
Create Autonomous Exadata VM Clusters
To create an Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster, navigate to the Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster list view page and select “Create Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster “.
Each Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster resource is network isolated by VLANs configured for the Exadata Cloud@Customer deployment. The networks are set up separately and at least one VLAN should be configured before creating your first cluster resource.
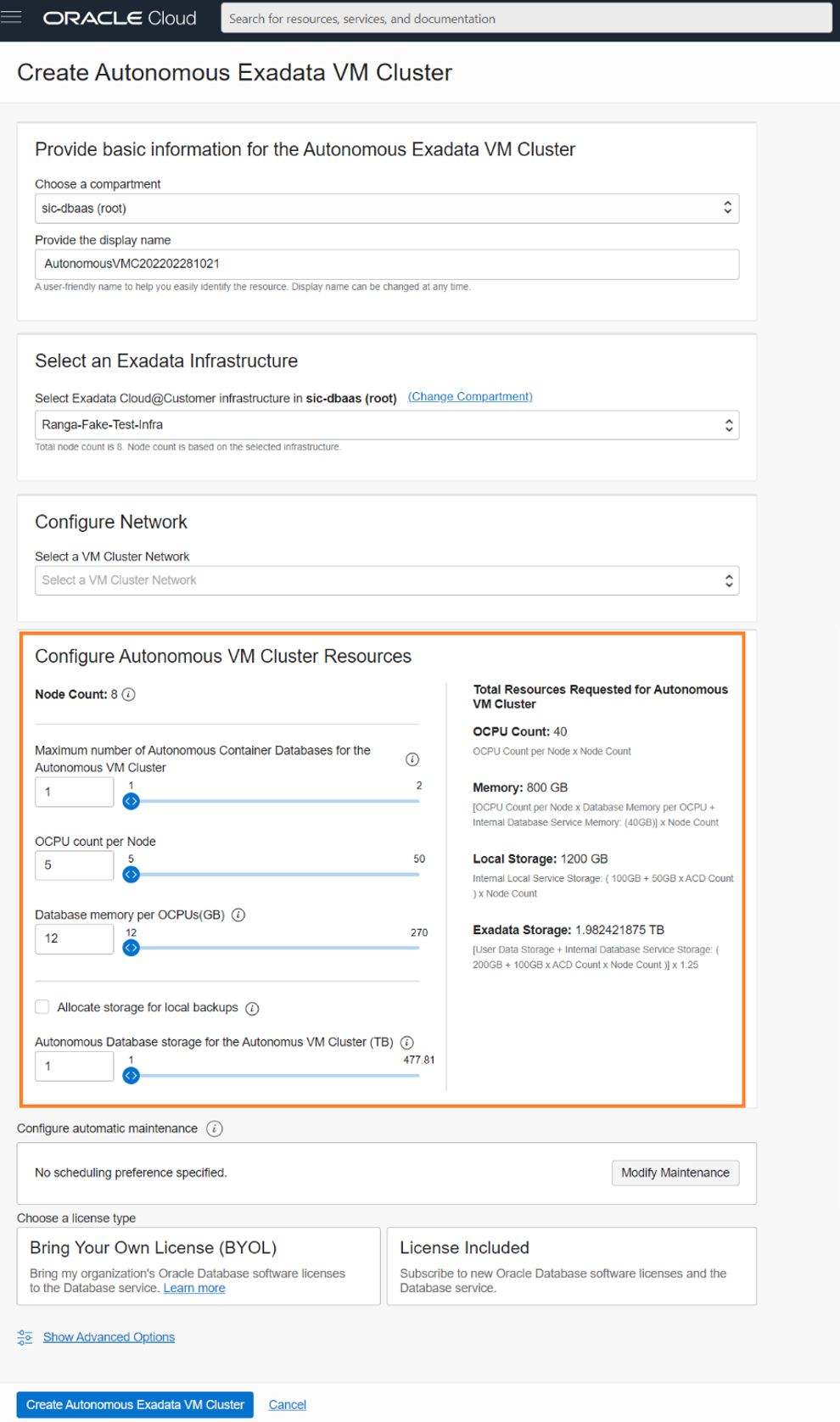
While creating an Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster, you must allocate resources that will be used for Autonomous Container Databases and Autonomous Databases. Key resource configuration parameters:
- Number of Autonomous Container Databases you plan to create in the Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster – Local storage is automatically allocated based on this value
- OCPU count per node – sets OCPUs per node in the Autonomous VM Cluster for Autonomous Databases
- Database memory per OCPU – sets total memory in the VM cluster for Autonomous Database workloads based on total OCPU allocation
- Autonomous Database Storage – User data storage for your Autonomous Databases
Resource configuration sliders default to the minimum values needed for the Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster.
Once the resource configuration parameters are set, the aggregate resources needed to create the Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster and the formulas used to calculate those values are displayed on the right side of the resource configuration section.
Each Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster has a separate maintenance schedule. Select the “Modify Maintenance” button to configure your Autonomous Maintenance preference. Set your maintenance schedule and click “Save Changes”.
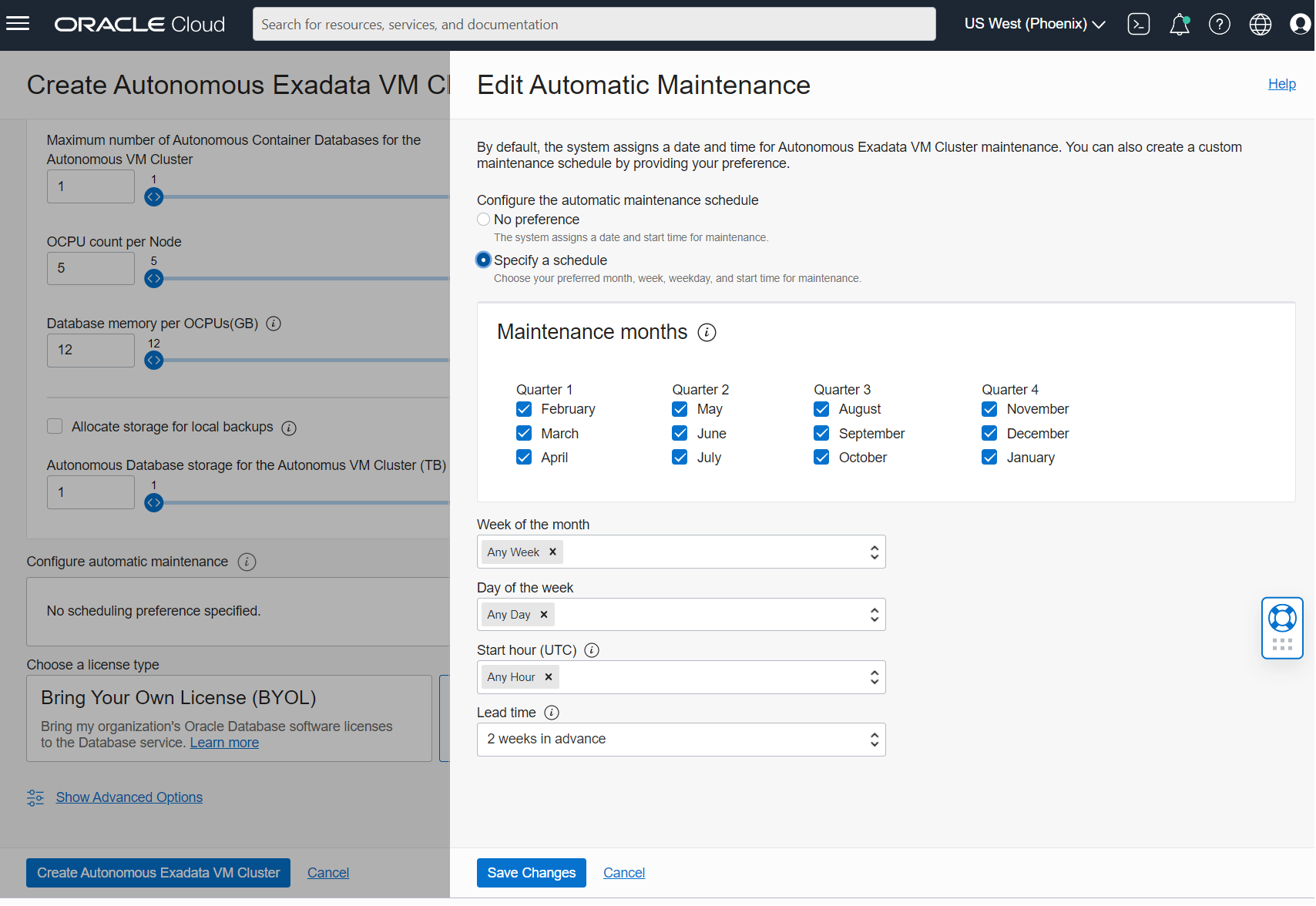
Note: Once the maintenance runs are scheduled, you can skip or reschedule them.
Select the license type and click “Create Autonomous Exadata VM Cluster”. With Multiple-VM Autonomous Database, you can have Autonomous Databases with different license types on the same Exadata Cloud@Customer infrastructure.
Note: The console experience for creating Exadata Cloud@Customer, Autonomous Container Database and Autonomous Database does not change with Multiple VM Autonomous Database functionality. Learn more about creating other resources here.
Availability
Console, SDK, CLI and Terraform for Multiple-VM Autonomous Database are available starting on March 16, 2022 in all OCI commercial regions.
Resources
Summary
Multiple VM Autonomous Database allows customers to create multiple Autonomous Database VM Clusters and Exadata Database VM Clusters on a single Exadata Cloud@Customer infrastructure. Support for multiple VM Clusters extends the value of Exadata Cloud@Customer investments from the X7 Gen 2 to the newest version.
- Single platform with both Exadata Database Service and Autonomous Database on Exadata Cloud@Customer
- Lowest cost to adopt Autonomous Database and set up a private DBaaS
- Flexible license types (BYOL and Included) on the same Exadata Cloud@Customer infrastructure
- Defer product costs for mission critical deployments with local DR testing
- Enable specialized workloads with customized Autonomous Exadata VM Clusters
- Secure environment separation with network isolated Dev-Test, Staging, and Production environments for different applications, projects, and lines of business.
Learn more about Autonomous Databases here.

