In this blog, we provide a general overview of the recently released Intel Optimized instances and outline why they’re superior to previous generation Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Intel instances. We also go a step further and benchmark these instances against existing Intel based instances from AWS. Not all clouds or processors are the same, and the performance and the savings you realize might surprise you. OCI Intel Optimized instances perform up to 58% better and provide two times better price-performance than comparable Intel instances from AWS.
Intel Optimized instances
Intel Optimized instances are built on the latest generation of Ice Lake processors from Intel. Ice Lake processors are based on 10-nm process technology as opposed to the 14-nm process technology used in previous generation processors. A lower process node translates to faster machines and more performance. Other benefits we get with Ice Lake include more memory channels and more PCIe lanes, eight channels of DDR4-3200 memory per socket, up to 64 lanes of PCIe Gen4 per socket compared to six channels of DDR4-2933, and up to 48 lanes of PCI Gen3 per socket for the previous generation. Ice Lake also integrates Intel’s Deep Learning (DL) Boost technology to improve AI application performance and adds features, such as Software Guard Extensions (SGX) and Crypto Acceleration to enhance security.
These instances are built on Intel 6354 with a base clock frequency of 3 GHz and a max Turbo frequency of 3.6 GHz. Per server, you get 36 OCPUs (36 cores and 72 threads) with 39 MB of L3 cache, 512 GB of RAM, and 100 Gbps of overall network bandwidth. These instances are superior compared to X7 Standard instance on several fronts. They’re 50% faster on both base and Max turbo frequency, they are built on the latest PCIe Gen4, and support two 50G networking, providing twice the IO and network bandwidth per server, compared to the Standard X7 instances.
Table 1: Instance shapes
| Instance | Cores | Memory (GB) | Storage | Network | Price | |
| VM.Optimized3.Flex | 1–18 | 1–256 | Up to 1 PB of block storage | Up to 50 Gbps | $0.054/core/hr $0.0015/GB |
|
| BM.Optimized3.36 | 36 | 512 | 3.84 TB NVMe |
|
$0.075/core/hr |
Intel Optimized instances are ideally suited for a wide variety of workloads, including high-performance computing (HPC) workloads and compute-intensive workloads that require the highest single thread performance. The following workloads can benefit from this instance type:
-
Video conferencing workloads that require high-CPU processing power
-
Media encoding workloads and high-performance web server applications
-
HPC workloads like scientific modeling, CFD, and machine learning
-
Software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications that require high processing power
-
EDA workloads that demand the highest performance and clock frequency per core
-
Genomics, data science, and AI inferencing
-
Crash modeling and real-time processing
Performance benchmarking
We ran extensive performance studies, including a comprehensive micro benchmark study to benchmark our instances against other instances that we carry and against competitive instances like AWS.
Table 2: Compute configurations for performance tests
| System configuration |
X7 Standard | E3 Standard | E4 Standard | Optimized |
| CPU | Two Intel Skylake 8167M, 26 cores per socket @ 2.0 GHz | Two AMD EPYC 7742, 64 cores per socket @ 2.25 GHz Base, and @3.4G Turbo | Two AMD EPYC 7J13, 64 cores per socket @ 2.55 GHz Base, and @3.5G Turbo | Two x86 Intel Ice lake processors, 18 cores per socket @ 3.0 GHz base, and @3.6G Turbo |
| Memory | 786 GB DDR4 | 2 TB DDR4 | 2 TB DDR4 | 512 GB DDR4 |
| Network | Two 25 Gbps | Two 50 Gbps | Two 50 Gbps | Two 50 Gbps |
We ran performance tests to exercise the CPU performance, floating point performance, and memory subsystem performance. We ran tests on vendor-recommended proprietary compilers and Oracle Linux operating systems. We ran the tests several times and averaged the results. All SPEC numbers are estimates.
Table 3: Performance tests and benchmark targets
| Test | Benchmark target |
| SPECrate 2017 integer | Integer performance |
| SPECrate 2017 floating point | Floating point performance |
| STREAM triad | Memory bandwidth |
| Server Side Java: Peak JOPS | Peak Java performance |
| Server Side Java: Pivotal JOPS | Pivotal Java performance |
SPEC, SPEC CPU, and the benchmark SPECrate are registered trademarks of Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation.
The following graphs show how the Intel Optimized instances compared against our X7, E3, and E4 Compute instances. All the runs used eight OCPU instances from AMD and Intel. The runs were done several times, and the results were averaged.
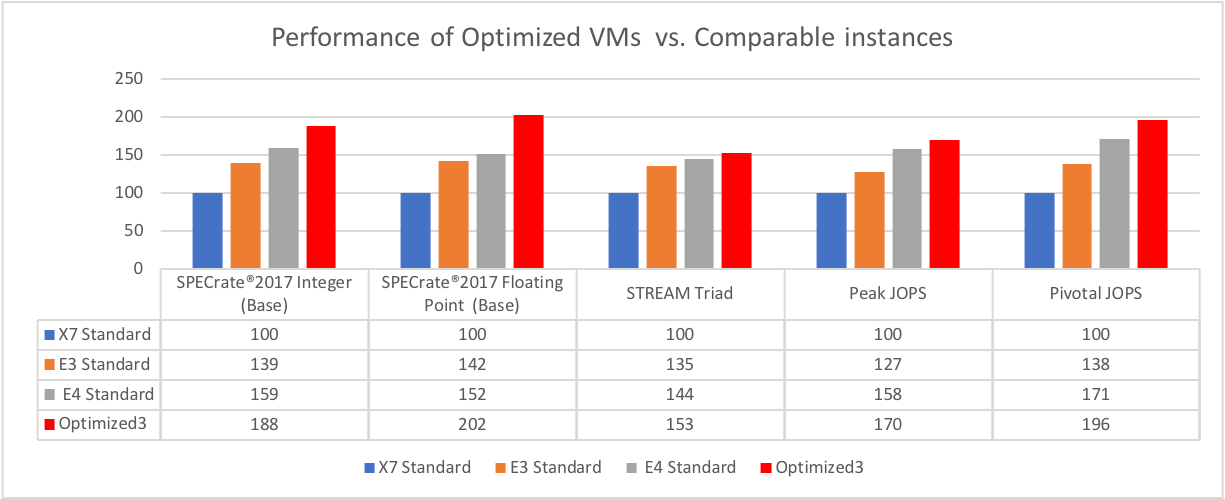
Figure 1: Performance of Optimized virtual machines (VMs) versus comparable instances
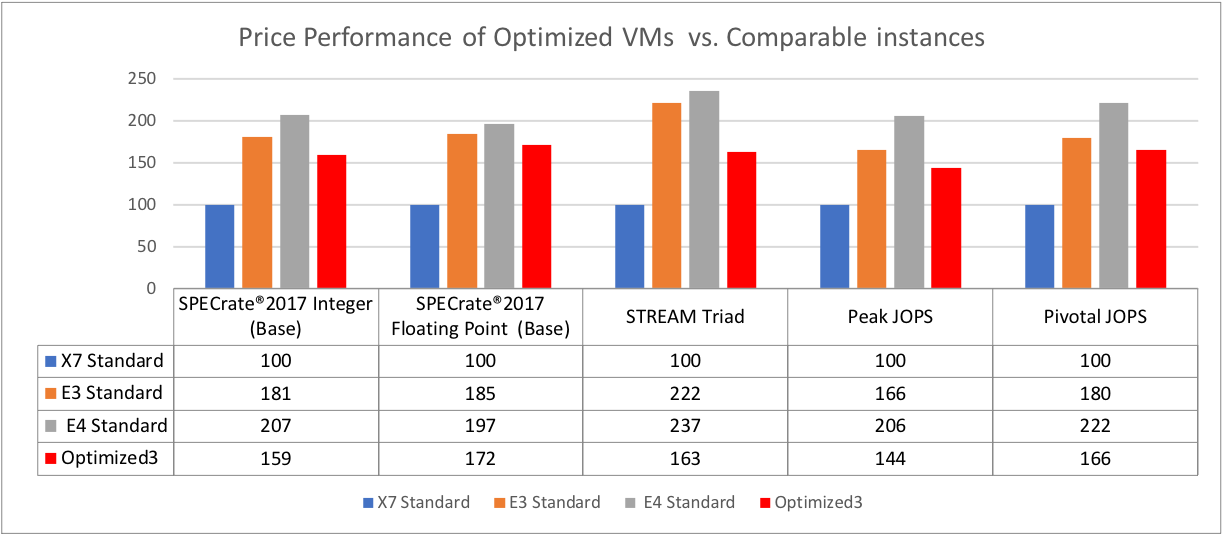
Figure 2: Performance of Optimized VMs versus comparable instances
As shown in the figures 1 and 2, the Intel Optimized instance handily beats the previous general intel instance on both performance/core and also on price performance.
Competitive benchmarks
We compared our offerings to what’s available from AWS. As shown in the following graphic, the Optimized instances outperformed the AWS instances both in absolute performance and price-performance, with up to an estimated 58% increase in performance per OCPU and up to an estimated 114% increase in price performance per OCPU versus comparable AWS instances.
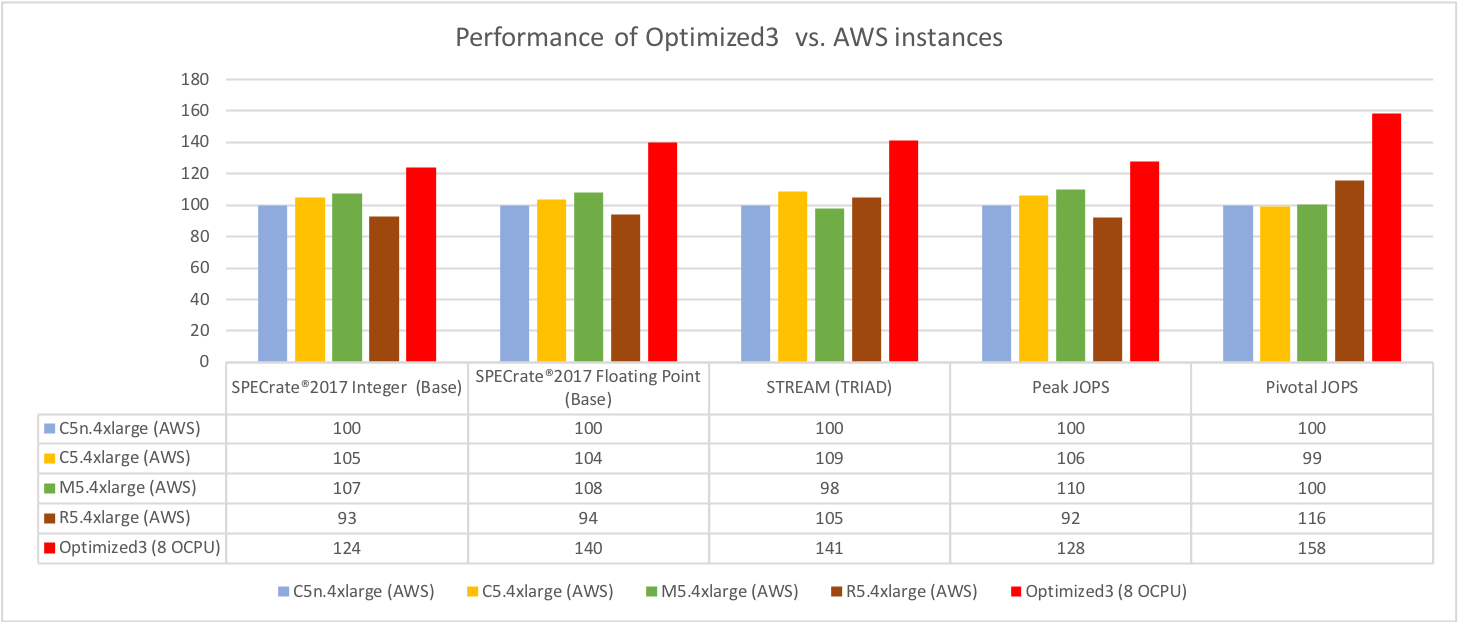
Figure 3: Performance of Intel Optimized versus AWS instances
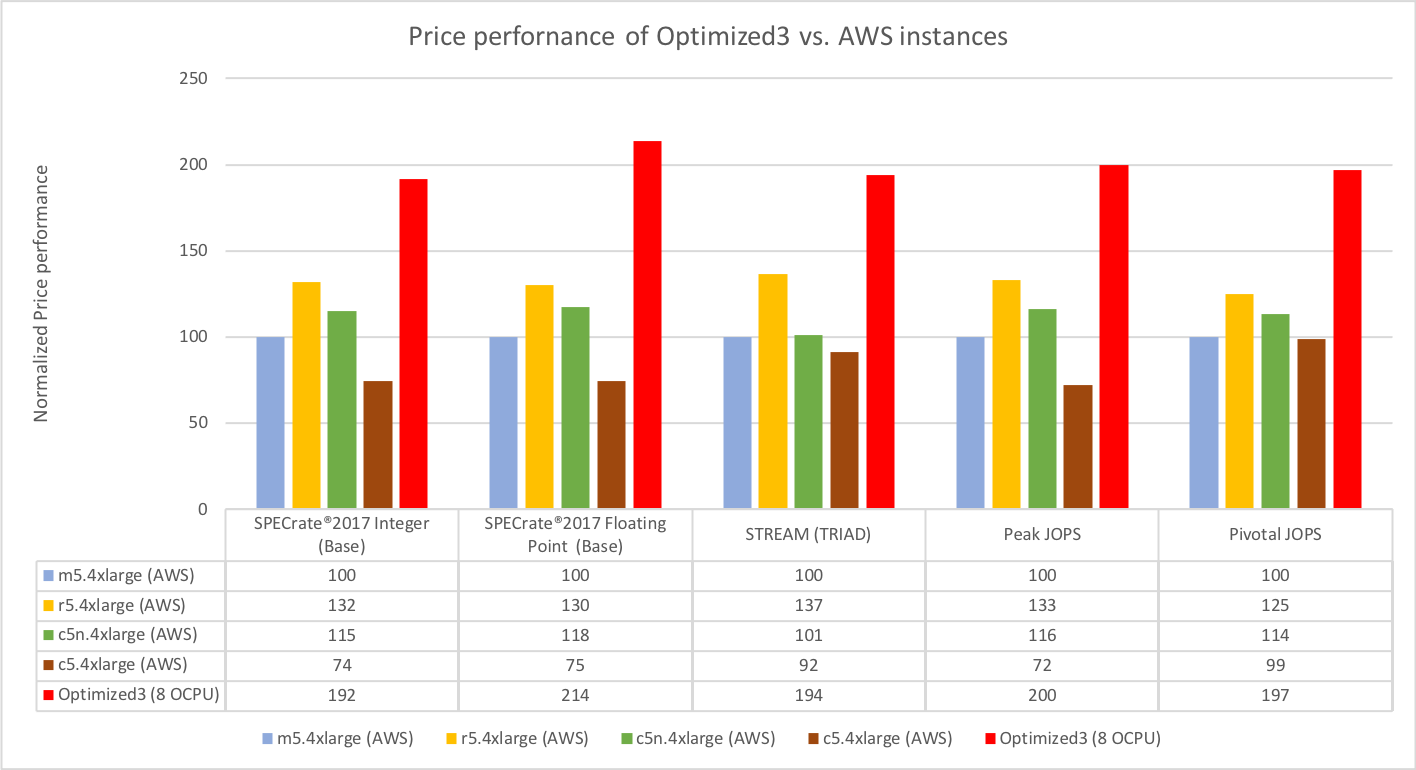
Figure 4: Price-performance of Optimized versus AWS instances
Conclusion
The latest Intel Optimized instances offer a new line of compute-intensive offerings for customers who crave for that extra performance per core. With an 88% increase in estimated integer performance, greater than an estimated 100% increase in SPEC FP, and a greater than 70% increase in Java performance, the Intel Optimized instances offer a sizeable performance boost compared to the X7 instances. The availability of RDMA NIC, high CPU frequency, and the ability to deploy in a low latency cluster network also make these instances ideal for HPC applications.
Our competitive study confirms that these instances outperform AWS C5, C5N, M5, and R5 instances on both absolute performance and price-performance. The choice of where we use these instances against the AMD line of instances is workload-specific and based on user preferences and performance versus price performance tradeoffs.
You can benefit from this performance by deploying and migrating your workloads to these Compute instances today. To get started with these instances, visit the OCI Console. You can read more about these instances in the documentation.