Making AI supercomputing widely accessible is a key step to enhancing and supporting risk prevention. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) has partnered with NVIDIA and RSS-Hydro to develop capabilities to predict and respond to extreme weather conditions that can help prevent the loss of life, property, and infrastructure. With the broadest set of cloud deployment options, OCI’s AI powered infrastructure accelerated by NVIDIA GPUs allows the development and deployment of AI-powered climate resilience models in both public and private cloud environments.
AI can help in complex decision-making
AI models can capture complexities in nonlinear behavior and interactions in climate systems and identify hidden patterns that traditional statistical models might miss. Climate risks are constantly evolving, and AI can provide real-time risk assessments, enabling adaptive responses to changing conditions. By analyzing vast amounts of data on climate impacts, AI can help develop and refine resilience strategies, such as infrastructure design, emergency response plans, and agricultural practices. AI and machine learning (ML) are changing the way that humans can interpret complex scientific model outputs and can make informed decisions faster and more accurately.
Modeling risk of flooding and sea-level rise and the impact on urban centers
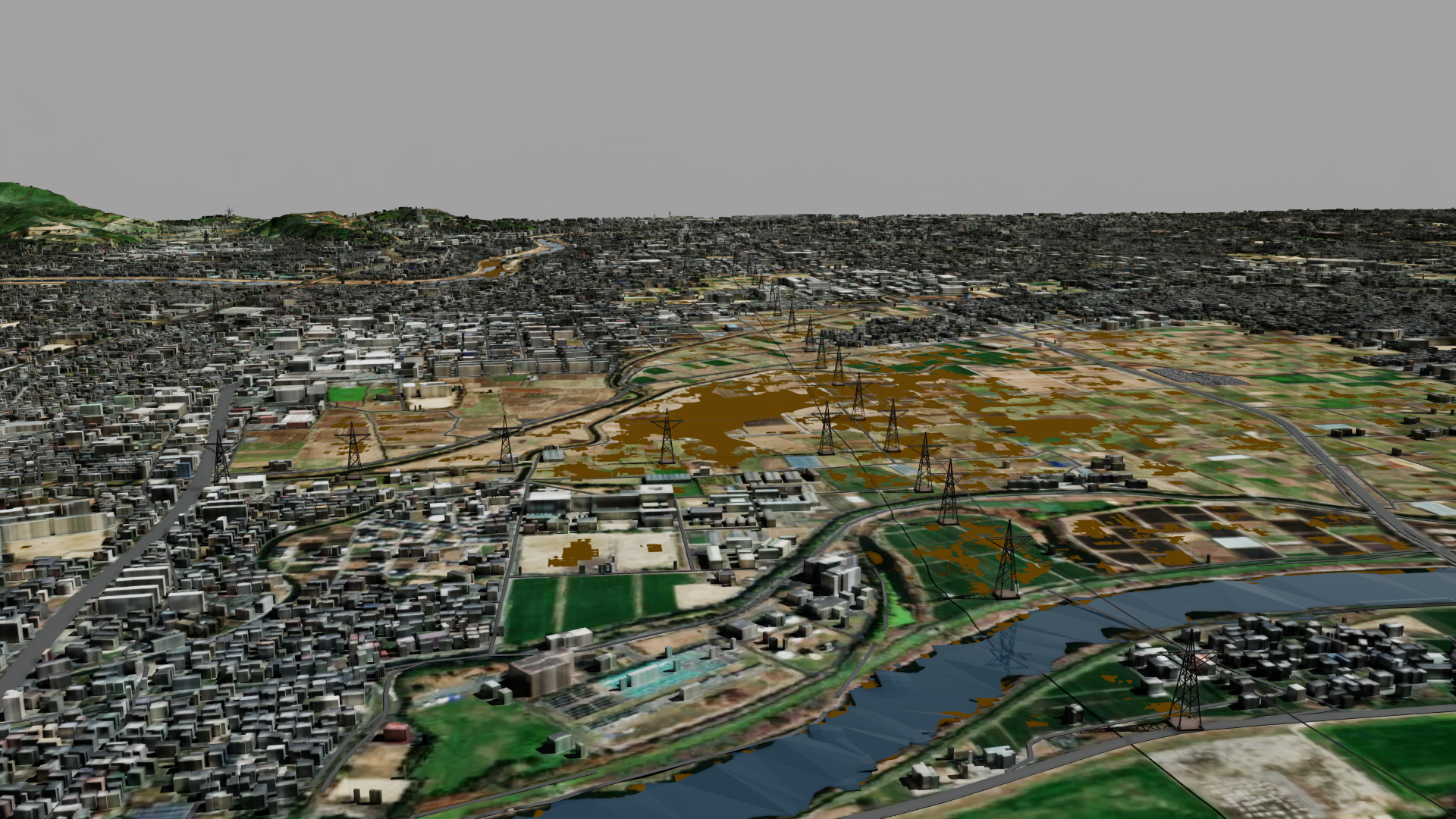
In this simulation, we show how to use pretrained RSS-Hydro FloodSENS ML models and hydraulic models to model flooding and inundation risk of an urban area in the Kumamoto region of Japan, based on potential precipitation and future sea-level rise. This region has coastline on one side and has rivers flowing through. Assuming a realistic precipitation scenario, the model simulates a large portion of the urban area being flooded because of a rise in the river water level, as shown in Figure 1. The model can be fine-tuned using images from actual flood event in 2020 as shown in Figure 2.
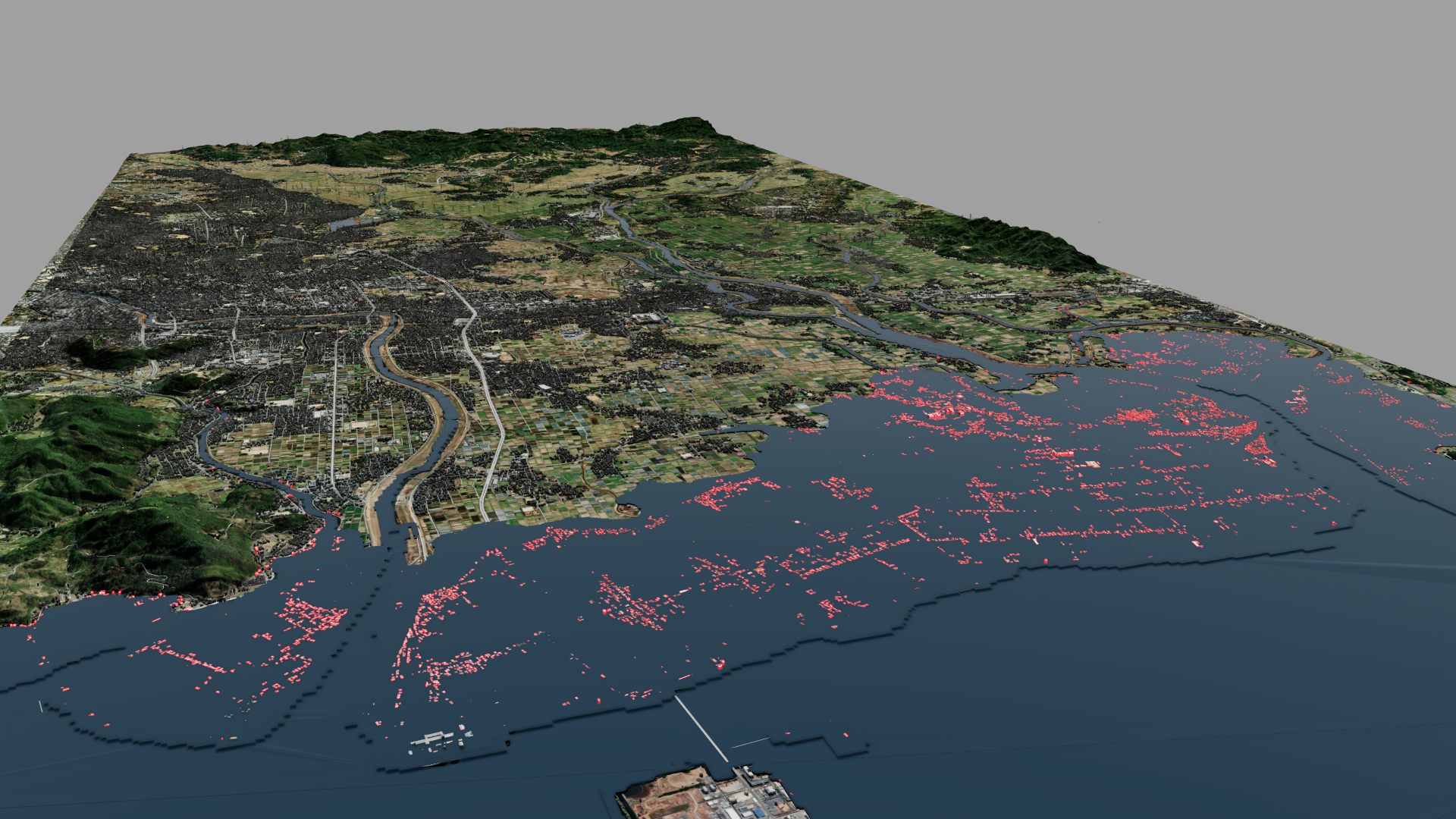
Assuming an extreme case, the model simulates the impact on the urban area being completely inundated because of a rise in sea-level by the year 2150, as shown in Figure 3. Buildings highlighted in pink are completely flooded. This rendering assumes no investments in infrastructure, such as sea walls, to protect against sea-level rise, which we note is an unlikely scenario.
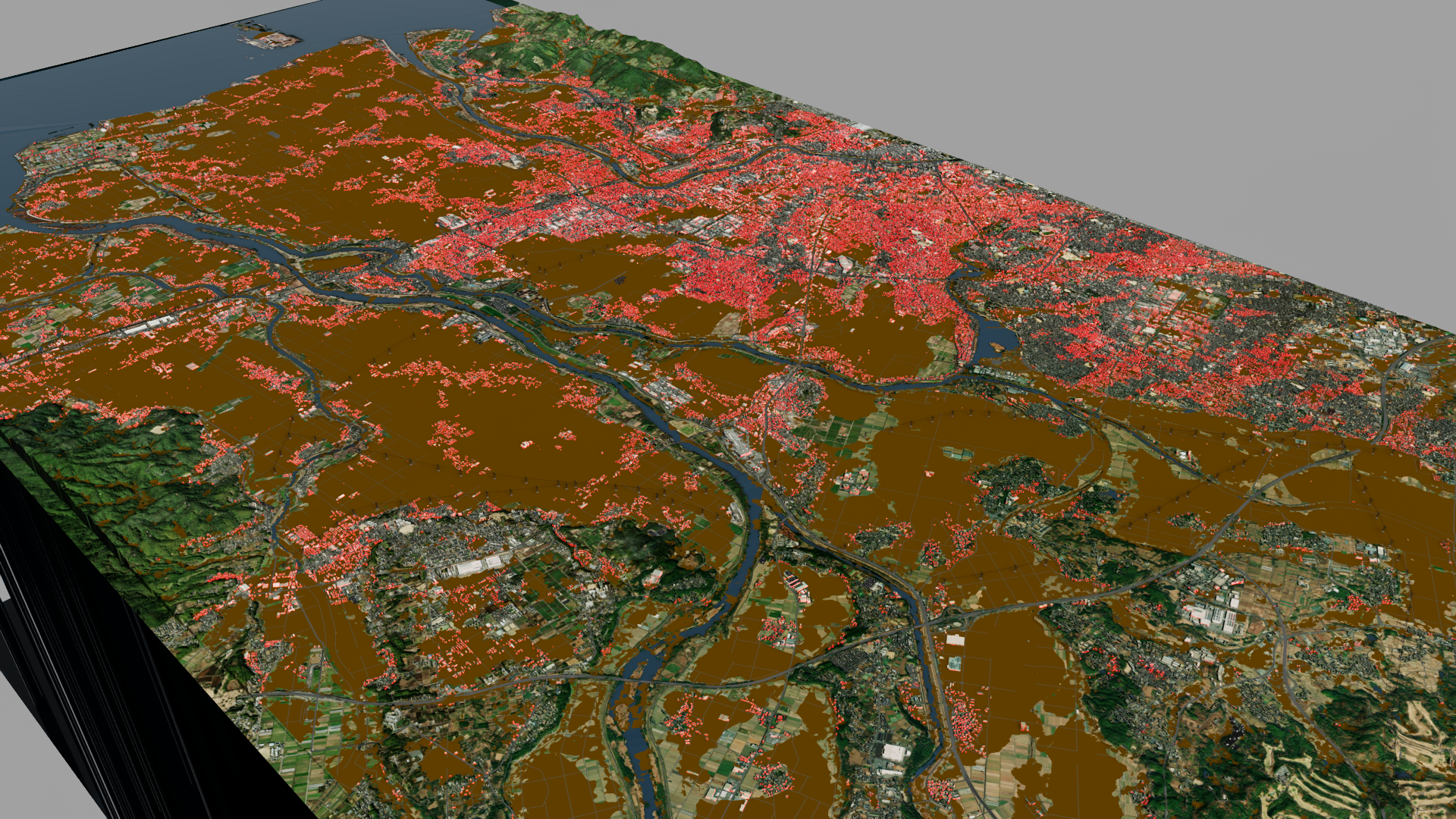
The data used to train and run these models are satellite images and precipitation data for the Kumamoto region in Japan. The output is compared against images of flooding post-rainfall and fine-tuned for accuracy. Training and fine-tuning are performed on a cluster of four NVIDIA L40S GPUs in an OCI public cloud region. The model is then used to simulate impact from rising river water and sea water levels on the geographic area, identifying buildings and key infrastructure that are potentially inundated.
RSS-Hydro brings a diverse set of data, including digital elevation models (DEMs) on buildings, high-precision geospatial data, 3D geographic maps, and the output of the FloodSENS model, all rendered inside an application developed on NVIDIA Omniverse, a platform of APIs and software development kits (SDKs) for building applications based on OpenUSD — an open and extensible ecosystem for describing, composing, simulating, and collaborating within 3D worlds. Users of the application can visually assess the flood impact on key locations, such as industrial zones and urban housing.
|
|
How can customers use this simulation to plan and mitigate the effects of severe weather?
By simulating and visualizing the data in the application, local governments and sovereign entities can plan and mitigate potential loss of life and property from flooding. Governments can use these simulations to anticipate inundation of urban areas, prioritize, and implement evacuation plans. Municipalities and urban planning can use these simulations to better lay out urban centers and invest in building structures to prevent flooding from sea levels rising. Service providers and utility companies can utilize these simulations to identify areas at higher risk of flooding and mitigate impact to critical infrastructure such as the electricity grid and telecom networks.
As shown in Figure 4, we deployed the simulation in an OCI public cloud region. The RSS-Hydro FloodSENS ML models are trained and then run on OCI virtual machines (VMs) accelerated by NVIDIA L40S GPUs from data stored in OCI Object Storage. The containerized application is deployed in a cloud-native manner using Oracle Kubernetes Engine (OKE). You can then fine-tune the models as needed. The output flood map from the model is stored in OCI Object Storage with high-precision geospatial data and rendered in an application developed on NVIDIA Omniverse.
Benefit of training, deploying, and visualizing the climate model on NVIDIA L40S GPUs on OCI
The NVIDIA L40S GPU delivers strong multi-workload acceleration for demanding AI training, inference, graphics, and rendering workloads. With accelerated AI compute and best-in-class visual computing capabilities, the L40S GPU serves as a universal GPU for generative AI and a great platform for running OpenUSD-based applications developed on NVIDIA Omniverse.
With third-generation NVIDIA RT Cores and multiple encode and decode engines, the L40S GPU is ideal for advanced visualization and digital twin applications, delivering exceptional performance for RSS-Hydro’s use case for rendering a digital twin of a city to visualize flood impacts in a physically accurate simulation.
In addition to graphics workloads, you can use the L40S GPU for small-to-mid-sized model training and fine-tuning. OCI’s AI infrastructure enables clustering of thousands of NVIDIA GPUs interconnected by ultra-high bandwidth network to train large modes and significantly improves price-performance relative to a local workstation. It can also easily scale to include large datasets for more accurate modeling across wider geography ranges. OCI Supercluster, which clusters up to 65,536 NVIDIA GPUs, offers more processing power than any other cloud provider, and enables customers to train over 100 billion-parameter LLMs.
Furthermore, you can deploy OCI’s AI Infrastructure almost anywhere using industry-leading distributed cloud solutions, such as Dedicated Regions, Alloy, Sovereign Cloud, or any of 50 public cloud regions in 24 countries across the world. Governments and other sovereign entities get complete control over where and how they deploy, train, and fine-tune ML models, such as RSS-Hydro’s FloodSENS. Data is stored and managed locally by the customer within their own geography, while maintaining cloud-scale availability and resiliency, thanks to Database solutions, such as Oracle’s Globally Distributed Autonomous Database. Oracle’s miniclusters further enable up to 64-GPU cluster deployments in smaller footprints within the customer’s own location using Oracle’s Dedicated Region for fine-tuning and inferencing of ML models.
RSS-Hydro innovates by providing geospatial and modeling intelligence for better disaster management. As the name suggests, it focuses on flood disasters. RSS-Hydro uses satellite Earth Observation data and numerical modeling, combined with the newest technologies in AI and computer graphics from NVIDIA to help clients increase resilience and preparedness.
Conclusion
Climate change is quickly becoming a reality that governments and local authorities are gearing up to face. The employment of AI in training models using satellite images, precipitation data, and 3D structure data — and subsequently using the models to simulate the potential impact of severe weather — can help local authorities in urban planning, infrastructure management, and disaster mitigation. RSS-Hydro FloodSENS ML models and innovative modeling intelligence help simulate the impact of flooding and inundation on urban centers from high levels of precipitation and sea-level rise. The use of NVIDIA L40S GPU clusters deployed on OCI significantly improves price-performance and scales to train over large datasets. Simulations can also be rendered in applications built on NVIDIA Omniverse with increased accuracy. Deployed across distributed cloud solutions, OCI’s AI Infrastructure enables governments and sovereign entities to build and train models, such as RSS-Hydro FloodSENS ML models, almost anywhere within their geography. Data to train models is also stored and managed within their geography.
The use of AI by sovereign entities in service of their own citizens and advancing their own economies and national interests isn’t limited to severe weather management but finds wide use cases across industries, such as healthcare and financial services. Read about how Widelabs is training one of Brazil’s largest LLMs with NVIDIA GPUs on OCI in Brazilian data centers to maintain data sovereignty, and see how NRI is leveraging Oracle Alloy and AI Infrastructure powered by NVIDIA GPUs, along with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Generative AI services, to serve Japan’s financial services industry.
To learn more, attend our Sovereign AI session at CloudWorld and visit our demo, Advancing Climate Resilience With RSS-Hydro Built on NVIDIA and OCI.


