Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) offers Arm-based processors to run cloud native and general purpose workloads with significant price-performance benefits. Currently, Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE) supports the ability to run containerized applications on Arm using managed nodes.
Today, we’re excited to share that you can now deploy and oversee any containerized task running on Arm architecture within OCI. This capability extends across OCI Container Instances, OCI Functions, and OKE, encompassing virtual nodes and managed nodes.
Reduce costs by running containers on Arm in OCI
Powered by Ampere Altra processors, the OCI Ampere A1 shape allows you to run containers with Arm cores at only $0.01 per core per hour and $0.0015 per GB of RAM per hour. For benchmarks, when running x264 video encoding workloads on OCI Ampere A1, Oracle saw up to a 10 percent performance increase and up to a 22 percent price-performance benefit compared to x86-based systems. For NGINX reverse proxy workloads on OCI Ampere A1, Oracle saw up to a 46 percent performance increase and up to a 62 percent price-performance benefit compared to x86-based systems.
You get the first 3,000 core-hours and 18,000 GB-hours free per month for instances created with Ampere A1 shape. This free-tier usage is shared across bare metal, virtual machine (VM), and Container Instances.
Run Container Instances on Arm
OCI Containers Instances is a serverless compute service that enables you to run containers instantly without managing any servers or VMs. It’s suitable for containerized applications that don’t require Kubernetes. A new flexible shape powered by Ampere A1 shape, CI.Standard.A1.Flex, is now available with Container Instances. It enables you to run containers on Arm-based processors. Get started with the following steps:
- Log in to your OCI account. If you don’t have an Oracle Cloud account yet, request a free trial.
- Open the navigation menu. Under Developer Services, go to Containers & Artifacts and click Container Instances.
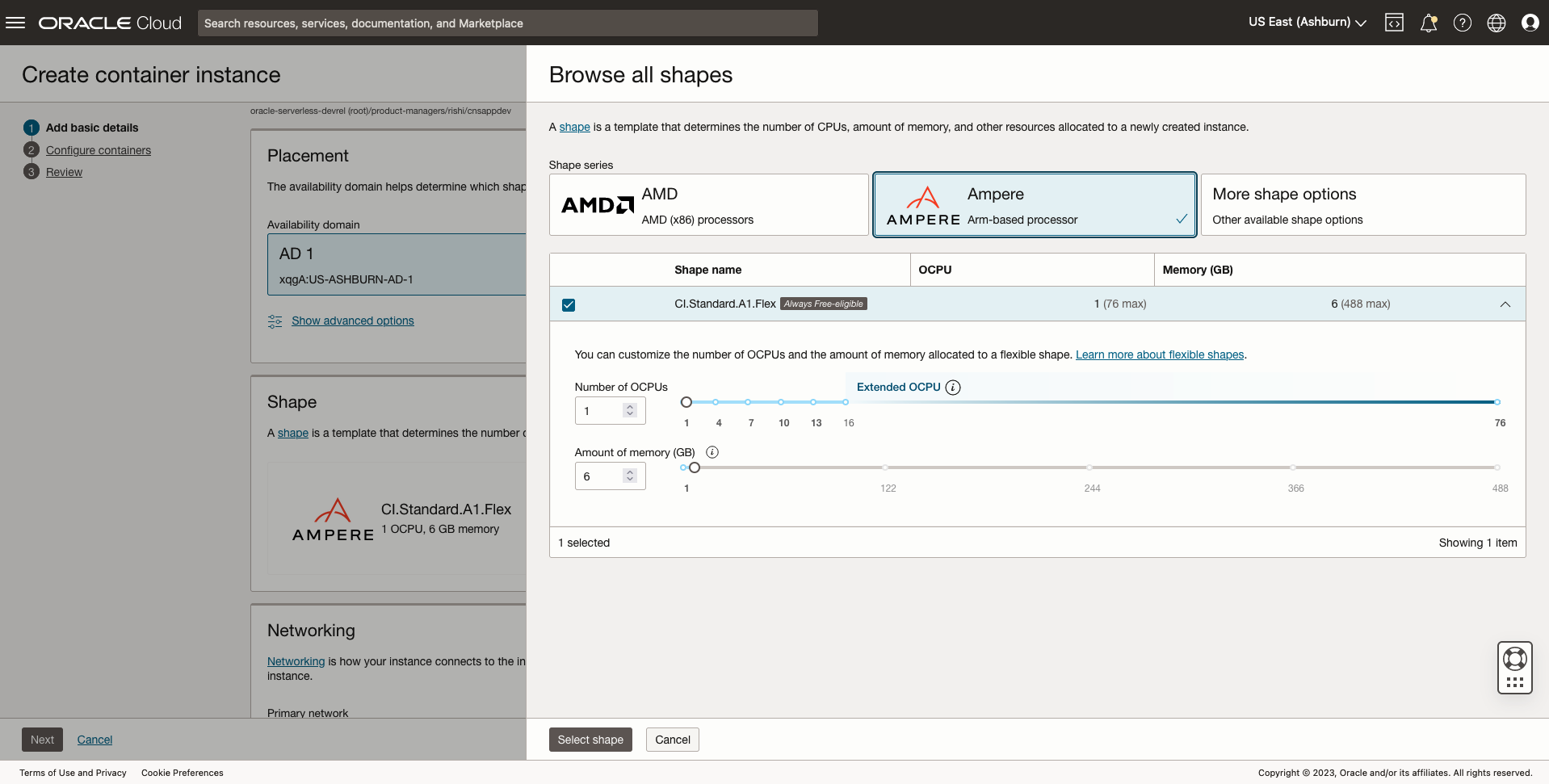
- Click Create Container Instance, go to the Shape selection, and select the CI.Standard.A1.Flex shape.
- When configuring containers to run on the container instance, provide container images built for Arm architecture or multiple architectures to run these containers on Arm processors.
The flexible shape enables you to customize the number of cores and amount of memory. You can choose to allocate up to 76 cores with extended OCPUs and up to 488 GB of memory to each container instance to run even the most demanding workloads.
Run OCI Functions on Arm
OCI Functions is a serverless functions-as-a-service (FaaS) platform in OCI. Functions seamlessly integrate with other OCI services, providing a complete serverless platform for building event-driven applications, and provision the compute required to run functions the customers deploy based on demand.
You can now run OCI functions powered by Ampere A1 using OCI interfaces, including Fn CLI, OCI CLI, and OCI software developer kits (SDKs). While deploying a function, you can specify the shape parameter on which you want to run the function. You can limit the function to running on a single architecture, such as Arm or enable the function to run on multiple architectures, such as both Arm and x86.
Use the following steps to specify the processor architecture on which to run a function:
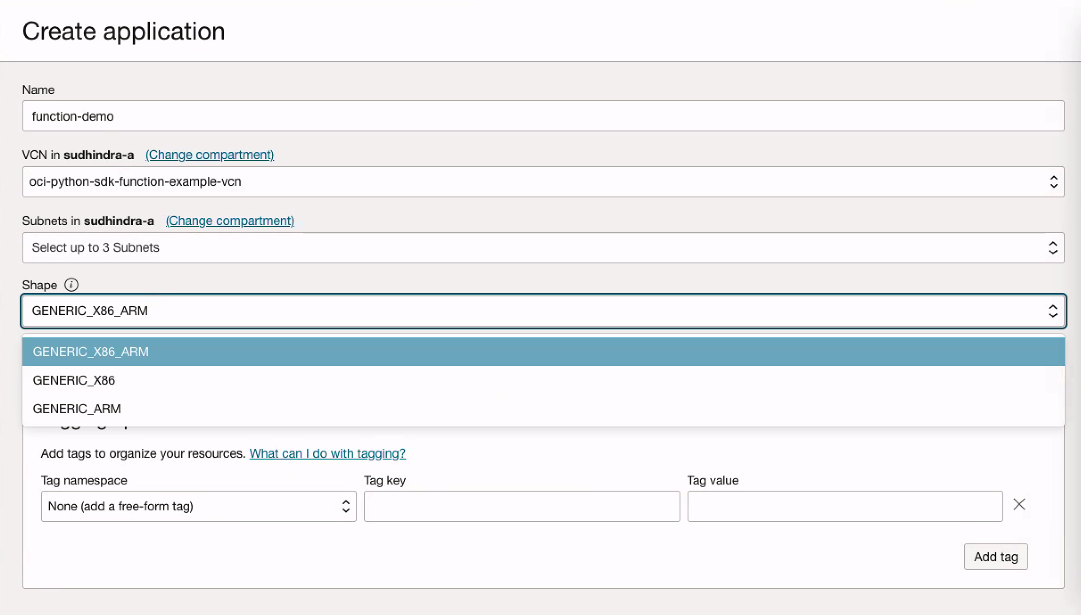
- In the navigation menu, under Developer Services, go to Functions and click Create Application.
- Select a shape for the application that supports the architecture on which you want to run the function.
- Create functions by building an image that contains the necessary dependencies for the architecture on which you want to run the function and deploy it.
This method uses the Fn CLI to build a multiple architecture image based on the application shape parameter and upload the manifest to OCIR. The Functions image architecture must be compatible with the applications shape definition. Run the following command:
fn -v deploy --app app_multiarch
- You can invoke your function using OCI, Fn or trigger integrated with Functions (e.g., API Gateway, Events).
fn invoke func_multiarch
Run Kubernetes pods on Arm
OKE lets you run containers on Arm processors in Kubernetes clusters using OKE with managed nodes. Now, you can also run containers on Arm using OKE virtual nodes. OKE virtual nodes eliminate the operational overhead of managing, scaling, upgrading, and troubleshooting worker nodes’ infrastructure.
- In the navigation menu, under Developer Services, go to Kubernetes Clusters (OKE) and click Create Cluster.
- In the Create Cluster window, select Custom Create and click Launch Workflow. Set up the cluster configuration as a part of the Cluster Create and Network Setup.
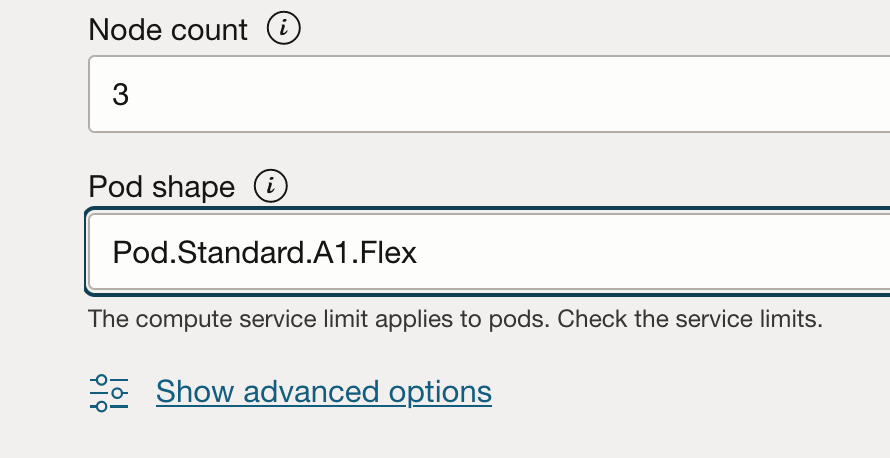
- In the Node Pools section, select Virtual and pick the pod shape within the Virtual node count and Pod shape sections.
You can create virtual nodes with the pod shape set to Pod.Standard.A1.Flex. The pods scheduled on those virtual nodes run on Arm processors, and you benefit from the price-performance that Arm processors provide.
Want to know more?
- Arm developer page
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Ampere A1 product page
- Oracle Unlocks Power of Arm-based Processors at One Cent per Core Hour, Expanding Ecosystem, and Speeding App Development
- Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE) support for Arm-based instances is now generally available
- Arm-based cloud computing is the next big thing: Introducing Arm on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure


