Today, we’re announcing the release of two features that give administrators more control over resource allocation and better tools to understand resource availability:
- Quotas let you allocate resources to projects or departments. Like service limits, quotas limit the use of resources. However, quotas are set by the customer administrators, whereas service limits are set by Oracle.
- A simplified Console experience and new Limits and Usage APIs make it possible to easily check resource availability by considering service limits, quotas, and current usage.
Quotas and the APIs are available in all regions with full support for Console, SDK, CLI, and REST APIs.
Key Use Cases for Quotas
Here are some key use cases for quotas.
Allocate Expensive Resources
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure gives enterprise customers flexibility and great performance through powerful resources like bare metal Compute and Exadata. Until today, these expensive resources could be deployed by anyone in the organization and on any project. Quotas enable administrators to allocate these high-value resources only to the compartments that they are intended for. As a result, only the projects, departments, or environments that should have access to these resources can deploy them. For example, you might want to implement controls to ensure that your Exadata resources are used only in specific production use cases. We have an example quota policy to help you implement this control (see the next section).
Restrict a Compartment’s Usage to a Small Set of Resources
With cloud, it’s often convenient for end users and operators to create a compartment for a specific task, such as running a demo, creating two VMs to run automation, or running a serverless app. Without quotas, users who manage these compartments could create any resources they want for any task, even demos. Enterprises need more control over cloud resources, and quotas let administrators create policies that limit VM counts or even disable services, when necessary.
Example Quota Policies
Quotas are defined using policies similar to Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies. The quota policy language gives administrators the flexibility and power to create the quotas that best meet the needs of their organizations. This blog post provides just a few examples to illustrate key use cases. The policy language is fully explained in the documentation.
Allocate all Exadata resources to the ProductionApp compartment
Unset database quota /*exadata*/ in compartment ProductionApp
Don’t allow bare metal Compute in a compartment
Don’t allow use of outbound email or notifications. Don’t allow any VM shapes other than 2-core X7.
Set compute quotas vm-standard2-2-count to 2 in compartment MyCompartment
Zero email-delivery quotas in compartment MyCompartment
Zero notifications quotas in compartment MyCompartment
Here’s an example of what a quota implemented for Exadata would look like in the Console.
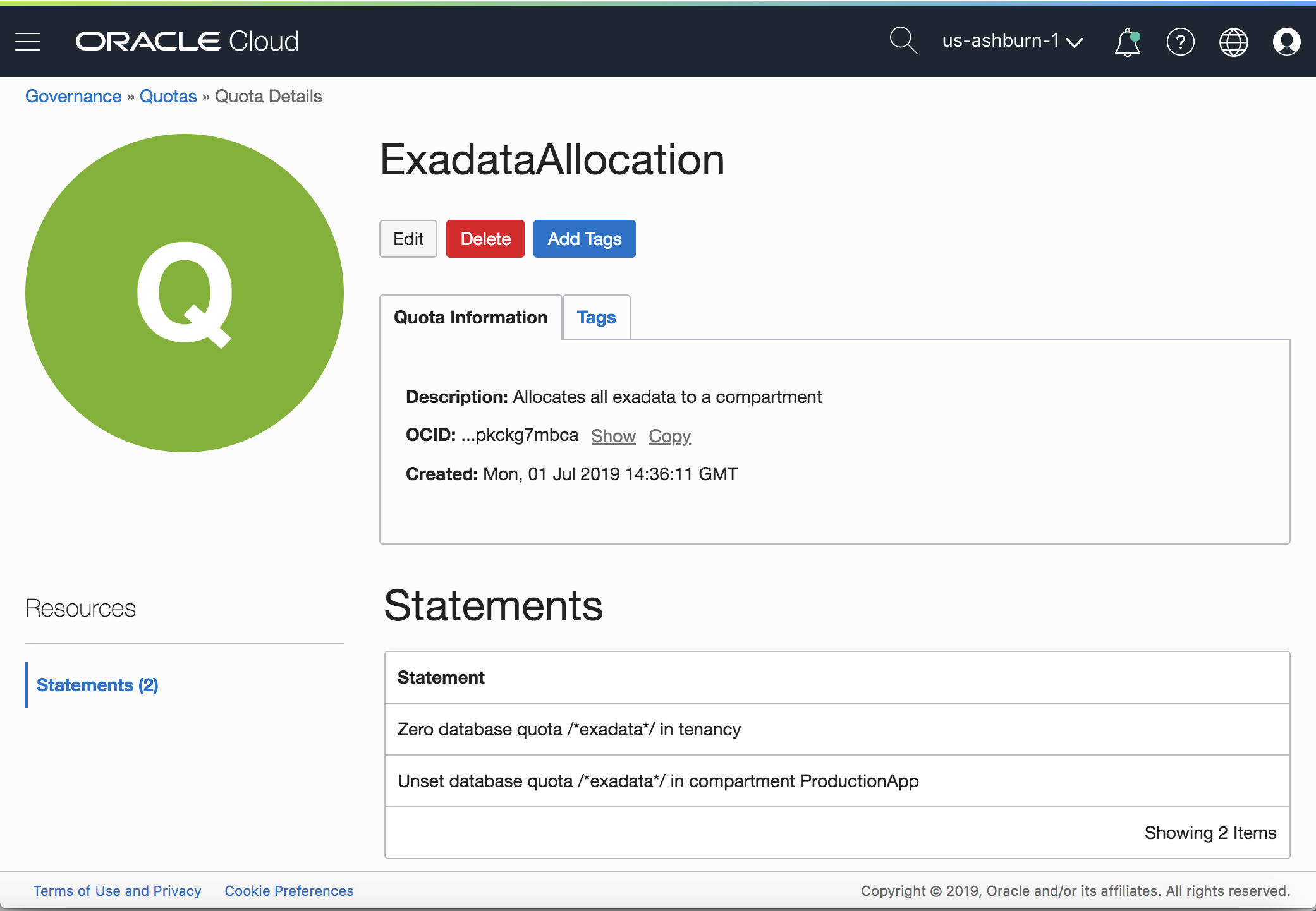
Figure 1: Example Quota Policy
Use Cases for the Limits and Usage APIs and Console Experience
Here are some use cases for the new Limits and Usage APIs and the updated Console experience.
Check Limits and Quotas Before a Deployment
Before now, it was difficult to automate limit checks before a deployment. As a result, a deployment job could run for a long time before failing because of a limits or quota issue. With the new Limits and Usage APIs, users and developers have better visibility into resource availability before starting a deployment. In addition, this enhanced visibility can allow you to avoid multiple requests to support to increase limits.
Check Limits in the Console and Request Limit Increases
In addition to getting better visibility into limits, quotas, and usage in the Console, administrators can request limit increases directly from the console, eliminating the need to file a service request.
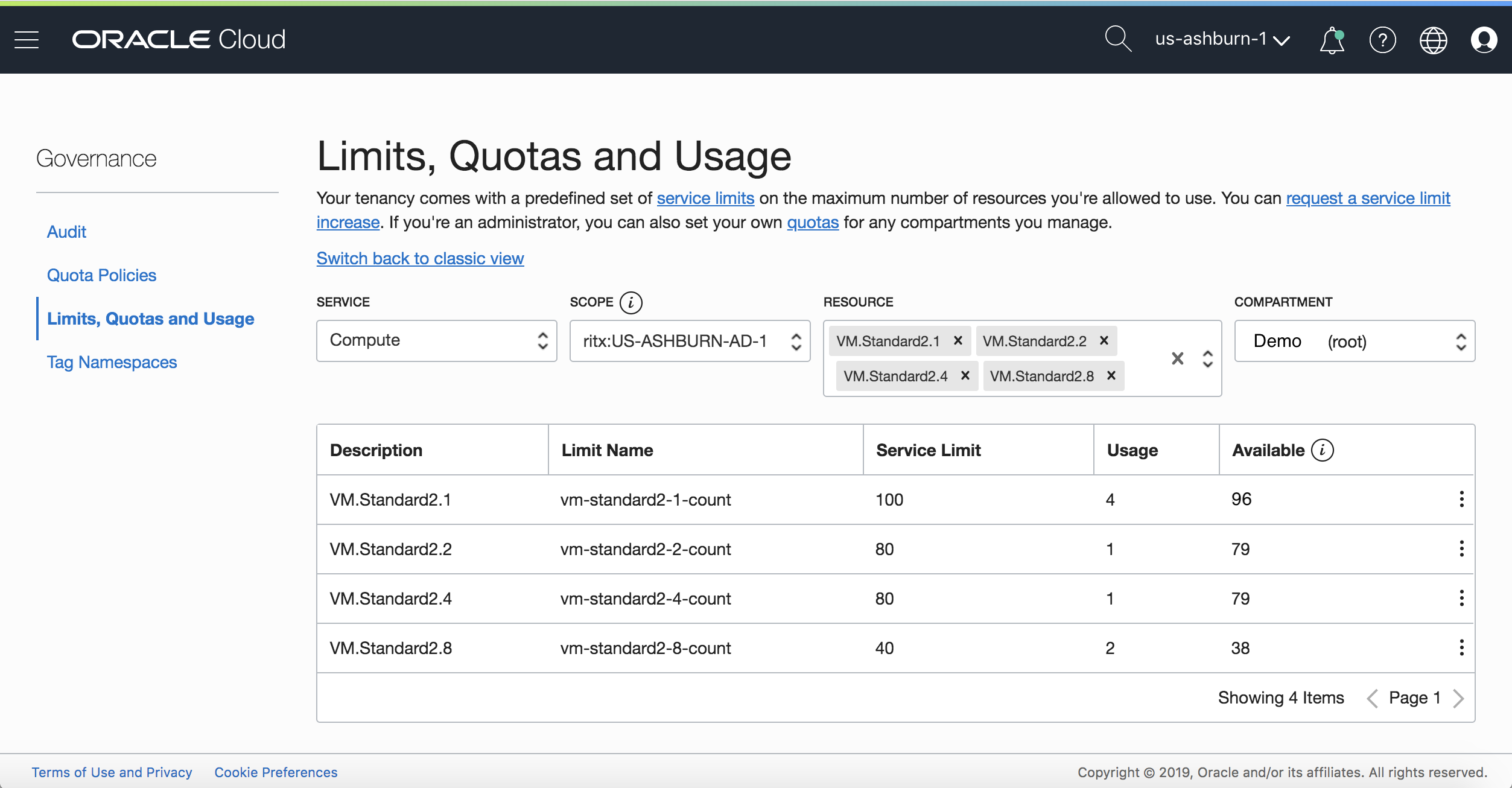
Figure 2: Checking Limits in the Console
Check out our Introduction to Cost Management video below.
Resources
- Quotas documentation, including a list of supported quotas and examples
- Console limits experience documentation, including how to request a service limit increase
- Limits API documentation
