We’re pleased to announce availability of a highly available network filesystem (NFS) cluster with automated failover and no data replication to deliver high availability. On Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, you can achieve 50% savings in storage cost, by using Shared Block Storage, instead of Distributed Replicated Block Device (DRBD) , which require double storage capacity. With Shared Block Storage, you can attach block volumes to multiple Compute instances in a shareable read and write mode.
Architecture
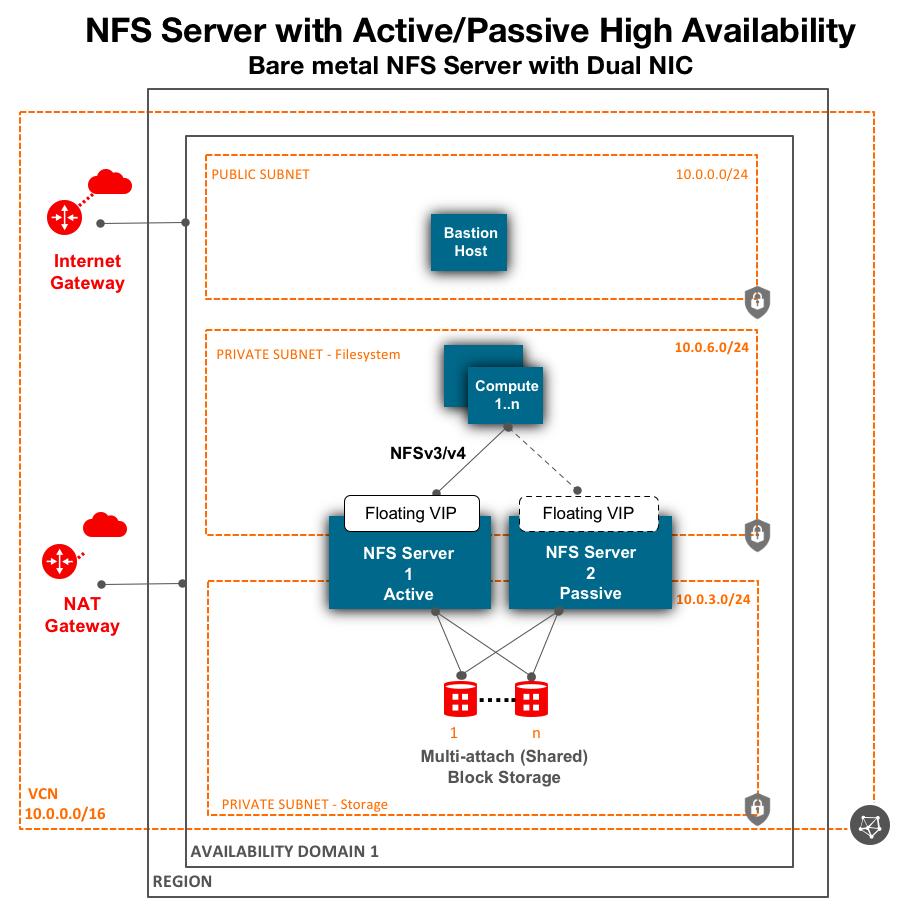
The following architecture shows how to deploy an NFS cluster using bare metal nodes with two network interface controllers (NICs)—in this case, two private subnets. The NICs segregate and separate data traffic between the NFS server and storage devices and between NFS clients and servers.
For the high-level architecture to deploy an NFS cluster on virtual machines, a single-node bare metal NFS server, or a single-node virtual machine NFS server, refer to the GitHub documentation.
Performance
For optimal performance, we recommend using bare metal standard Compute shapes. With two physical NICs at 25 Gbps each on bare metal shapes, data traffic between NFS server and storage devices can be segregated from data traffic between NFS clients and servers. We also support virtual machines for NFS file servers.
High Availability
This solution uses Pacemaker, Corosync, Shared Block Volumes Storage, and floating virtual or secondary IP to deploy a high availability NFS cluster. At a given time, only one node is active and performs read and write to shared storage. Corosync and Pacemaker installed on both instances of NFS cluster provides the required functionality to configure and manage required NFS resources as an atomic group for failover, including Logical Volume Manager, Filesystem, NFS service, and floating Virtual IP. On Oracle Cloud, you can add a secondary private IP to an instance. If the instance has problems, Corosync and Pacemaker as part of failover to passive instance reassigns the secondary private IP to the passive instance.Storage
You can deploy an NFS with 1 petabyte (1 PB) storage capacity. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers network attached Shared Block Volumes, which can be attached to multiple Compute instances in shareable read and write mode to build an active or passive high availability NFS server with automated failover.
Deployment
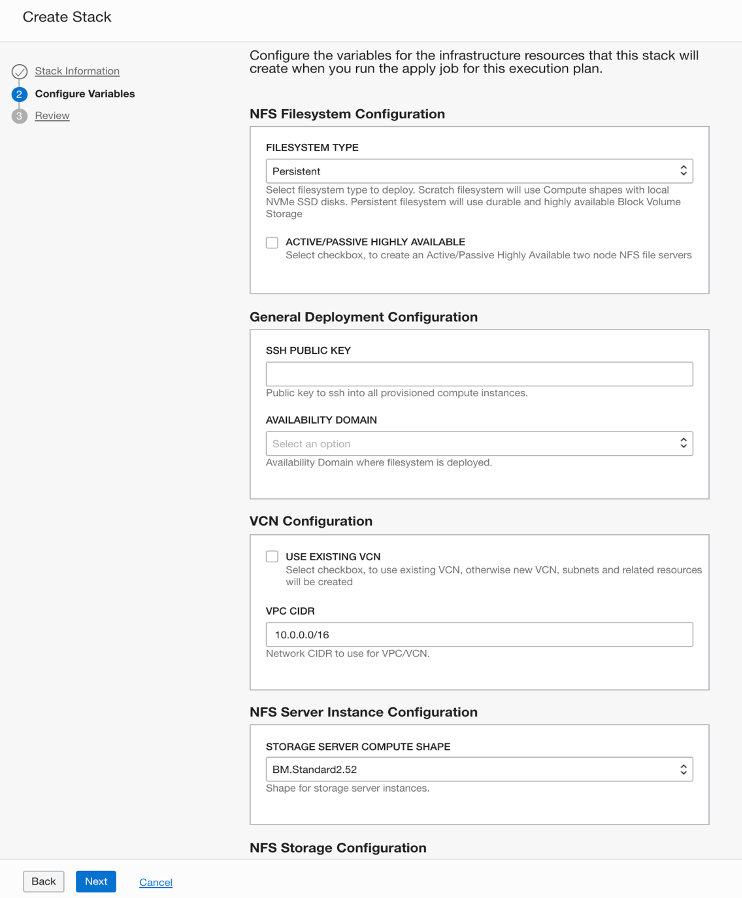
You can easily deploy the NFS cluster in a few minutes through the Oracle Cloud Marketplace or Terraform template in a new or existing VCN. Network-attached Block Volume storage, more durable and highly available, are used for persistent filesystems, versus local nonvolatile memory express solid-state drives (NVMe SSDs) for Scratch filesystem. To deploy a highly available NFS cluster, select the persistent filesystem type, and select “Active/Passive Highly Available.” The solution also supports deploying a single node NFS server using either Block Volume storage or local NVMe SSDs. For single-node NFS servers, select the persistent filesystem type and uncheck “Active/Passive Highly Available” or select the Scratch filesystem type.
Try it Yourself
Every use case is different. The only way to know if Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is right for you is to try it. To try, you can select either Oracle Cloud Free Tier or 30-day free trial (with US$300 in credit) to get you started with a range of services, including compute, storage, and network.
