Domain name system (DNS) management is crucial for a company in many aspects. Its proper implementation can solve significant problems and be the decisive key in many infrastructure, disaster recovery, and workload management strategies. A DNS delegation zone, also known as a delegated domain or subdomain, is a segment of a larger domain that is assigned to a separate entity or organization for management of its own DNS records.
How DNS delegation works
In the DNS, a hierarchical naming system translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses, and a delegation zone represents a subdivision of a parent domain. It involves assigning authority to a different set of DNS servers to handle the resolution of records within that specific zone.
When a delegation occurs, the parent domain delegates control over a subdomain to another entity. You can achieve this delegation by creating a delegation record, known as a name server (NS) record, in the parent domain’s DNS zone. The NS record specifies the authoritative DNS servers responsible for managing the subdomain’s DNS records.
By delegating a zone, organizations or individuals can exercise control over their own DNS infrastructure and make changes to their DNS records independently, without relying on the parent domain’s DNS administrators. This independence allows for efficient management, flexibility, and autonomy in configuring DNS settings for a specific subdomain.
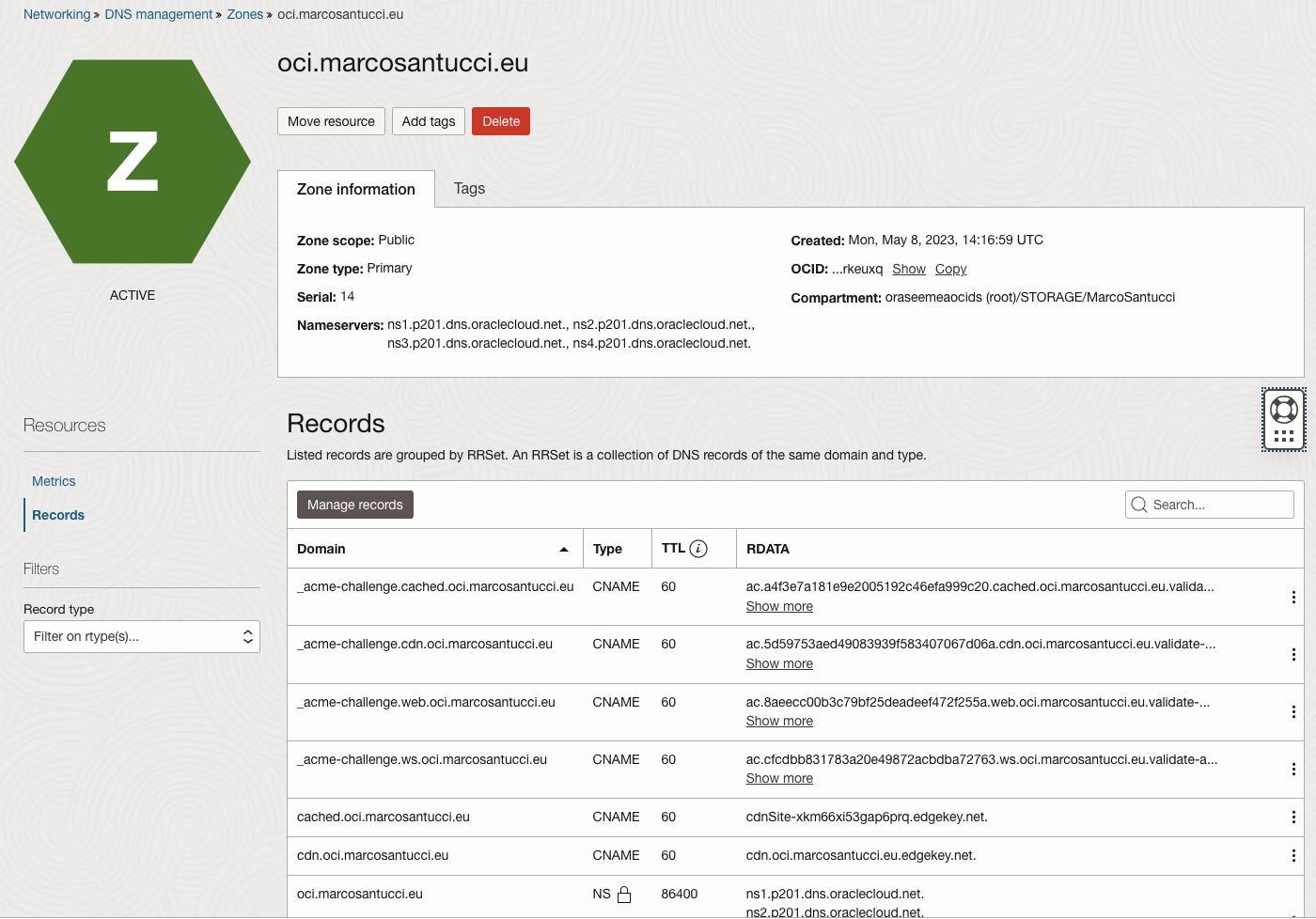
Delegating a zone from the registrar to an OCI public DNS
Create a public zone in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
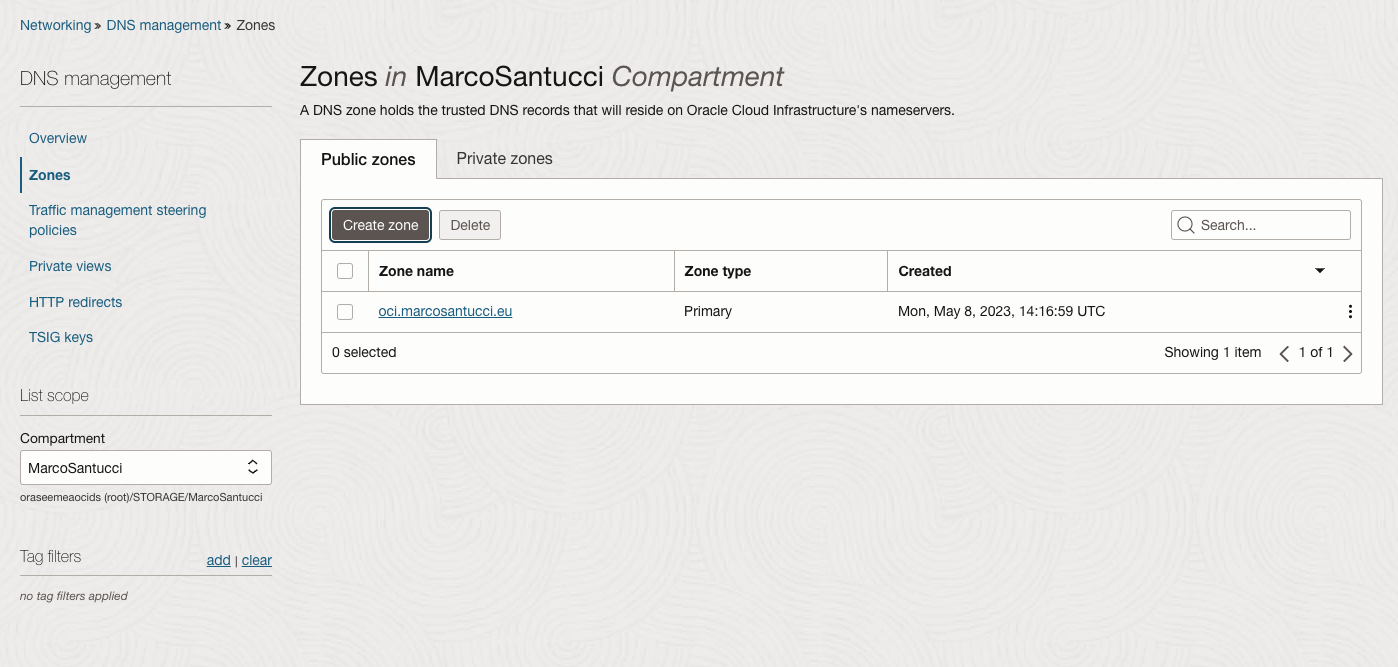
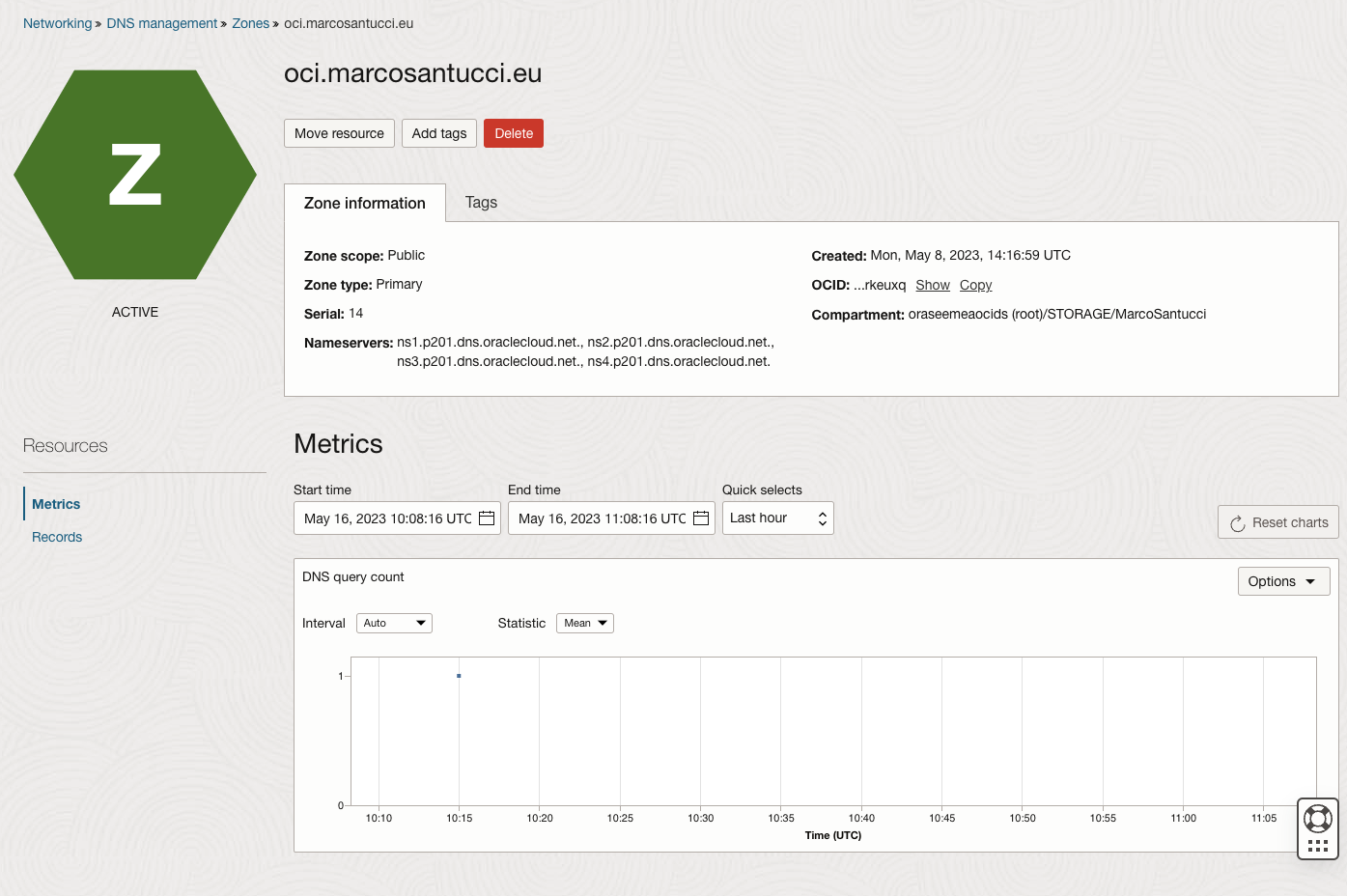
Note the public NS records of OCI.
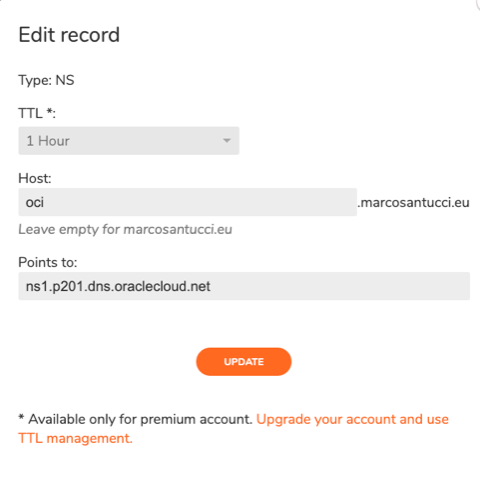
Create at least two NS records on your DNS registrar that point to Oracle NS servers. My DNS registar is cloudns.net.

You’re done! Now, you can directly manage all records in the oci.marcosantucci.eu zone with Oracle DNS.
Conclusion
The implementation and management of a public DNS zone on OCI can bring many benefits to your infrastructure. By implementing DNS with the other OCI’s services, such as geolocation steering, failover, and load balancing, you can design modern infrastructures that offer top-tier business availability in the market. For more information, see our DNS documentation.
