Introduction to Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation
Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation is an integrated suite of cloud storage and data services for the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. It provides a highly available, software-defined storage solution that delivers persistent storage for containerized applications running on OpenShift in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
OpenShift Data Foundation offers a scalable, unified, and easy-to-manage storage solution, consisting of several open source operators that provide file, block, and object storage capabilities for your containerized workloads in OpenShift on OCI.
Key Storage Services in OpenShift Data Foundation
OpenShift Data Foundation provides storage services to applications via storage classes, representing the following components:
- Block storage(ceph-rbd): Ideal for database workloads such as PostgreSQL.
- Shared sile storage(cephfs): Suitable for software development, data aggregation workloads, and services like the Red Hat Container Platform Registry or WordPress.
- Object storage(ceph-rgw): Provides an S3 API Endpoint that supports data abstraction and retrieval from multiple object stores.
Subscription Requirements and Feature Supports
With the OpenShift Platform Plus subscription, you can install Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation Essentials on any cluster entitled with OpenShift Platform Plus. OpenShift Data Foundation is available in two versions: Essentials and Advances. For detailed feature comparisons between these versions, refer to the OpenShift Data Foundation Subscription Guide.
ODF Installation Modes in OCI
You can install OpenShift Data Foundation by using OCI Block Storage in one of the following modes:
- Internal or local mode
- External or remote mode
Internal or Local Mode
OCI block volumes are attached to the worker nodes as underlying cloud storage in local mode. To use this mode, ensure that the same-size block volume is attached to each worker node in the OpenShift cluster. Optionally, dedicate infrastructure nodes specifically for building the OpenShift Data Foundation storage architecture.
OpenShift Data Foundation abstracts the underlying OCI Block Storage into a virtualized storage layer, enabling the creation of file, block, or object persistent volume claims (PVCs). OCI block volumes range from 50 GB—32 TB and offer various performance tiers based on IOPS and throughput requirements. These tiers are defined by virtual performance units (VPUs), ranging from 0–120 VPUs per block volume, delivering Balanced, High Performance, and Ultra High Performance storage options to meet diverse workload needs. For more details about the VPU refer to the Block Volume Performance.
External or Remote Mode
In external mode, you can consume OCI block volumes through the CSI driver without directly attaching them to the worker nodes. This mode provides the same storage capabilities as the local mode. This blog post focuses on the local installation method of OpenShift Data Foundation in OCI.
OpenShift Data Foundation Availability Architecture in OCI
OCI regions are defined by geographical locations and can have either multiple availability domains or a single availability domain within the region. Availability domains are physical data centers within an OCI region. Multi-availability domain regions contain three availability domains connected by a high-bandwidth, low-latency network. Each availability domain is further divided into three fault domains, which are isolated server racks offering redundancy.
These availability constructs are key to designing a resilient OpenShift cluster in OCI, helping ensure high availability and redundancy for storage provided by OpenShift Data Foundation.
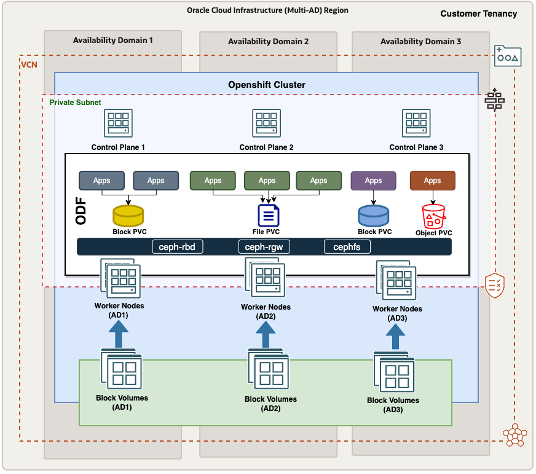
The architecture contains the following components:
- Availability domains: In a multi-availaiblity domain deployment, the OpenShift cluster is distributed across three OCI data centers, which are connected by high-bandwidth, low-latency backbone connectivity. As shown in the architecture diagram, OpenShift cluster nodes are spread across the availability domains in a round-robin mode to help ensure full redundancy.
- OCI Block Volume: OpenShift Data Foundation uses the OCI block volumes attached to the worker nodes in local mode to create a software-defined storage layer, providing persistent storage. Block volumes are utilized in multiples of three, with data replication occurring across these volumes to help ensure resiliency. These block volumes are fully redundant and backed by OCI’s service license agreement (SLA). Block volumes are specific to each availability domain and are only accessible within the corresponding availability domain.
- Regional subnets: Regional subnets are Layer-3 networks that span across the three availability domains in an OCI region, providing a flat network service for the OpenShift cluster.
- High availability OCI’s architecture provides redundancy that allows the OpenShift cluster to tolerate the complete failure of an availability domain. OpenShift Data Foundation supports high availability by replicating data across multiple block volumes, enabling it to continue operating even if access to block volumes in one availability domain is lost. This design offers availability domain-specific redundancy for the OpenShift cluster.
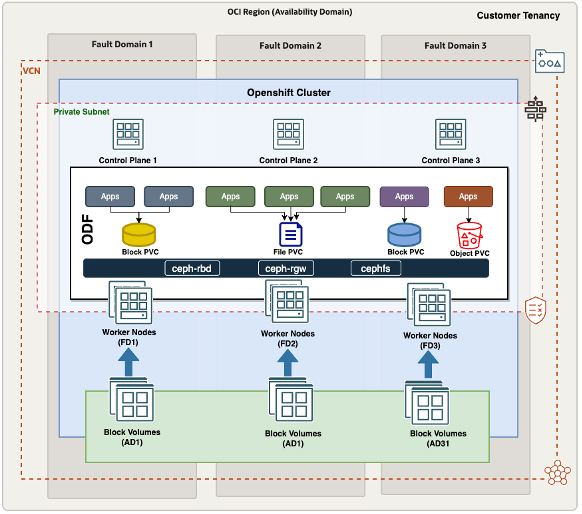
The architecture contains the following components:
- Availability domains: In a single-availability domain deployment, the OpenShift cluster is stretched across three fault domains within a data center. OpenShift cluster nodes are distributed across these fault domains to offer rack-level redundancy.
- Block volumes: Similar to multi-availability domain deployments, OpenShift Data Foundation utilizes block volumes attached to worker nodes in local mode to provide persistent storage. Block volumes are used in multiples of three, with data replicated across these volumes. The underlying block volumes remain redundant and are supported by OCI’s SLA. Block volumes remain confined to a single availability domain, meaning data is contained within that availability domain.
- Regional subnets: In single-availability domain regions, regional subnets are stretched across three fault domains, providing connectivity for the OpenShift cluster.
- High availability: In single-availability domain deployments, OCI provides redundancy to tolerate a complete fault domain failure. However, to ensure availability at the availability domain level, implement a disaster recovery strategyin a secondary OCI region. All OCI regions are interconnected by a high-throughput, low-latency backbone network, helping ensure high-performance redundant architecture for the OpenShift cluster.
Key Components of OpenShift Data Foundation
The OpenShift Data Foundation architecture contains the following key components when deployed in OCI:
- Ceph storage: Ceph is the core storage engine for OpenShift Data Foundation, providing scalable, distributed storage. It replicates data across multiple nodes, helping ensure fault tolerance and high availability.
- Rook operator: The Rook operator simplifies storage management in Kubernetes by automating the deployment, configuration, and scaling of the Ceph storage cluster. This operator ensures seamless integration with OpenShift.
- Storage: OpenShift Data Foundation supports the following types of storage, which allows users to choose the most appropriate storage type for their workloads:
- Object storage: Suitable for unstructured data.
- Block storage: Ideal for databases and applications.
- File storage: Useful for shared file systems.
These components work in harmony to create a resilient, highly available storage infrastructure. Through the use of distributed storage and automated management, OpenShift Data Foundation enhances availability, helping ensure data durability and minimizing downtime in cloud environments.
OpenShift Data Foundation Operator
The ODF operator is a Kubernetes operator that automates the deployment, configuration, and management of storage resources in an OpenShift cluster. It simplifies the setup process by handling the following tasks:
- Provisioning storage through Ceph clusters.
- Managing scalability as workloads grow.
- Encouraging resiliency by monitoring storage health and performance.
By using the OpenShift Data Foundation operator, managing persistent storage in OpenShift becomes easier and more efficient, reducing the manual intervention required for day-to-day operations.
Conclusion
Running OpenShift Data Foundation in OCI offers a powerful combination of scalability, resiliency, and high availability. Whether deployed across multi-availability domain regions or within single-availability domain environments, OpenShift Data Foundation helps ensure that your containerized workloads are backed by robust, software-defined storage with full support for block, file, and object storage.
With OCI’s redundant architecture, including fault and availability domains, and OpenShift Data Foundation’s distributed Ceph storage, enterprises can achieve seamless data replication, high fault tolerance, and minimal downtime, helping ensure business continuity even during infrastructure failures. The integration of OpenShift Data Foundation with OCI’s low-latency, high-bandwidth network further enhances performance, making it an optimal solution for mission-critical applications.
Additionally, the Rook operator and other automation capabilities simplify management, reduce operational overhead, and enable dynamic scaling, making OpenShift Data Foundation in OCI an ideal choice for organizations looking to modernize their infrastructure with containerized workloads while maintaining data integrity and operational efficiency.
Overall, OpenShift Data Foundation in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure delivers a flexible, scalable, and resilient storage solution for enterprises, supporting modern application architectures with confidence and security.
For more information, see the following resources:
- Oracle Cloud Regions and Availability Domains
- Getting started with OpenShift Container Platform in OCI
- Overview of Oracle Cloud Block Volumes
- Block Volume Performance
- Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation
