This blog is part 5 of our multipart series on data sovereignty in the cloud.
Each year, we’re witnessing exponential growth in the amount of data generated around the globe. We’re also seeing organizations and individuals starting to ask more questions about where all this data goes and how it’s used. The term “data sovereignty” has moved beyond just being discussed by privacy experts and can now be seen regularly making headlines across major news outlets. However, data sovereignty can be complex and nuanced, often leaving people with more questions than answers.
Instead of looking at data sovereignty as an outcome, we’ve written this series to explore the different components organizations can use to build a sovereign cloud strategy, including location, realm isolation, access management, and personnel requirements.
Earlier in the series, we talked about how managing access to cloud resources and data, along with other safeguards, can help prevent unauthorized access, collection, use, or disclosure of data. In this post, we look at the ways you can implement more layers of security to protect sensitive data, strengthen your security posture, and build trust with your end customers.
Enhance your data security with vaults and hardware security modules
You can use cryptographic solutions to maintain confidentiality, integrity, availability, and control access to your data. Let’s take a closer look at managing cryptographic keys and secrets with vaults and hardware security modules (HSM).
Vaults
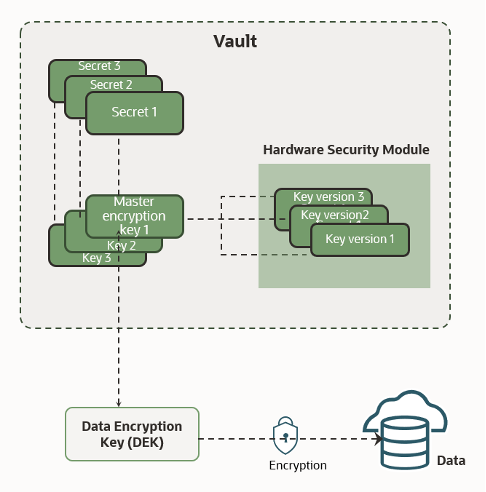
Vaults are logical entities that create and securely store keys and secrets, such as passwords, certificates, SSH keys, or authentication tokens. Oracle’s key management service, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Vault, currently offers two vault types to accommodate your organization’s needs and budget. The type of vault you select determines the features and functionality, such as the degree of key storage isolation, access to management and encryption, scalability, backups, and pricing. Both options store your keys on an HSM, but you can use either a dedicated or multitenant HSM partition.
In a dedicated partition, you have virtual private vaults, which offer more isolation, backup and restore, and cross-region replication. Virtual private vaults include 1,000 key versions by default. If you don’t require this degree of isolation or the ability to back up the vault, you don’t need a virtual private vault. Without a virtual private vault, you can help manage costs by paying for key versions individually, as you need them.
No matter which option you choose, OCI Vault is designed to maintain the security and integrity of the encryption keys and secrets stored in the vault.
Hardware security modules
An HSM is designed to provide dedicated cryptographic functionality, including key generation, key storage, and digital signing, on a one-to-one basis to their host applications. HSMs are specialized hardware that’s harder to access than normal server memory, making them part of a traditional security best practice design. OCI Vault uses HSMs that meet Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) 140-2 Security Level 3 security certification. This certification means that the HSM hardware is tamper-evident, has physical safeguards for tamper-resistance, requires identity-based authentication, and deletes keys from the device when it detects tampering.
OCI Vault can use HSMs to generate and store a root of trust (RoT) that protects encryption keys used by OCI Vault to safeguard users’ keys and credentials. When using OCI Vault service with an HSM, keys and credentials can be read if the RoT stored in the HSM is available. Because HSMs are designed to make the RoT difficult to extract, this system significantly mitigates the risk of compromise of users’ keys and credentials.
One thing that global data protection laws have in common is that they require appropriate security measures to be taken to protect personal data and, by extension, sensitive personal data. By using trusted cryptographic solutions like OCI Vault and HSMs, organizations can limit the risk of unauthorized transfer, use, or access to the data they place in OCI. Let’s look at some of the ways that these cloud services can enhance your cloud security posture and, in turn, help strengthen your data sovereignty strategy.
-
Secure key management: OCI Vault provides a centralized and secure approach to key management. Keys are crucial components in cryptographic systems, and their protection is vital to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. OCI Vault and HSM can help organizations generate, store, protect, and manage cryptographic keys throughout their lifecycle, including key generation, distribution, rotation, revocation, and destruction. Additionally, customers can use their own security keys hosted on the HSM to encrypt their data.
-
Compliance and regulatory requirements: Many industries and jurisdictions have specific compliance and regulatory requirements for protecting personal and sensitive data. OCI Vault and HSM solutions enable organizations to meet these requirements by providing a robust framework for encryption and key management. Compliance frameworks, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and guidance issued under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), require the use of secure key management practices.
-
Data integrity: OCI Vault and HSM play a crucial role in ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data. By securely managing cryptographic keys, organizations can encrypt sensitive information and protect it from unauthorized access or tampering. OCI Vault can help enforce strong encryption practices and enable organizations to maintain control over their data, even if when it’s stored or processed by third-party services or cloud providers.
-
Enhanced security for applications and systems: OCI Vault and HSM offers a higher level of security for applications and systems that require cryptographic operations. By migrating key management and cryptographic operations to dedicated hardware or secure services, organizations can benefit from the robust security features provided by OCI Vault, including protection against attacks, such as key theft, tampering, or unauthorized usage.
-
Protection against insider threats: OCI Vault and HSM can help mitigate risks associated with insider threats. With proper access controls and separation of duties, organizations can limit the exposure of cryptographic keys to authorized personnel only. OCI Vault and HSM provide audit logs and monitoring capabilities, allowing organizations to track and detect any unauthorized or suspicious activities related to key management.
-
Trust and assurance: Utilizing OCI Vault and HSM can enhance trust and assurance in the security of an organization’s cryptographic operations. By adopting industry-standard practices and technologies, organizations demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive information. This aspect can be particularly important for businesses that handle sensitive customer data because it helps build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
OCI Vault and HSMs are available in all OCI’s distributed cloud deployment models and provide centralized management of the encryption of customer data with keys that you control.
Protect data in use with confidential computing
Another critical component of a modern data sovereignty strategy is securing data actively being accessed and processed. With confidential computing, customers can ensure that data remains encrypted, not just at rest and in transit but also in use. Confidential computing encrypts and isolates in-use data and the applications processing that data at the hardware level.
A confidential instance is a compute virtual machine (VM) or bare metal instance where both the data and the application processing the data are encrypted and isolated while the application processes the data, preventing unauthorized access or modification of either the data or the application. Currently, OCI offers confidential computing on bare metal and VMs that use AMD EPYC processors.
Confidential computing has several benefits for organizations to consider as they decide how to augment their security posture to include confidential computing VMs or bare metal servers. By providing security through foundational layers of hardware, confidential computing minimizes the list of trusted parties, including OS, ecosystem partners, and administrators, reducing the risk of data exposure. By providing a smaller attack surface and more security of data in use through a tightened hardware-based root of trust, it protects against some types of vulnerabilities, such as insider threats and firmware compromises.
Confidential computing has the following main benefits:
-
Improved isolation using real-time encryption
-
Data and applications are encrypted using a key unique to the VM that is not accessible from any applications, VM or instance, the hypervisor, or to OCI
-
No change is required to the application to enable confidential VMs
-
Protects data in-use with minimal performance impact to the applications
-
You can implement with no extra cost on top of OCI Compute instance pricing
In highly regulated industries, such as finance, healthcare, and defense, protecting data throughout its entire lifecycle is critical. Using confidential computing to encrypt and isolate data in use on OCI Compute instances can help meet and maintain regulatory compliance and support sovereign cloud strategies.
Getting started with Oracle sovereign cloud solutions
Having the right tools to secure your data—be it at rest, in transit, or in use—is critical to a successful sovereign cloud strategy. With OCI, customers have access to the latest cryptographic solutions at the hardware and software level. Unlike some other cloud providers, these offerings aren’t confined to specific regions or deployment models. Whether you’re running workloads in one of OCI’s public cloud regions, OCI Dedicated Region, or another one of OCI’s cloud deployments, you get access to over 100 OCI services.
The capabilities of OCI’s distributed cloud are designed to give you the control to decide where your data is located, how it’s secured, and who has access to it. Knowing this information, we’re actively developing new and intuitive solutions in this space. Though the key management solutions discussed in this post will meet most customers’ data sovereignty requirements, certain organizations want to keep their encryption keys separate from any cloud provider. In our next post, we continue the theme of cryptography by looking at OCI External KMS.
If you have any questions about vaults, HSMs, or confidential compute, or want to learn more about Oracle sovereign cloud solutions, contact one of our representatives. To learn more about the various deployment models that Oracle offers, see the following resources:
