The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) File Storage service provides a snapshot feature that creates a read-only copy on the write file system. Snapshots are helpful in keeping a local backup of a file system for the following use cases:
- Upgrades and patching: You’re making upgrades or major patches where you need a backup to recover from any failure
- File revisioning: Users need a past state of a file or folder.
- File restoration: A file or folder is accidentally deleted, and you need to restore them.
Learn more about how to take snapshot and snapshot management.
This blog post talks about how you can use policy-based snapshots and replication together to create a robust, easy-to-configure, and faster-to-recover backup solution for your OCI File Storage file system.
The policy-based snapshot of OCI File Storage allows you to create an hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly schedule so that the snapshots are automatically created based on the schedule. Because the snapshots reside in the file system, an inadvertent deletion of file system also deletes the snapshots.
The replication feature replicates the file system to a target file system that can be in the same or different availability domain or region based on user choice.
Backup options
When choosing a backup site, you have the options available based on how isolated each backup is:
- Availability Domain or Region: For the source file system in an availability domain, the replication is created in the same availability domain as the source or a different availability domain in the same region or different regions, as shown in the following two diagrams.


-
- Same Availability Domain: This option is helpful in cases such as application patching, where you want the backup to be close to the application environment.
- Different Availability Domain: Because File Storage is scoped at the availability domain, having the backup in another availability domain helps enable access to the file system if the availability domain of the source file system fails.
- Different Region: This option of file system backup is helpful in the crosscountry or crosscontinent disaster recovery setup.
- Different Compartment: The compartment can be another layer of isolation in addition to the availability domain or region layer. If the backup site needs a restriction access policy where only a few users access the backup, while regular users and groups that have access to the source file system shouldn’t access the backup site, you can choose a different compartment.

- Hybrid or Combination: The File Storage replication feature allows up to three active replications, which allows you to have three different replicas in different locations. The following example uses a combination of different replications:
- Replica 1 is in the same availability domain and same region in the same compartment.
- Replica 2 is in a different availability domain in the same region, but a different compartment.
- Replica 3 in a different region and in a different compartment
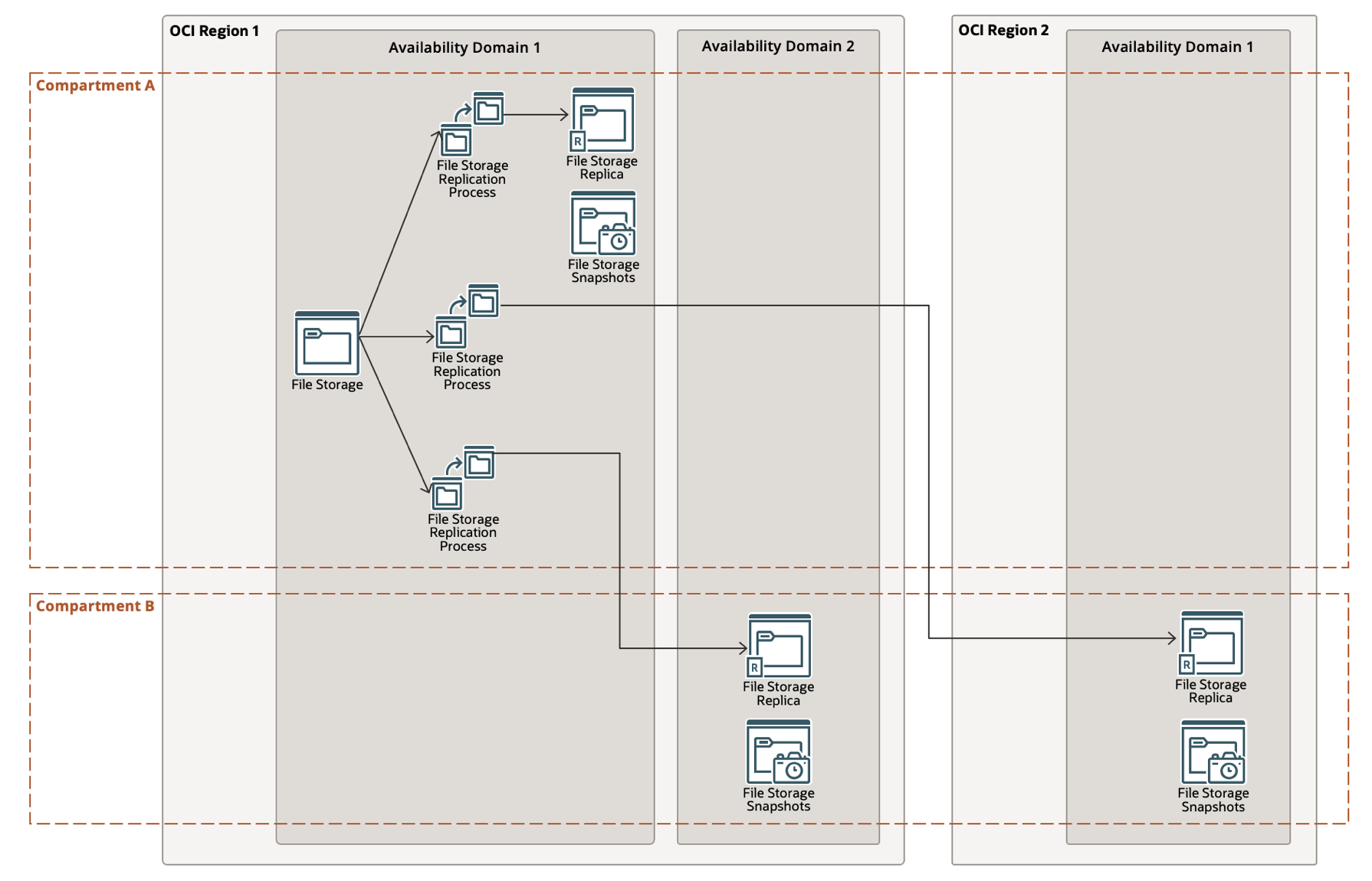
The hybrid model gives the option of having a local availability domain backup for patching for quick recovery of missing files and enabling cross-country or cross-continent disaster recovery for a file system. These backups are isolated and secured in a compartment that’s different from the source file system so that only restricted users have access to them.
Try it yourself!
The policy-base snapshot and replication features of OCI File Storage have their own independent purpose and benefits. When used together, we can accomplish a backup plan for OCI File Storage file systems that’s easily configurable, quickly recoverable, and highly available across logical and physical boundary.
If you’re a first time user of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage, we encourage you to create file systems and try yourself the backup methodology with the following steps:
- Configure policy-based snapshot and attach the file system.
- Configure replication.
- After a few replication cycles, create a clone from the latest replication snapshot of target file system.
- Mount the clone file system on a destination instance and validate the snapshots created by the policy-based snapshot feature.
For more information, see our documentation on How to create Policy Based Snapshot and How to create File System Replication.