As more companies come to the cloud, what type of deployment strategy are they deciding is best for them? For most, it’s multicloud.
A multicloud strategy is the use of two or more cloud-based compute services. Multicloud can refer to any deployment of multiple software-as-a-service (SaaS) or platform-as-a-service (PaaS) cloud offerings. However, it usually refers to a mix of public infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) environments.
Organizations choose to implement a multicloud strategy for many reasons: to enable flexible distribution of workloads, increase security, improve reliability, enable versatile DevOps environments, and, of course, reduce costs.
This post describes how to use Megaport Cloud Router (MCR) to enable multicloud connectivity between Oracle Cloud Infrastructure virtual cloud networks (VCNs) and Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) without deploying physical infrastructure (as shown in the following diagram). For information about connecting to other cloud service provider virtual networks, see the instructions from Megaport.
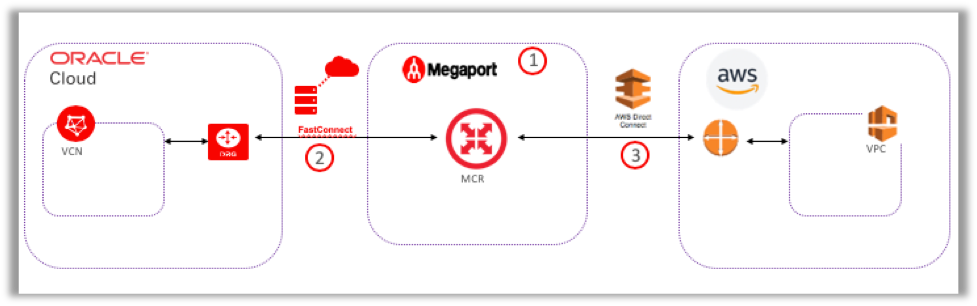
The following high-level steps are required to create this connection:
- Create an account with Megaport.
- Create an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect connection and add the connection to MCR.
- Add an Amazon VPC connection, by using AWS Direct Connect, to MCR to enable routing between the virtual networks.
This post covers steps 2 and 3 in detail.
Before You Begin
Perform the following actions in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure:
- Get the necessary Identity and Access Management permissions.
- Meet the Fast Connect requirements.
Perform the following actions in AWS:
- Get the necessary permissions to use AWS Direct Connect and Amazon VPC.
- Create or select an Amazon VPC with at least one subnet and route table that contains the resources that you want to connect. Verify that the IP address space doesn’t overlap with the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure environment.
Perform the following action in Megaport:
When you connect to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure via FastConnect with Megaport, the Virtual Cross Connect (VXC) forms the Layer 2 component of the connection. Layer 3 BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) connectivity is established directly between the customer and Oracle.
The example in this post uses a private peering connection.
Create a FastConnect Connection on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
To create a FastConnect connection, you must first create a VCN, create a Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG), and attach the VCN to the DRG. Then, you configure the FastConnect circuit that the DRG will use to reach the Amazon VPC.
Create a VCN
- Sign in to your tenancy in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console.
- Ensure that you’re in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region that matches the destination region that you’re going to configure. This example uses the Frankfurt region.
- In the Quick Actions section of the home page, click Create a virtual cloud network.
- In the Create Virtual Cloud Network dialog box, enter a name for the VCN (in this example, it’s VCN-MCR). If you leave this field blank, the date and time of creation is used for the VCN name.
- Select a compartment. If one is preselected, ensure that you want your VCN to reside there, or select another one. This example uses Megaport.
- Select Create Virtual Cloud Network Plus Related Resources. This option assigns a default CIDR block, creates a subnet in each availability domain, adds an internet gateway, generates a security list, and generates a route table with a rule that routes to the open internet. If you want to customize your own settings, select Create Virtual Cloud Network instead and then create each of these resources.
For more information about creating a VCN, see VCNs and Subnets. - Click Create Virtual Cloud Network.
The VCN details page is displayed.
Create a DRG and Attach the VCN to It
A DRG is a virtual router that provides a pathway for private traffic between your VCN and other networks.
- On the left side of the Console, under Networking, click Dynamic Routing Gateways.
- Click Create Dynamic Routing Gateway.
- In the Create Dynamic Routing Gateway dialog box, select the compartment where you want the DRG to reside, and give the DRG a name (in this example, DRG-MCR).
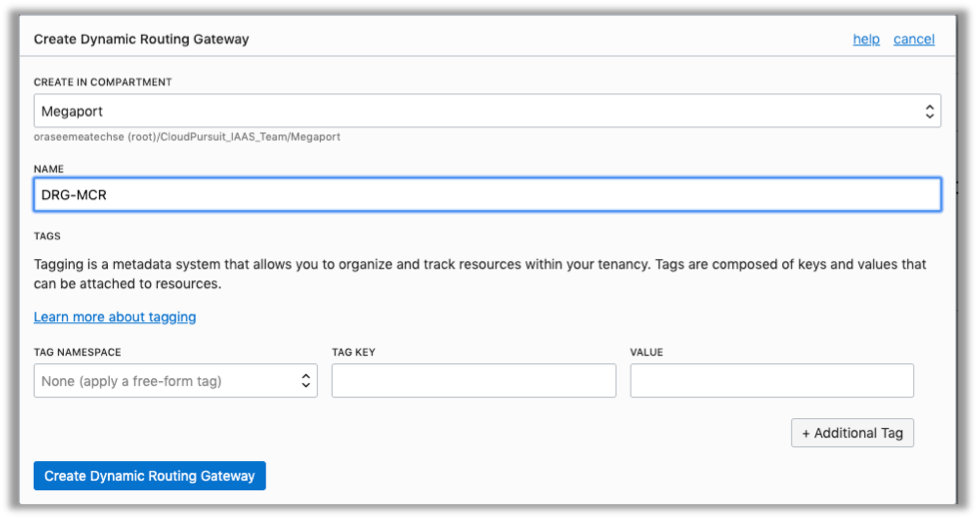
- Click Create Dynamic Routing Gateway.
- After the DRG is provisioned, select it.
- On the left side of the Console, under Resources, click Virtual Cloud Networks.
- Click Attach to Virtual Cloud Network.
- In the Attach to Virtual Cloud Network dialog box, select the same compartment where your VCN resides, and then select the VCN (in this example, VCN-MCR). You can ignore the Associate with Route Table settings.
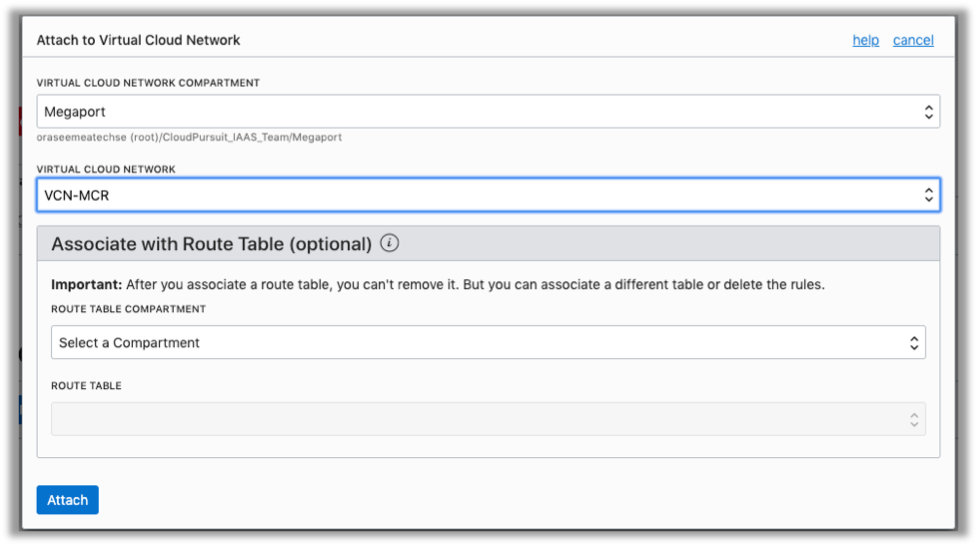
- Click Attach.
The VCN is now attached to the DRG.
Add a Rule to the Route Table
The next step is to add a rule to the DRG on your route table. A VCN uses virtual route tables to send traffic out of the VCN.
- Go back to the Networking section and select your VCN (in this example, VCN-MCR).
- Under Resources, click Route Tables.
- Click Default Route Table for VCN-MCR.
- Click Edit Route Rules.
- Click +Another Route Rule.
- In the expanded dialog box, provide the following information:
- For Target Type, select Dynamic Routing Gateway.
- For Compartment, select the same one that you’ve been using throughout this exercise (Megaport).
- For Destination CIDR Block, enter the on-premises network CIDR block. This example uses 10.20.0.0/16.
- For Target Dynamic Routing Gateway, select the DRG that you just created (in this example, DRG-MCR).

- Click Save.
Create a FastConnect Circuit
The final step on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is to configure the FastConnect circuit that the DRG will use to reach the Amazon VPC. For these steps, you need to know the BGP IP addresses and the Autonomous System Number (ASN). Megaport provides this information.
- Go back to the Networking section.
- Under Networking, click FastConnect.
- Click Create Connection.
- In the Create Connection dialog box, select Connect Through a Provider, and then select Megaport Service.
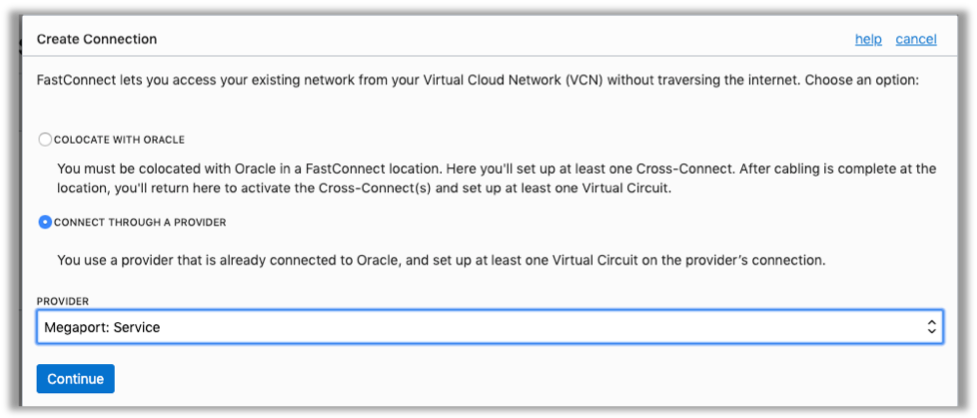
- Click Continue.
- In the new Create Connection dialog box, provide the following information. The values provided here are specific to this example.
- Name: Give the connection a name (in this example, OCI).
- Compartment: Select the same compartment that you’ve been using throughout this exercise (Megaport).
- Virtual Circuit Type: Private Virtual Circuit
- Dynamic Routing Gateway Compartment: Megaport
- Dynamic Routing Gateway: DRG-MCR
- Provisioned Bandwidth: 1 GBPS
- Customer BGP IP Address: 10.0.0.22/30
- Oracle BGP IP Address: 10.0.0.21/30
- Customer BGP ASN: 133937
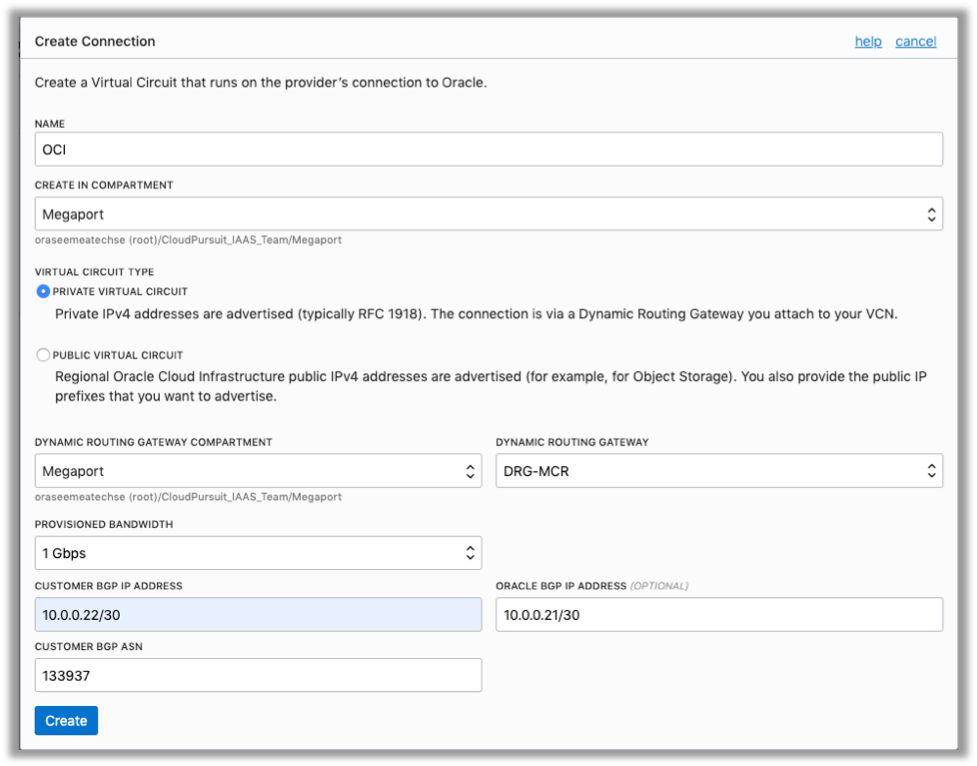
- Click Continue.
The connection is created from Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. - On the details page for the connection, copy the OCID. You need it to provision the virtual connection from Megaport in the next section. You can also click the Megaport link, which takes you to their main site, where you can log in to their portal (for the next section).

Create an MCR and Connect It to Oracle Cloud
- Log in to the Megaport portal.
- Click Services, and then click Create MCR.
- Select a location where you want to connect to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and Amazon, and then click Next.
- On the Configure page, provide the following values, and then click Next:
- Specify a rate limit, which determines the speed for all connections through the MCR.
- Specify a name (for example, MCR).
- Leave the default Megaport ASN value, 133937.
- Click Add MCR.
- Order the MCR instance.
- After the MCR is available, add a connection to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure by clicking Oracle Cloud in the Add Connection area.

- On the Select Port page, provide the following information, and then click Next:
- In the Oracle Virtual Circuit ID box, enter the OCID that you copied from the previous section.
- In the Choose from available Oracle Ports section, select where you want to create the connection.
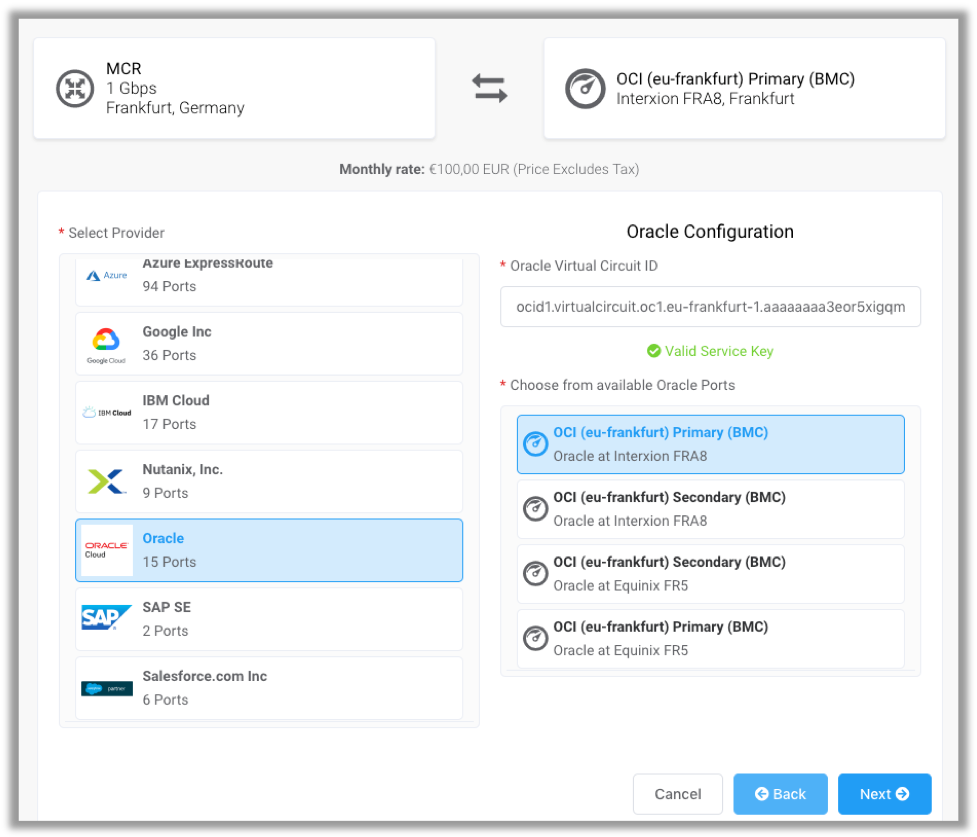
- On the Connection Details page, provide the following information, and then click Next:
- Enter a name for your MCR connection, for example, OCI.
- Enter a rate limit that doesn’t exceed the total rate limit for the MCR. Allow bandwidth for any additional connections that you might add to other cloud service providers.
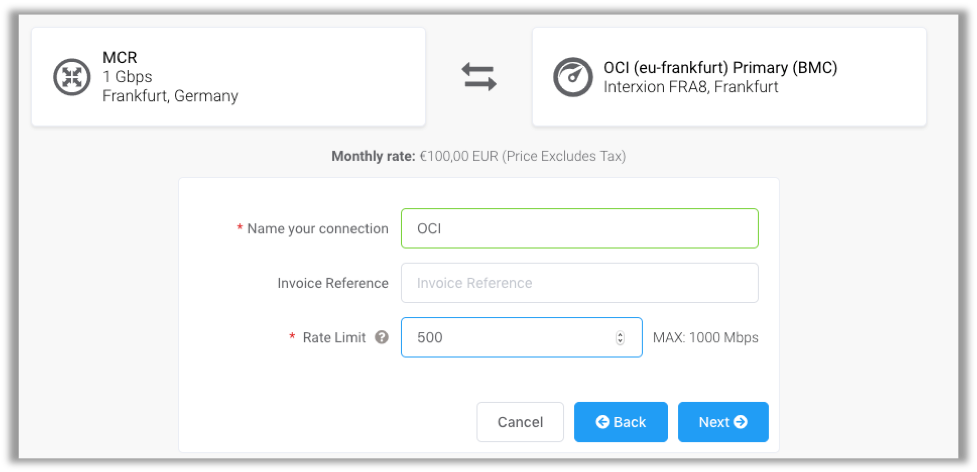
- Click Order, and then click Order Now.
After a few minutes, you have a fully deployed MCR with a connection to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. The MCR and connection are deployed when their icons change to green in the Megaport portal.
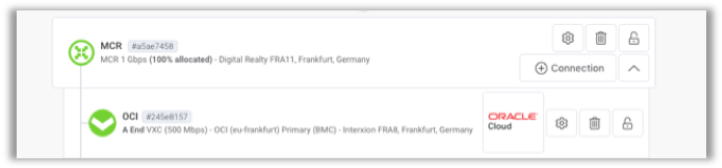
Add a Connection to Amazon VPC
Now that you have an MCR connected to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, you can add connections to other cloud service providers to your MCR. The following steps are for an AWS Direct Connect connection to an Amazon VPC.
- In the Megaport portal, click Services.
- Next to the MCR, click + Connection.
- Click Cloud as the destination type, and then click Next.
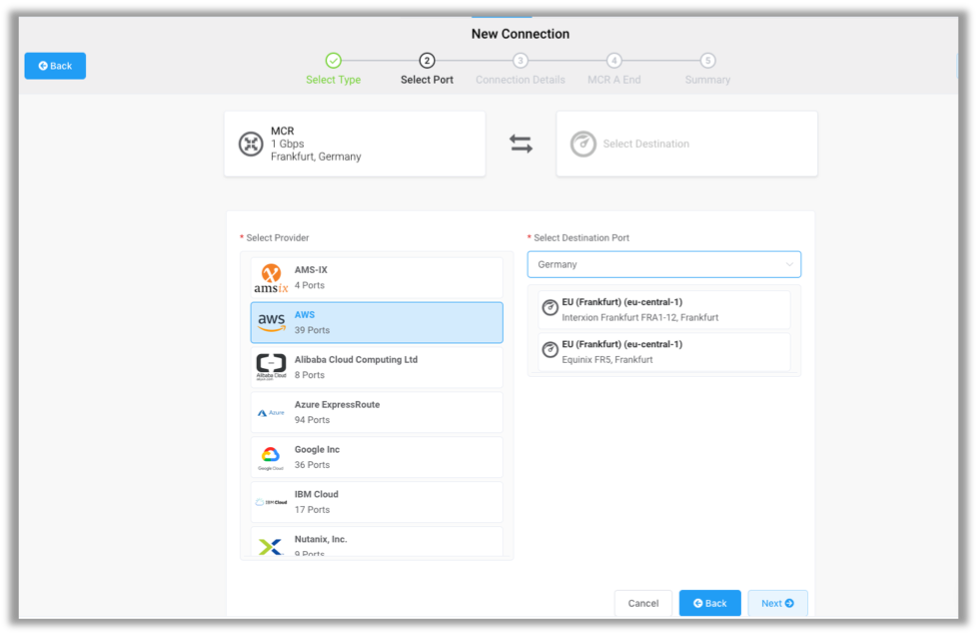
- On the Select Port page, perform the following actions and then click Next:
- Under Select Provider, click AWS.
- Under Select Destination Port, select the AWS region and the interconnection point that’s close to your MCR.
- On the Connection Details page, enter a name for the connection (for example, AWS), and enter the same rate limit that you entered for the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure connection. Then, click Next.
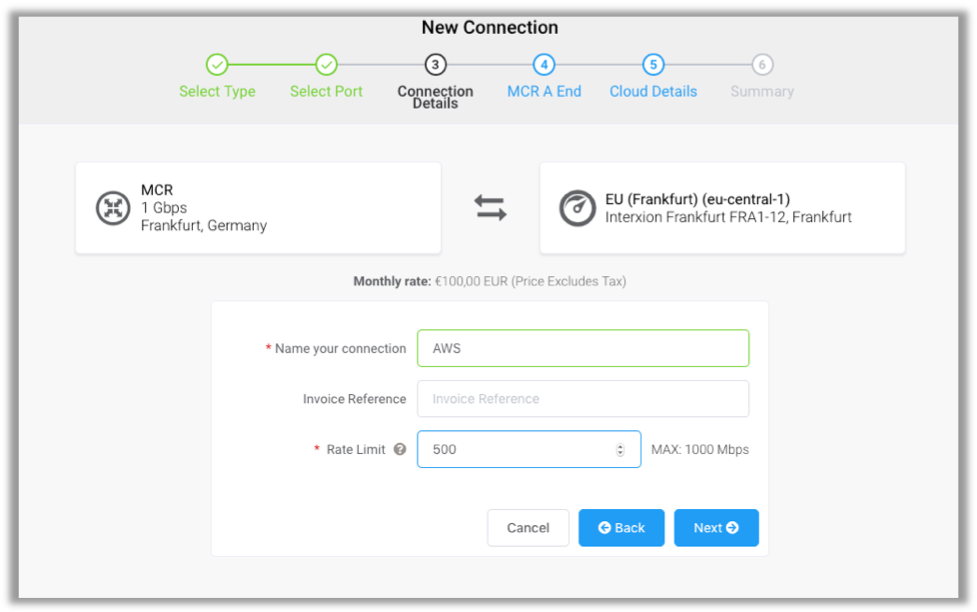
- On the MCR A End page, click Next.
- On the Cloud Details page, under Connection details for AWS Service, provide the following information, and then click Next:
- Provide a name for the connection (for example, megaport-aws). This name appears in AWS Direct Connect.
- Enter an AWS account ID.
- In the Amazon ASN field, enter the AWS ASN of the virtual private gateway or Direct Connect gateway that you want to connect to. For this example, use the AWS default ASN value of 64512.
- Click Add VXC, click Order, and then click Order Now.
After a few minutes, the connection appears in the portal. A green icon indicates that the connection is deployed.

Configure AWS Direct Connect
The final step to create the connection between Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and the Amazon VPC is to configure AWS Direct Connect.
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console.
- Switch to the region where the connection terminates.
- Go to Services > Direct Connect > Virtual Interfaces.
The connection that you created in the previous section (megaport-aws) is listed and has a status of confirming. You’ll accept the connection in a later step. - Go to Services > VPC > Virtual Private Gateways.
- Click Create Virtual Private Gateway, and then perform the following actions:
- Enter a name, for example, vpg-megaport.
- Click Amazon default ASN.
- Click Create Virtual Private Gateway.
- Click Close.
- To attach the virtual private gateway to the VPC, perform the following actions:
- Select the check box next to the virtual private gateway (vpg-megaport).
- From the Actions menu, select Attach to VPC.
- Select the VPC to connect to, and then click Yes, Attach.
- Wait for the virtual private gateway to attach to the VPC.
- Go to the Route Tables section of the VPC Dashboard.
- Select the route table that’s associated with the subnets that you want to use.
- Click the Route Propagation tab, and then click Edit route propagation.
- Select the Propagate check box next to the virtual private gateway, and then click Save.
- Go back to Services > Direct Connect > Virtual Interfaces.
- Click the ID next to the connection (megaport-aws), and then click Accept.
- In the Accept virtual interface dialog box, click Virtual Private Gateway.
- From the Virtual Private Gateway list, select the gateway that you created, and then click Accept virtual interface.
After a few minutes, the virtual interface is available and there is direct connectivity between AWS and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
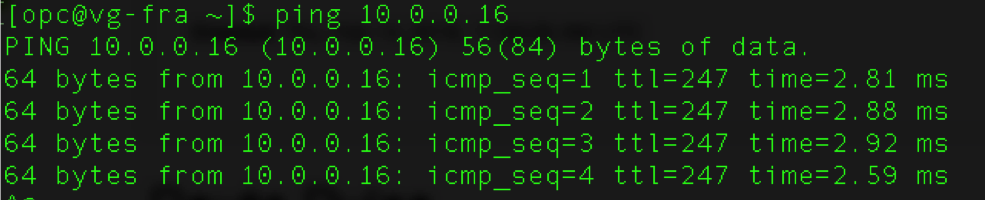
Verify the Connection
You can test the connection between the two clouds by launching a terminal window and launching a ping command, as shown in the following example:
Summary
This post provides a straightforward process for connecting Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to AWS by using a flexible, on-demand connectivity traversing Megaport’s private, API-driven SDN network. You can also use these steps to connect Oracle Cloud Infrastructure other cloud service providers.
